Updated July 29, 2023
Difference Between Nominal vs Real Interest Rates
Interest rates are a very crucial part of financial instruments and the financial industry as a whole. They help investors and financial managers to make the decision to choose the right instruments for their needs and risk profile. But simply analyzing the interest rates will not suffice for long-term investments, as inflation also plays a major role. This is why we have two interest rates: Nominal Interest Rates and Real Interest rates. Let us dig deep and understand both Nominal vs Real Interest rates.
Nominal Interest Rates
Nominal interest rates are the rate of return that an investor or borrower will get or have to pay in the market without any adjustment for inflation. For example, the interest rate on bank accounts, bonds, loans, etc., is nominal. It is really easy to understand. For example: if you have deposited $100 in your bank account and your bank is offering a 5% per annum interest rate, you will have $105 (100 + 0.05*100 ) in your account by the end of the year. Similarly, if you have borrowed $100 from someone and he is charging 3% interest, you have to pay back $103 at the end of the year.
Real Interest Rates
Nominal interest is quite an easy concept to understand. But when we see the effect of inflation on top of that, things become more interesting. Continuing the above example, depositing money in a bank will give us 5% interest, earning $5. But if the inflation is 3% per annum, it means that for goods and services, we can buy at, say, $100, we have to pay $103 now for the same amount. So effectively, we have earned only $2 ($5 – $3). So basically, real interest rates will give the real picture of the consumer’s purchasing power.
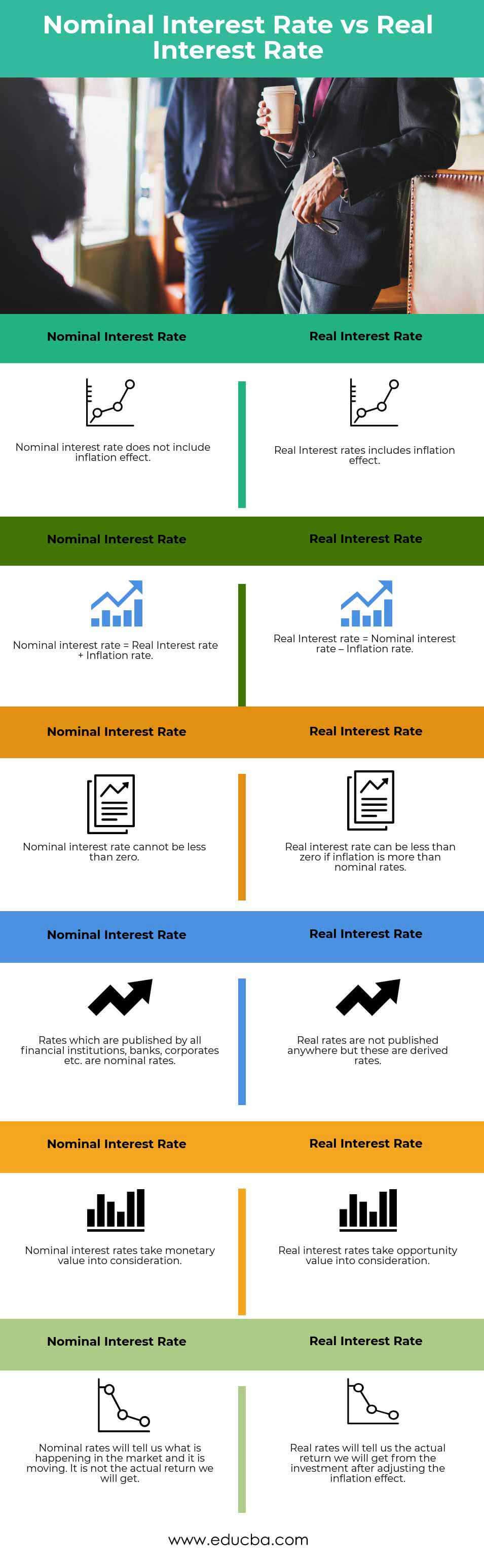
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Nominal vs Real Interest Rates (Infographics)
Below is the top 6 difference between Nominal vs Real Interest Rates:
Key Differences Between Nominal vs Real Interest Rates
Although both Nominal vs Real interest rates give us an idea of what we can earn on investment or need to pay if we take up any loan, let us discuss some of the major differences :
- As discussed earlier, the nominal interest rate is the market rate of return/interest earned by/charged to the customer. In contrast, the real interest rate is the effective rate that an investor will realize.
- The nominal interest rate has no effect of inflation incorporated, while the real interest rate is calculated after removing the inflation effect.
- Bank interest rates, loan interests, etc., all are nominal interest rates. Real interest rates are derived from nominal rates.
- A real interest rate is based on the principle of the time value of money; inflation, etc., will change the value continuously with time. This effect will get captured in real rates. No such adjustments happen at nominal rates.
- A nominal rate cannot be negative and can only go down to 0%, while the real rate can be negative. For example: If the nominal rate in the market is 3%, but inflation is 5%, the investor will lose money and have a negative real interest rate.
Nominal vs Real Interest Rates Comparison Table
Let’s look at the top 6 Comparison between Nominal vs Real Interest Rates
|
Nominal Interest Rate |
Real Interest Rate |
| The nominal interest rate does not include the inflation effect. | Real Interest rates include the inflation effect |
| Nominal interest rate = Real Interest rate + Inflation rate | Real Interest rate = Nominal interest rate – Inflation rate |
| The nominal interest rate cannot be less than zero. | The real interest rate can be less than zero if inflation is more than nominal rates. |
| Rates published by all financial institutions, banks, corporates, etc., are nominal rates. | Real rates are not published anywhere, but these are derived rates. |
| Nominal interest rates take monetary value into consideration. | Real interest rates take opportunity value into consideration. |
| Nominal rates will tell us what is happening in the market and it is moving. It is not the actual return we will get. | Real rates will tell us the actual return from the investment after adjusting the inflation effect. |
Conclusion
Nominal interest rates are commonly used to determine the return on investment or the cost of borrowed money. Financial institutions, banks, and corporations typically provide quotes based on nominal interest rates. However, in practical terms, the real interest rate holds greater significance than the nominal rate. The real interest rate offers a clearer and more accurate understanding of the amount of money or returns that can be earned on investments over time. It also enables borrowers to assess the true cost of obtaining a loan. Real interest rates play a crucial role in deciding whether it is advantageous to repay a loan early or to maintain the existing arrangement. Therefore, investors need to monitor both nominal and real interest rates. Nominal interest rates inform them about prevailing market conditions and trends, while real rates indicate the actual returns they can expect to grow their capital.
Recommended Articles
This has guided the top difference between Nominal vs Real Interest Rates. We also discuss the key differences between the Nominal vs Real Interest Rates with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.