What is Normative Economics?
Normative economics studies citizens’ judgments on economic events and decisions to form solutions for a nation’s development. For example, “The government should provide basic education to all citizens” is a value-based statement. It is a personal perspective of what the government should do.
It stems from individual points of view and viewpoints that one considers during the decision-making process. Government or regulatory boards use these normative assertions to evaluate and advocate economic policy changes. They represent people’s ideas and suggest specific actions to take in light of the financial situation.
Key Highlights
- It specifies what should happen on the basis of the personal opinions of individuals.
- It suggests strategies that can significantly impact economic decisions or recommends changes in economic policies.
- All subjective statements related to any economic program are examples of such statements.
- While normative economics revolves around value judgments and opinions of people, positive economics is an objective approach to financial analysis.
- Normative statements are valued reviews or opinions of individuals. It is not possible to test or verify them.
How Does Normative Economics Work?
This concept entirely works around normative statements. The statements typically make value judgments, simply the speaker’s opinion. Rather than following a mathematical approach to examining the political economy, normative economists provide their perspectives in the analysis.
The primary aim is to convince policymakers to enact laws to create an economic environment that they think is ideal for society. Its emphasis is primarily on theoretical and opinion-driven statements related to economic activities.
It asks people what should happen and then strives to identify whether specific economic programs, conditions, or events are desirable for them. It then recommends strategies for altering monetary policy or impacting economic decisions.
Examples
#1: “We should cut taxes in half to increase disposable income levels.”
#2: “Laborers should get a greater portion of capitalist profits.”
#3: “Working citizens should not pay for health care.”
History
- The roots of it lie in Pigou’s economic welfare concept.
- The concept became prominent as per the new economic theories in the 1930s.
- The economists evaluated the effectiveness of normative claims on policies using the Pareto and Compensation principles.
- Social choice theory and public economics are the new normative versions.
- However, Bob Sugden, a behavioral economist, recently stated that we should consider all normative statements equal rather than ranking them.
- It will help provide more choices and solutions to the economy.
Difference Between Normative vs. Positive Economics
|
Normative Economics |
Positive Economics |
|
Definition |
|
| It is an economic science based on opinions, values, and judgments. The statements are the personal perspectives of individuals. | Positive economics is an economic science that revolves around facts or phenomena and figures. |
|
Purpose |
|
| It is all about determining what should be in the context of any economic situation and proposing solutions based on personal values. | It relies on present and past data to predict the future of any economic condition. |
|
Nature |
|
| Prescriptive: it provides assertions where no credible data supports them. | Factual and descriptive: It provides more relevant statements backed by solid data. |
|
Type |
|
| Subjective | Objective |
|
Testing |
|
| Statements are not testable or verifiable, as they are individuals’ beliefs. | Using scientific methods, it is possible to test or verify every positive statement for approval or disapproval. |
|
Study |
|
| It emphasizes ’what should/ought to be’. | Positive economics deals with ‘what is’ in terms of any economic condition |
|
Economic Issues |
|
| It provides a solution to an economic issue based on personal views. | It depicts an economic issue and provides a scientific clarification on it. |
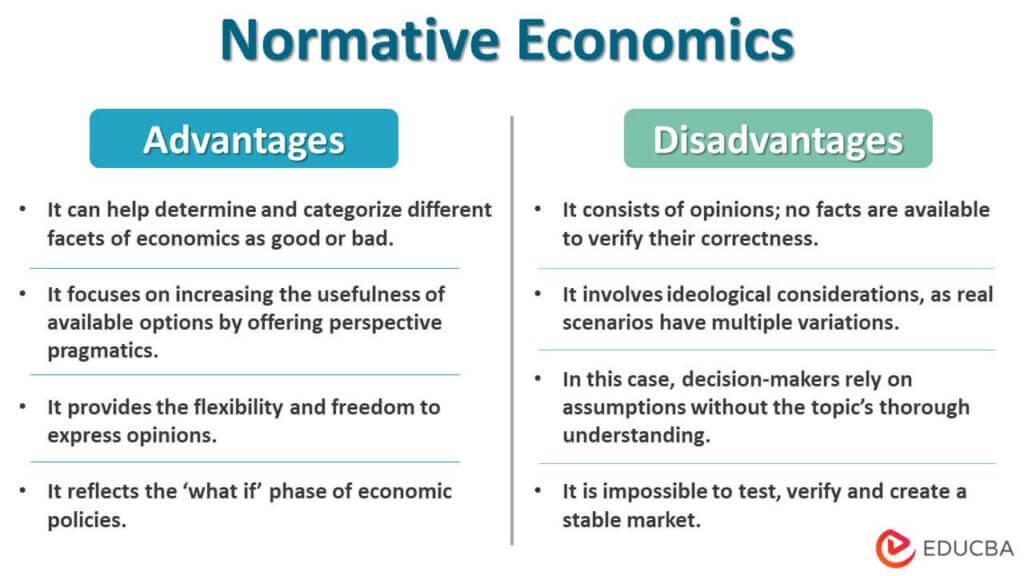
Advantages and Disadvantages
Final Thoughts
In a nutshell, normative economics suggests or prescribes solutions to economic programs, situations, and conditions. It proposes solutions to some financial issues or requirements based on personal perspectives. It helps generate new ideas and thoughts, allowing economists to express their opinions. Although normative assertions are value-based and subjective, they serve as the basis for the tweaks that can entirely alter a given economic choice. The only downside is that facts or figures do not back it. Hence, it is not verifiable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is normative economics?
Answer: Normative economics is a branch where citizens share their opinions or statements and tell what they think about specific economic activities. These statements can neither be verified nor tested. They may hold true for some people but may not work for others.
Q2. How do positive and normative economics differ?
Answer: Positive economics is in contrast to normative. While personal opinions form a basis for normative economics, facts, and phenomena are the foundation for positive economics.
Q3. What is a normative economic statement? Give an example.
Answer: A normative economic statement makes value judgments associated with economic activities, which are typically the opinions of speakers or economists. Furthermore, it is impossible to establish the validity of either of those opinions.
Normative economics statements generally include’ should’ or’ ought.’ One example is, “The government should not encourage discrimination among citizens.”
Q4. Why is it called normative economics?
Answer: The main aim of one of the branches of economic analysis is to provide recommendations to people about the working economic environment. Since it is similar to the term’ normative,’ which means rule, standard, or principle, it is called normative economics.
Q5. What are the characteristics of normative economics?
Answer: Normative economics can act as a guide for economic facts and expresses subjective and personal opinions. These opinions help derive the ideas or plans necessary to improve economic strategy and manage the economy. It is entirely according to theories and approaches toward personal criteria.
Recommended Articles
This article explains everything about Normative Economics. To know more, visit the following articles: