Updated March 18, 2023
Introduction to Number Patterns in Java
Number Patterns are quite a trend for freshers to get as part of interview questions as it provides a good brainstorming session to analyze a person’s creativity and innovation. Solving more of patterns show logical and mathematical capability. It is indeed a good way to form different patterns using all these conditional loops and syntaxes in java. It helps in improvising the skills of optimization and helps develop logical and analytical aptitude. It can be substituted with any character or symbol. If you learn number pattern, you can frame any of the patterns based on java.
Top Examples of Number Patterns
Here we will learn how to face some of the good Number Patterns. Let’s have a peek at some of the good Number Patterns in java with examples and code implementation, which are explained below in detail:
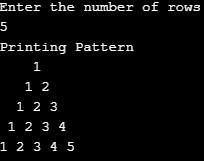
Example #1
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern1 {
public static void main (String [] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows ");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
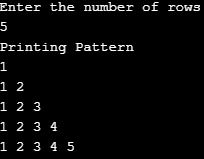
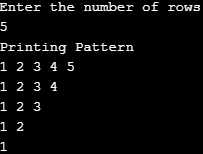
}Output:
Example #2
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern2 {
public static void main (String [] args) {
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
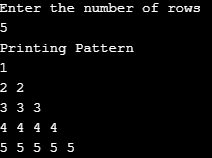
}Output:
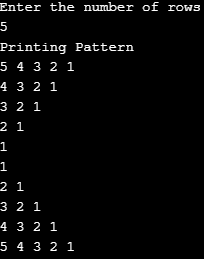
Example #3
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern_3 {
public static void main (String [] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = rows; i >= 1; i--)
{
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
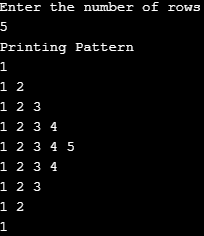
}Output:
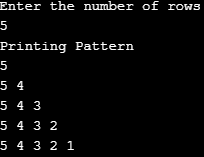
Example #4
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = rows; i >= 1; i--)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
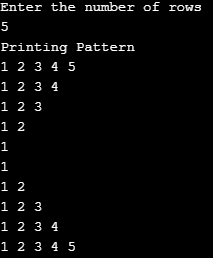
}Output:
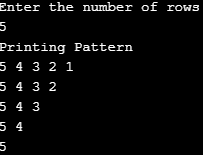
Example #5
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern5 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = rows; i >= 1; i--)
{
for (int j = i; j >= 1; j--)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j >= 1; j--)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
Example #6
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows ");
int rows = scanner. nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = rows; j > i; j--)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int k = 1; k <= i; k++)
{
System.out.print(k + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
Example #7
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern7 {
public static void main (String [] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows ");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = rows; j >= i; j--)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
Example #8
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern8 {
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = rows; i >= 1; i--)
{
for (int j = rows; j >= i; j--)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
Example #9
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern9
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern ");
for (int i = rows; i >= 1; i--)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
Example #10
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern10
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
int k = 1;
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
System.out.print(k + " ");
k++;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
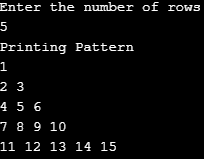
}Output:
Example #11
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern11
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);
System.out.println("Enter number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Printing Pattern");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j >= 1; j--)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
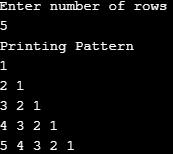
}Output:
Example #12
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern12
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Pattern Printing");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
int temp = i;
for (int j = i; j >= 1; j--)
{
System.out.print(temp + " ");
temp = temp + rows;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
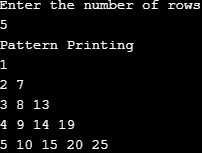
}Output:
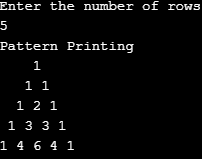
Example #13
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern13
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Pattern Printing");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = rows; j > i; j--)
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
int temp= 1;
for (int k = 1; k <= i; k++)
{
System.out.print(temp + " ");
temp = temp * (i - k) / (k);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
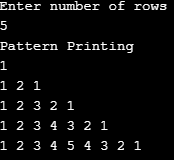
Example #14
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pattern14
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter number of rows");
int rows = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Pattern Printing");
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
for (int k = i - 1; k >= 1; k--)
{
System.out.print(k + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
Conclusion
Solving number Patterns or any design pattern improves a person’s analytical and logical building aptitude. In bigger domains, it provides an overview of how to create and fulfil requirements given for a project and how effectively it can be tackled with confidence.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Number Patterns in Java. Here we discuss the introduction and top 14 examples of number patterns in java along with its code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-