Updated May 9, 2023
Introduction to NumPy Arrays
Numpy arrays are a good substitute for Python lists. They are better than Python lists. They provide faster speed and take up less memory space. Let’s begin with its definition for those unaware of numpy arrays. They are multi-dimensional matrices or lists of fixed size with similar elements.
1D-Array
2D-Array
A typical array function looks something like this:
numpy.array(object, dtype=None, copy=True, order='K', subok=False, ndmin=0)Here, all attributes other than objects are optional. So, do not worry, even if you do not understand other parameters much.
- Object: Specify the object for which you want an array
- Dtype: Specify the desired data type of the array
- Copy: Specify if you want the array to be copied or not
- Order: Specify the order of memory creation
- Subok: Specify if you want a sub-class or a base-class type array
- Ndmin: Specify the dimensions of an array
Attributes of an Array
An array has the following six main attributes:
- Size: The total number of elements in an array
- Shape: The shape of an array
- Dimension: The dimension or rank of an array
- Dtype: Data type of an array
- Itemsize: Size of each element of an array in bytes
- Nbytes: Total size of an array in bytes
Example of NumPy Arrays
Now, we will take the help of an example to understand the different attributes of an array.
Example #1 – To Illustrate the Attributes of an Array
Code:
import numpy as np
#creating an array to understand its attributes
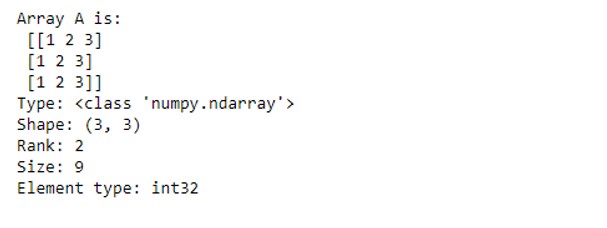
A = np.array([[1,2,3],[1,2,3],[1,2,3]])
print("Array A is:\n",A)
#type of array
print("Type:", type(A))
#Shape of array
print("Shape:", A.shape)
#no. of dimensions
print("Rank:", A.ndim)
#size of array
print("Size:", A.size)
#type of each element in the array
print("Element type:", A.dtype)Output:
How to Create an Array in NumPy?
Numpy provides several built-in functions to create and work with arrays from scratch. An array can be created using the following functions:
- ndarray(shape, type): Creates an array of the given shape with random numbers
- array(array_object): Creates an array of the given shape from the list or tuple
- zeros(shape): Creates an array of the given shape with all zeros
- ones(shape): Creates an array of the given shape with all ones
- full(shape,array_object, dtype): Create an array of the given shape with complex numbers
- arange(range): Creates an array with the specified range
Example #2 – Creation of a NumPy Array
Code:
import numpy as np
#creating array using ndarray
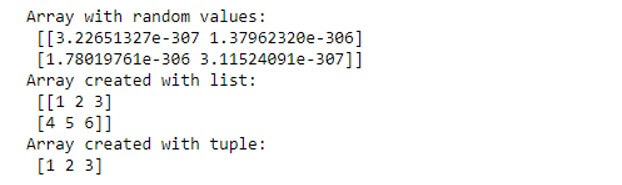
A = np.ndarray(shape=(2,2), dtype=float)
print("Array with random values:\n", A)
# Creating array from list
B = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print ("Array created with list:\n", B)
# Creating array from tuple
C = np.array((1 , 2, 3))
print ("Array created with tuple:\n", C)Output:
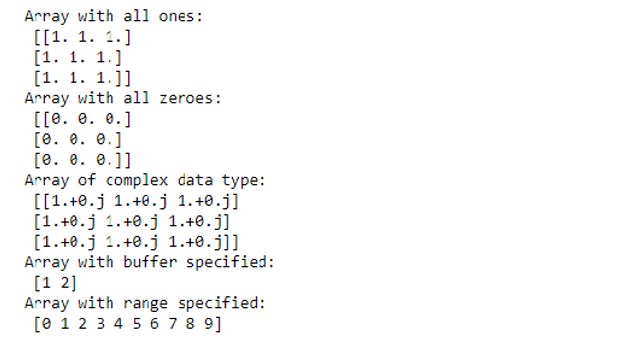
Code:
# Creating array with all ones
D = np.ones((3, 3))
print ("Array with all ones:\n", D)
# Creating array with all zeros
E = np.zeros((3, 3))
print ("Array with all zeroes:\n",E)
# Creating an array with complex data type
F = np.full((3, 3), 1, dtype = 'complex')
print ("Array of complex data type:\n", F)
#creating an array with buffer
G = np.ndarray((2,), buffer=np.array([1,2,3]),dtype=int)
print ("Array with buffer specified:\n", G)
#creating an array with range
H = np.arange(10)
print ("Array with range specified:\n", H)Output:
How to Access Array Elements in NumPy?
We can access elements of an array by using their indices. We can take the help of the following examples to understand it better.
Example #3 – Element Accessing in a 2D Array
Code:
import numpy as np
#creating an array to understand indexing
A = np.array([[1,2,1],[7,5,3],[9,4,8]])
print("Array A is:\n",A)
#accessing elements at any given indices
B = A[[0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2]]
print ("Elements at indices (0, 0),(1, 1), (2, 2) are : \n",B)
#changing the value of elements at a given index
A[0,0] = 12
A[1,1] = 4
A[2,2] = 7
print("Array A after change is:\n", A)Output:
Example #4 – Array Indices in a 3D Array
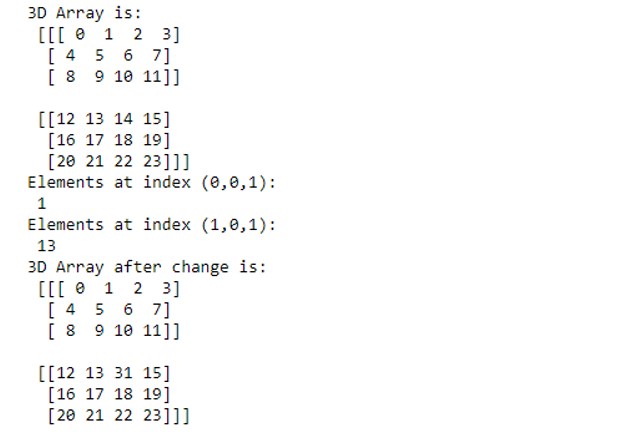
Code:
import numpy as np
#creating a 3d array to understand indexing in a 3D array
I = np.array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])
print("3D Array is:\n", I)
print("Elements at index (0,0,1):\n", I[0,0,1])
print("Elements at index (1,0,1):\n", I[1,0,1])
#changing the value of elements at a given index
I[1,0,2] = 31
print("3D Array after change is:\n", I)Output:
Array Operation in NumPy
The example of an array operation in NumPy is explained below:
Example
Following is an example to Illustrate Element-Wise Sum and Multiplication in an Array
Code:
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
B = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
# adding arrays A and B
print ("Element wise sum of array A and B is :\n", A + B)
# multiplying arrays A and B
print ("Elementwise multiplication of array A and B:\n", A*B)Output:
Conclusion – NumPy Arrays
A NumPy array is a multidimensional list of the same type of objects. It is immensely helpful in scientific and mathematical computing. As such, they find applications in data science and machine learning.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to NumPy Arrays. Here we have discussed how to create and access array elements in numpy with examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-