What is Offshoring?
“Offshoring” refers to relocating business processes, like manufacturing or supporting activities, from one country to another. Typically, a company opts for offshoring due to various operational benefits, such as a lower-cost labor market, skilled labor, presence in a foreign country, favorable tax regime, etc.
How Does Offshoring Work?
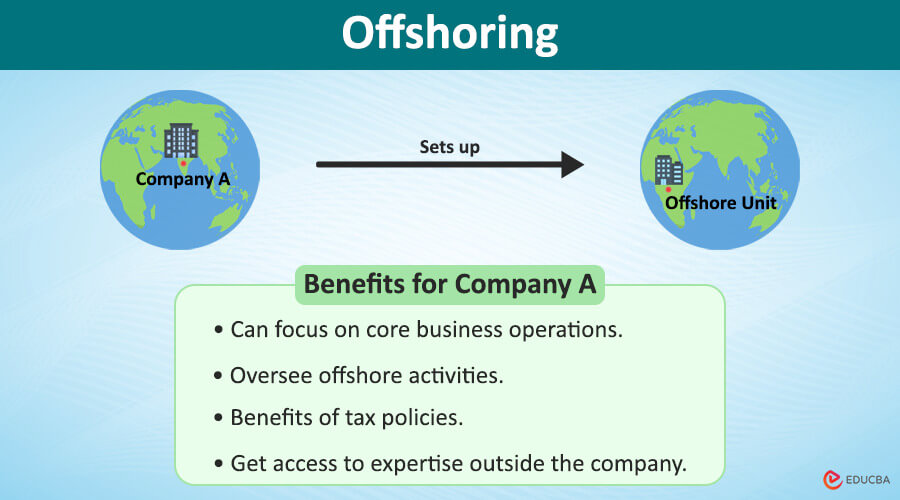
The parent company thoroughly analyzes the work scope to initiate the offshoring process. After multiple rounds of meetings and consultations, the company creates detailed documentation that elaborates on the specifics of the operational requirements, such as job role, work hours, KPIs, etc. Once the requirements are finalized, the company determines the cost involved in the process. After setting up the offshore unit, the parent company can focus on its core business operations while the foreign unit oversees offshored activities. In some cases, the parent company can also enjoy the benefits of favorable tax policies and other incentives that help the bottom line to a great extent.
Examples of Offshoring
Now, let us look at some real-life examples currently available today.
1. WhatsApp
In 2009, WhatsApp offshored its software development unit to Eastern Europe, relying on the offshore unit to maintain the backstage, provide design solutions, and take care of main application development. It allowed WhatsApp’s in-house team to focus on client-related activities (say customer support) and solve other relevant business challenges.
2. Amazon
In 2018, Amazon employed an offshoring route for expansion wherein it acquired the startup Ring, which had an R&D set up in Ukraine. The acquired entity specialized in designing outdoor home security solutions, and this expertise boosted Amazon’s market position in the security system industry. Within a year, Amazon opened another offshore unit in the country to expand its market dominance.
3. People.ai
People.ai is a software company that uses machine learning technologies to accelerate B2B sales. It went for offshoring to hire exceptionally talented engineers who are good at developing AI algorithms. Accordingly, the San Francisco-based company set up its R&D unit in Ukraine.
Types of Offshoring
The offshoring process can be divided into two broad categories as follows:
1. Production Offshoring
In this type, a company sets up its manufacturing unit in another country, imports the finished goods, and then sells them in the domestic market. The company intends to leverage the availability of rich sources of raw materials and cheap labor to optimize its operational capability. For instance, a company may look into the costs of offshoring vs. nearshoring in Mexico or other similar countries and decide to set up the manufacturing unit of heavy machinery in a country with an adequate supply of iron and cheap local labor skilled in such a task.
2. Services Offshoring
In this type, a company relocates its services by setting up units in another country to carry out operations such as marketing, customer care, human resource, accounting, etc. In this case, the company employs a highly skilled workforce relatively cheaply in a foreign country. For instance, a software company may relocate its R&D unit to a country where the human resources possess strong technical knowledge but are comparatively cheaper than the domestic workforce.
Benefits of Offshoring
Some of the major benefits are as follows:
- The parent company can focus more on its business’s core functions.
- It allows companies to hire competent and cost-efficient labor from developing nations.
- It ensures that a dedicated team works in the offshore unit and completes the assignment efficiently.
- Many developing nations offer incentives to lure foreign companies’ investments, such as tax holidays.
- It results in diversified operations across multiple countries lowering the country’s risk to a large extent.
Disadvantages of Offshoring
Some of the major disadvantages are as follows:
- A company entering a developing country owing to offshoring may find it difficult to communicate because of a huge gap between their native language and the local language of the foreign country.
- Offshore units are geographically dispersed in distant locations, making it difficult for the management to control the subsidiaries.
- Being acquainted with the local culture and society may result in various socio-cultural issues.
- The offshore units may face threats of lockout or closure if the local people find the operations unethical or harmful to the nation’s identity.
Key Takeaways
Some of the key takeaways of the article are:
- Offshoring refers to the relocation of business processes from one country to another. These business processes usually include manufacturing processes and various other supporting activities.
- Once the offshoring set-up is established, the parent company can pay more attention to the business’s core operations.
- There are two broad categories – production offshoring and services offshoring.
- One of the major shortcomings of offshoring is the huge gap between the local language of the foreign country and the native language of the parent company, which results in miscommunication in many cases.
Conclusion
So, it can be seen that offshoring has many advantages, such as cheap raw materials, skilled labor at comparatively low cost, tax benefits, etc. However, it also has certain disadvantages, such as communication issues, lack of management control, etc. Moreover, offshoring doesn’t straightaway relieve the parent company of the responsibilities. They have to weigh all pros and cons, select the most beneficial country for offshoring, and finally choose the right partner for collaboration.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Offshoring. Here we also discuss the definition, working, example, and types of offshoring, along with its benefits and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

