Updated July 15, 2023
What is the Oil ETF?
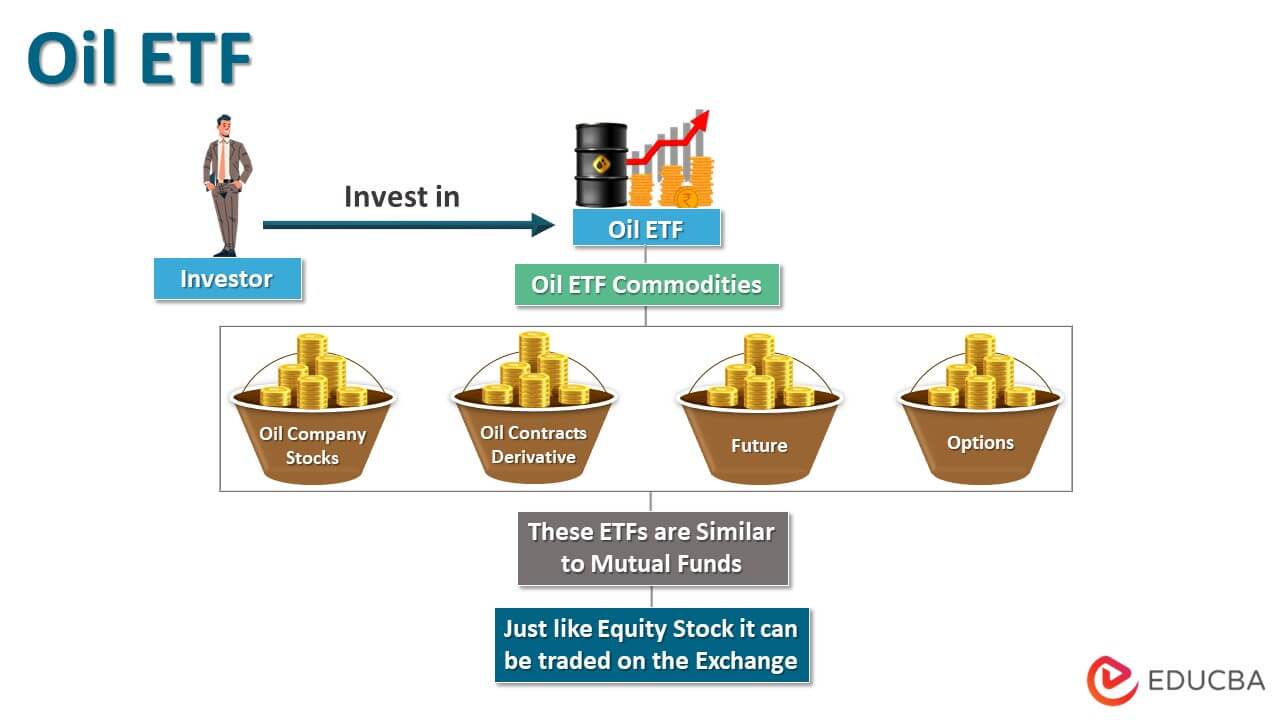
“Oil ETF” refers to the exchange-traded fund (ETF) that invests in companies engaged in the oil and gas industry. The companies included in an Oil ETF basket usually produce, discover, distribute, and retailst in the stocks of the companies; some hold limited partnership interests in the firms, and the rest invest in a pool of derivative contracts such as options and futures.
Explanation of Oil ETF
The purchase of Oil ETFs is a simple way for investors to gain indirect exposure to the performance of oil commodities without owning any physical oil. This either invests in company stocks or purchases futures, options, and other derivative contracts, which track the performance of oil as a commodity or indexes liked to oil. In other words, by buying these ETFs, the investor purchases exposure to oil price movement without purchasing any physical oil barrels. These ETFs are similar to mutual funds, with the significant difference that the former can be traded on the exchange in real time, just like any other equity stock.
Features of Oil ETF
Some of the main features are as follows:
- Unlike mutual funds, an Oil ETF can be traded on the exchange, similar to any common stock.
- Most Oil ETFs charge fees that are relatively lower than that of mutual funds, which makes them an attractive option for investors.
- The investors don’t require storage space as there is no physical commodity delivery.
- Investors always have a high demand for oil commodities, which are ubiquitous in the global economy.
Examples of Oil ETF
It is important to note that the value of Oil ETFs has been severely impacted since 2014-15, owing to various supply factors and geo-political tensions resulting in declining performance. Now, with the fact mentioned above in mind, let us look into some of the popular global ETFs that are available in the international market:
- United States Oil (USO): This fund falls under the category of US Fund Commodities, and its investments are primarily focused on companies with a credit rating of AA or above. As of September 10, 2020, its total asset stood at $4.0 billion. During 2019, the fund has been able to generate returns of 33.37%, which was one of the best performances in this category. However, the fund is down by 73.61% in YTD 2020. The fund’s adjusted expense ratio is 0.79%, which is relatively higher in its category.
- Vanguard Energy ETF (VDE): This fund falls under the US Fund Equity Energy, and as the name suggests, more than 97% of the fund invests in the US. As of September 10, 2020, its total asset stood at $2.5 billion. During 2019 and YTD 2020, the fund generated returns of 9.32% and -45.14%, respectively. The fund’s adjusted expense ratio is 0.1%, which is relatively low.
- Alerian MLP ETF (AMLP): This fund falls under the US Fund Energy Limited Partnership category; more than 99% of the fund invests in the US. As of September 10, 2020, its total asset stood at $3.2 billion. During 2019 and YTD 2020, the fund generates returns of 5.82% and -45.17%, respectively. The fund’s adjusted expense ratio is 0.87%, which is higher.
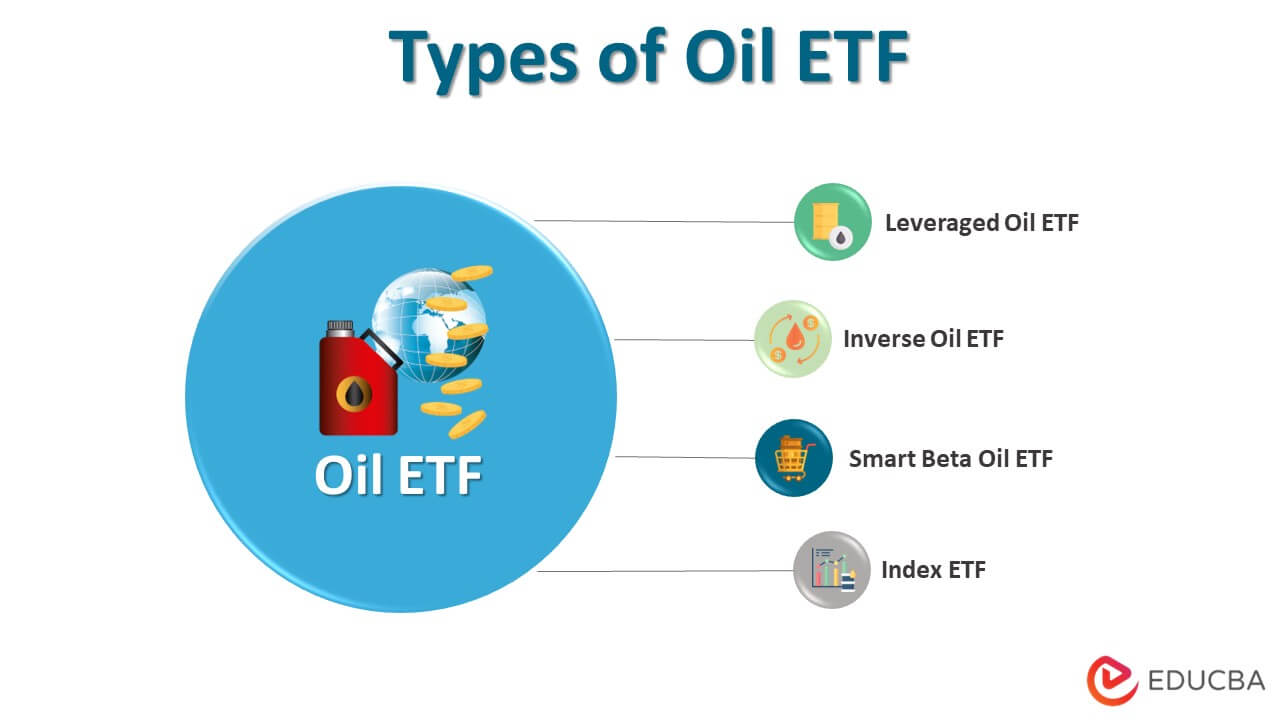
Types of Oil ETF
It can broadly categorize into four major types. They are as follows:
- Leveraged Oil ETF: These funds primarily focus on generating higher returns than the benchmark index while minimizing the chances and quantum of losses. ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Crude Oil (UCO) andProSharesUltraShort Bloomberg Crude Oil (SCO) are examples of Leveraged Oil ETFs.
- Inverse Oil ETF: These funds use an investment strategy that reduces the fund’s value when oil prices fall. In other words, these funds generate returns when the oil price moves adversely. ProSharesUltraShort Bloomberg Crude Oil (SCO) also falls under the category of Inverse Oil ETF.
- Smart Beta Oil ETF: These types of funds don’t have a specific investment strategy, but they focus on generating maximum returns by implementing intelligent, unconventional tactics. As such, these funds are hazardous and equally rewarding.
- Index ETF: These funds are plain vanilla products that intend to mimic the performance of a basket of securities from varying product ranges.
Advantages
Some of the significant advantages are as follows:
- There is a high demand for crude oil and oil-related derivatives contracts, which results in increased liquidity. Even 5-year and 10-year contracts are reasonably liquid.
- Purchase of Oil ETF provides the best hedge for retail and institutional investors with existing positions in oil commodities.
Conclusion
So, it can be seen that Oil ETF has economic importance given the status of the underlying commodity in the global economic and political scenario. Undoubtedly, the oil industry is the always under the scanner of all investors and traders as it influences the performances of the most capital-intensive industries. Hence, Oil ETFs and derivative contracts are very popular among the investor community.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oil ETF. Here we also discuss the introduction and types of oil ETF, its features, and advantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –