What is Oligopsony?
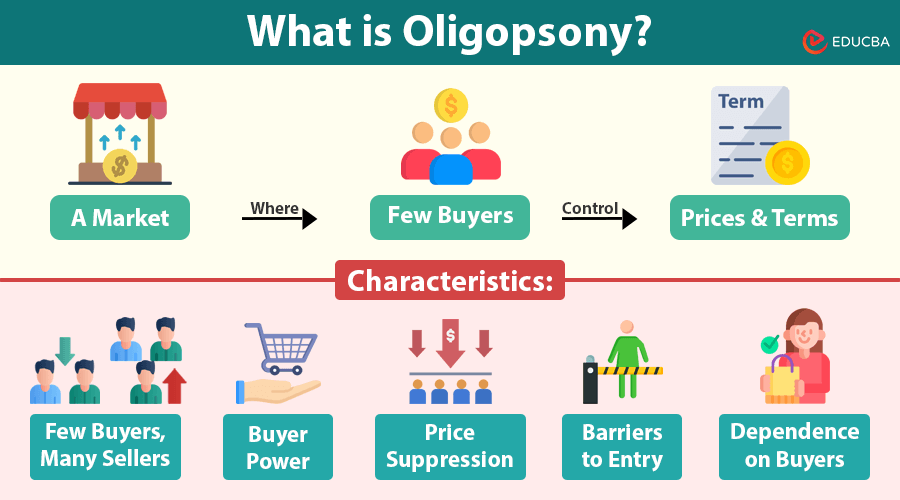
An oligopsony is a market where a few buyers have most of the power, allowing them to influence prices and buying conditions. This situation arises when there are few large buyers but many sellers, leading to an imbalance in market power. Since the buyers hold the upper hand, they can dictate prices, often to their advantage, while sellers struggle to negotiate better deals.
An example of oligopsony is the agricultural industry. Large supermarket chains or food processing companies buy products from thousands of small farmers. Since only a few companies control the majority of food purchases, they can force farmers to sell their produce at lower prices, reducing their profit margins.
Characteristics of Oligopsony
Oligopsony has several defining characteristics that set it apart from other market structures:
- Few Buyers, Many Sellers: A handful of buyers dominate the market, whereas numerous sellers compete for their business.
- Buyer Power: Buyers have the upper hand in determining transaction prices, terms, and conditions.
- Price Suppression: Due to limited market competition, sellers may receive lower prices for their goods or services.
- Barriers to Entry: New buyers find it difficult to enter the market due to high costs, regulatory constraints, or existing relationships between buyers and suppliers.
- Dependence on Buyers: Sellers often rely heavily on a small number of buyers for their income, making them vulnerable to changes in purchasing policies.
Differences Between Oligopsony, Monopoly, and Oligopoly
Oligopsony is often confused with monopoly and oligopoly, but they have distinct characteristics:
- Monopoly: A market with one dominant seller and many buyers, allowing the seller to set high prices.
- Oligopoly: A market where a few big sellers control prices and competition.
- Oligopsony: A market where a few big buyers set the prices.
Understanding these differences helps in analyzing market dynamics and identifying power imbalances.
Effects of Oligopsony on the Economy
Oligopsony has both positive and negative effects on markets, businesses, and consumers.
Advantages:
- Lower Costs for Buyers: Large buyers can negotiate better deals, reducing procurement costs.
- Efficiency in Supply Chains: Buyers streamline sourcing and distribution, improving efficiency.
- Standardized Products and Services: Large buyers ensure the quality and consistency of products.
Disadvantages:
- Reduced Profits for Sellers: Since buyers dictate prices, sellers often earn lower margins.
- Limited Innovation: If sellers receive lower compensation, they may lack resources for research and innovation.
- Labor Market Implications: Workers in oligopsonistic markets may face lower wages and fewer job opportunities.
Real-World Examples of Oligopsony
Several industries operate under oligopsony conditions. Here are a few notable examples:
- Supermarkets and Farmers: Large retail chains like Walmart or Tesco buy produce from farmers, giving them strong control over pricing.
- Fast-Food Chains and Potato Suppliers: Companies like McDonald’s buy potatoes in bulk, influencing supplier prices.
- Tech Companies and Chip Manufacturers: A few major tech firms (Apple, Samsung) purchase most of the semiconductor chips, affecting market rates.
- Coffee Industry and Farmers: Big coffee brands (Nestlé, Starbucks) source beans from farmers, often dictating prices.
- Book Publishing and Authors: A few major publishers control book deals, impacting author earnings.
How Sellers Can Overcome Oligopsony Challenges?
While oligopsony can put sellers at a disadvantage, there are strategies to counter its effects:
- Diversify the Customer Base: Selling to multiple buyers can reduce dependence on a few dominant players.
- Collaborate with Other Sellers: Forming cooperatives or alliances can increase bargaining power.
- Enhance Product Differentiation: Unique products or specialized services can give sellers more negotiation leverage.
- Lobby for Fair Regulations: Governments can enforce policies that prevent price suppression and market exploitation.
Final Thoughts
Oligopsony is a significant market structure that affects various industries worldwide. While it allows buyers to control prices and streamline supply chains, it also poses challenges for sellers, leading to reduced profits and limited innovation. Understanding oligopsony helps businesses and policymakers create fairer market conditions and promote economic growth.
By implementing strategies like diversifying customers and collaborating with peers, sellers can more effectively navigate oligopsony markets. Ultimately, balancing power dynamics between buyers and sellers is crucial for a sustainable and competitive economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How does an oligopsony impact consumers?
Answer: While oligopsony primarily affects sellers, it also indirectly impacts consumers by reducing product variety, limiting innovation, and potentially raising retail prices if buyers do not pass down cost savings.
Q2. Can sellers negotiate better terms in an oligopsony?
Answer: Yes, but it requires strategic action. Sellers can negotiate better terms by forming cooperatives, diversifying their buyer base, offering unique products, or leveraging alternative distribution channels.
Q3. What role does globalization play in oligopsony markets?
Answer: Globalization can intensify oligopsony effects as multinational corporations consolidate their buying power. However, it can also open new markets for sellers, reducing dependence on a small group of dominant buyers.
Q4. Can oligopsony exist in online marketplaces?
Answer: Yes. Large e-commerce platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Alibaba can create oligopsony conditions by controlling market access and dictating pricing and selling conditions for independent sellers.
Q5. Is there a way for governments to protect sellers in an oligopsony?
Answer: Yes, governments can introduce minimum price laws, anti-trust regulations, and fair-trade policies to prevent dominant buyers from exploiting sellers and to ensure fair competition.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on oligopsony has been insightful. Check out these recommended articles for more insights on market structures, economic dynamics, and business strategies.

