Updated July 31, 2023
Difference Between Operating Profit vs Net Profit
Operating Profit is the profit that is earned from the regular activities of the business or the enterprise. After arriving at the Gross Profit and from that, when operating expenses (i.e. indirect expenses) like salary, rent, depreciation, insurance, telephone expenses, and electricity are subtracted from it, we get Operating Profit. This can also be termed Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT), which should not be any Non-Operating Income. Net Profit is the positive value (surplus) that remains with the company or the firm after deducting or accounting for all expenses, interest, and taxes. After arriving at the Operating Profit margin figure, one needs to deduct the interest on long-term debt and corporate taxes from it, and the resultant figure will be Net Profit. It depicts the present or the current profitability position of the firm or the company.
Along with that, it will also reflect the success and failure of the company or the entity. Net Profit can also be referred to as Earnings After Taxes (i.e. EAT). Net Profit is shown in the income statement’s last or the bottom line.
Head To Head Comparison Between Operating Profit vs Net Profit (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between Operating Profit vs Net Profit
Key Differences Between Operating Profit vs Net Profit
Both Operating Profit vs Net Profit are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major Difference Between Operating Profit vs Net Profit:
- The income remaining after deducting all the indirect expenses incurred to run the business from the gross profit figure is known as operating profit. On the other hand, Net Profit is the final profit figure or says it is net of all expenses, interest, and corporate taxes.
- Operating Profit depicts the operating effectiveness of the company or the entity. Still, on the other side, the Net Profit figure will reveal the actual profit made during the financial year.
- Operating Profit will help in knowing those unnecessary expenses which can be eliminated. In contrast, the Net Profit figure will provide an overview of the management of the entire current position of the company or the entity.
- EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and tax) is another term for operating profit, whereas EAT (Earnings After Tax) is another term for net Profit.
Operating Profit vs Net Profit Comparison Table
Below are the 7 topmost comparisons between Operating Profit vs Net Profit
| Basis Of Comparison |
Operating Profit |
Net Profit |
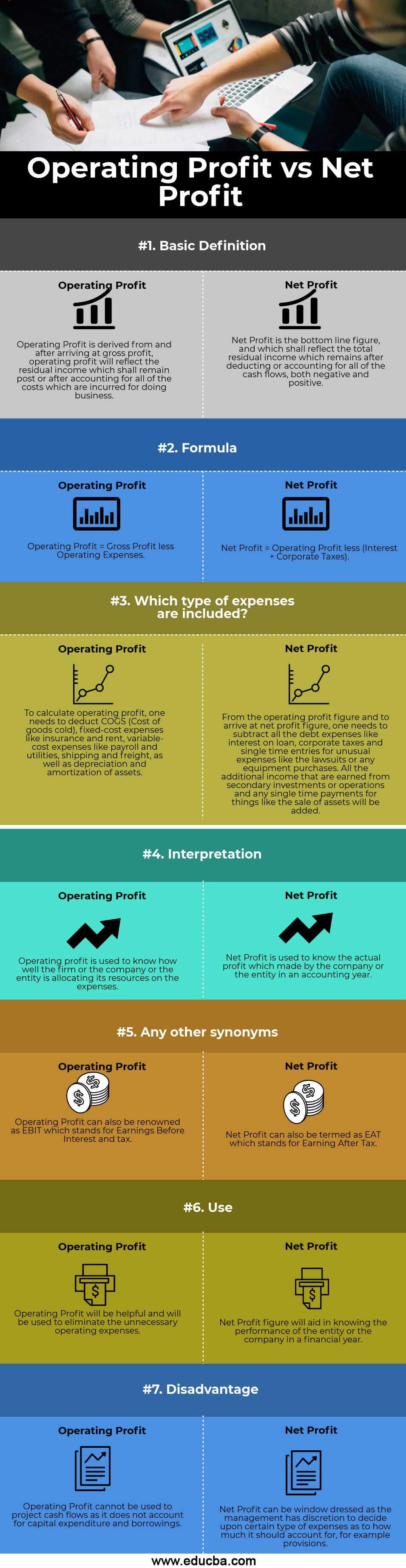
| Basic Definition | Operating Profit is derived from, and after arriving at gross profit, operating profit will reflect the residual income, which shall remain post or after accounting for all the costs incurred for doing business. | Net Profit is the bottom line figure, and it shall reflect the total residual income which remains after deducting or accounting for all of the cash flows, both negative and positive. |
| Formula | Operating Profit = Gross Profit less Operating Expenses | Net Profit = Operating Profit less (Interest + Corporate Taxes) |
| Which type of expenses are included? | To calculate operating profit, one must deduct COGS (Cost of goods sold), fixed-cost expenses like insurance and rent, variable-cost expenses like payroll and utilities, shipping and freight, and depreciation and amortization of assets. | From the operating profit figure and to arrive at the net profit figure, one needs to subtract all the debt expenses like interest on a loan, corporate taxes, and single-time entries for unusual expenses like lawsuits or equipment purchases. All the additional income earned from secondary investments or operations and any single-time payments for things like the sale of assets will be added. |
| Interpretation | The firm, company, or entity utilizes operating profit to assess how effectively it allocates resources to expenses. | The company or entity uses the net profit to determine the profit made during an accounting year. |
| Any other synonyms | Operating Profit can also be renowned as EBIT, which stands for Earnings Before Interest and tax. | Net Profit can also be called EAT, which stands for Earning After Tax. |
| Use | Operating Profit will be helpful and used to eliminate unnecessary operating expenses. | Net Profit figures will aid in knowing the performance of the entity or the company in a financial year. |
| Disadvantage | Using operating profit to project cash flows is not viable as it needs to account for capital expenditure and borrowings. | Net Profit can be window dressed as the management has the discretion to decide upon certain types of expenses as to how much it should account for, for example, provisions. |
Conclusion
The two types of profit, i.e. Operating Profit vs Net Profit, which we have discussed, are among the three slices of the term Profit. The meaning of these two Operating Profit vs Net Profit is apparent; further, there is no contradiction in understanding these terms.
At the fundamental level, gross profit is the initial profit figure derived by deducting all direct expenses. At the intermediate level, operating profit obtains by subtracting all indirect expenses incurred in running the business from the gross profit figure. However, when calculating operating profit, interest and tax must be excluded.
Lastly, the net profit figure at the bottom level represents the finest form of profit. It derives by deducting all expenses, corporate taxes, and interest from the operating profit. To provide a comprehensive view of the overall profit, we add any other non-operating income, such as income from the sale of assets like furniture or buildings or income from the sale of investments. As stated earlier, the management uses all three figures separately, which serves a different purpose.
Recommended Articles
This has guided the top difference between Operating Profit and Net Profit. Here we also discuss the Operating Profit vs Net Profit key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –