Updated July 26, 2023
Definition of Operating Ratio
The term “operating ratio” refers to the metric that measures the ability of a company to manage its operating expenses in a normal business setup.
In other words, it gauges the efficiency of a company’s management to keep its operating expenses low while generating revenue. The expenses-to-sales ratio, known as the OR, considers individual and group expenses.
The lower the ratio means, the higher the efficiency of the company to generate dollars versus the operating expenses, which will leave a portion of the sales to result in a higher profit margin or higher returns for the investors. On the other hand, a higher ratio results in a less favorable situation as it indicates lower profitability and so lower returns for the investors.
Formula
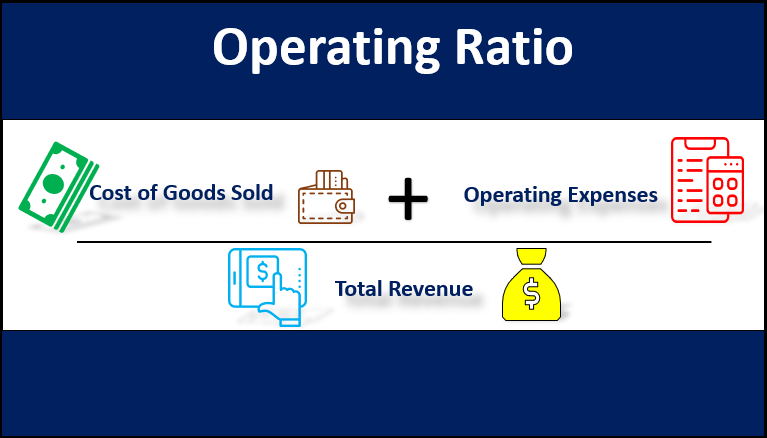
The formula for an OR can be derived by dividing the sum of the cost of goods sold and the operating expenses by the total revenue of the subject company. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Here, the cost of goods sold includes all the direct manufacturing costs, such as raw materials and labor wages. In contrast, operating expenses include all the indirect production costs, such as selling & distribution expenses, office & administration expenses, etc.
Examples of Operating Ratio (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the OR in a better manner.
Example – #1
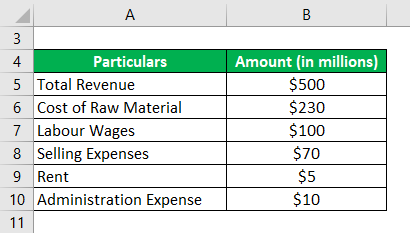
Let us take the example of a company named ZXC Ltd to illustrate the concept of operating ratio. As per the latest income statement, the following information is available:
Solution:
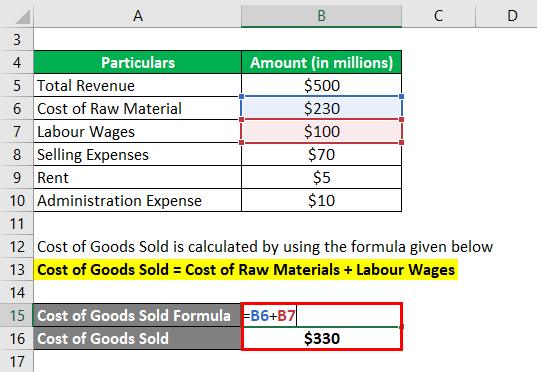
Cost of Goods Sold is calculated by using the formula given below
Cost of Goods Sold = Cost of Raw Materials + Labour Wages
- Cost of Goods Sold = $230 million + $100 million
- Cost of Goods Sold= $330 million
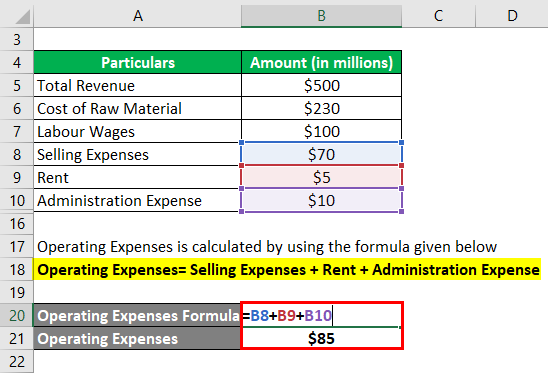
Operating Expenses is calculated by using the formula given below
Operating Expenses= Selling Expenses + Rent + Administration Expense
- Operating Expenses = $70 million + $5 million + $10 million
- Operating Expenses = $85 million
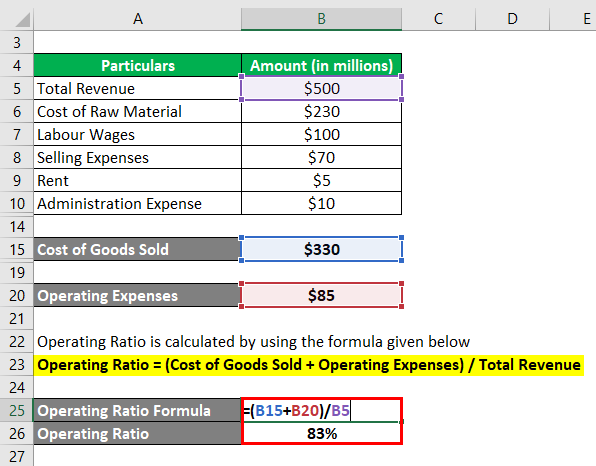
Operating Ratio is calculated by using the formula given below
Operating Ratio = (Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses) / Total Revenue
- OR = ($330 million + $85 million) / $500 million
- OR = 83%
Therefore, the operating ratio of ZXC Ltd is 83% for the latest year.
Example – #2
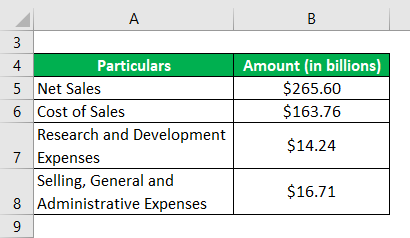
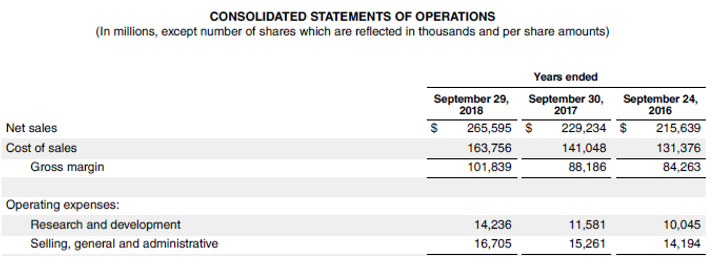
Let us take the example of Apple Inc. and calculate its operating ratio for the year 2018. As per the annual report for the year ending on September 29, 2018, the following information is available:
Solution:
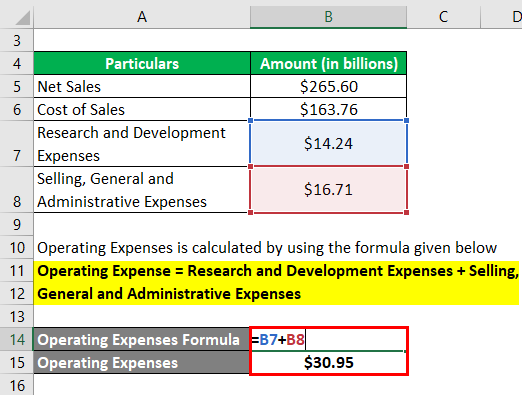
Operating Expenses is calculated by using the formula given below
Operating Expense = Research and Development Expenses + Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
- Operating Expense = $14.24 billion + $16.71 billion
- Operating Expense = $30.95 billion
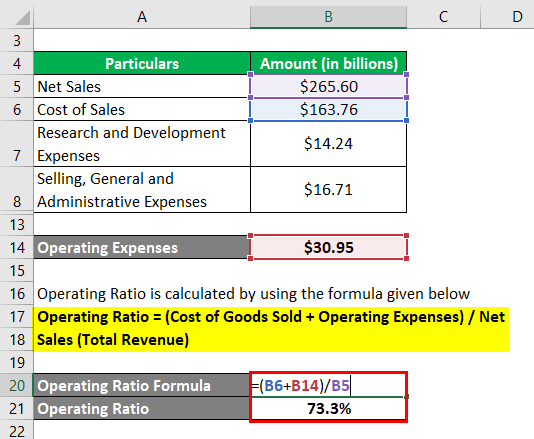
It can be calculated by using the formula given below
Operating Ratio = (Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses) / Total Revenue
- OR = (Cost of Sales + Operating Expenses) / Net Sales
- OR = ($163.76 billion + $30.95 billion) / $265.60 billion
- OR = 73.3%
Therefore, the operating ratio of Apple Inc. stood at 73.3% during the year 2018.
Source: Apple’s Annual Report
Example – #3
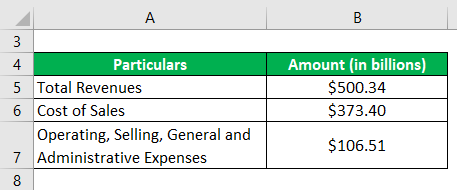
Let us take the example of Walmart Inc. and calculate its operating ratio for the year 2018. As per the annual report for the year ending on January 31, 2018, the following information is available:
Solution:
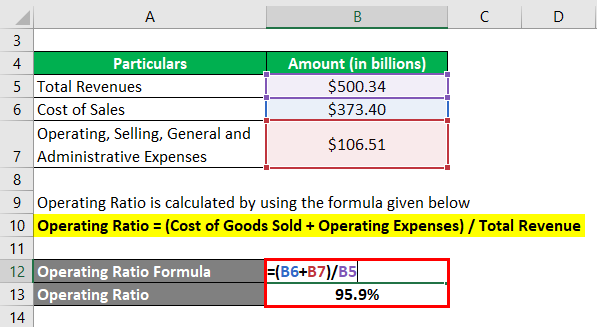
Operating Ratio = (Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses) / Total Revenue
- OR = ($373.40 billion + $106.51 billion) / $500.34 billion
- OR = 95.9%
Therefore, the operating ratio of Walmart Inc. stood at 95.9% during the year 2018.
Source: Walmart Annual Reports (Investor Relations)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Operating Ratio
Below are some of the advantages and disadvantages of the operating ratio
Advantages
- The ratio is a great indicator of the operational efficiency of a company’s management. A lower value of the ratio indicates better operational acumen of the management.
- Higher profitability is the eventual goal of any company, and this ratio provides a measure of the same.
Disadvantages
- Since the ratio doesn’t consider the effect of interest expense, companies with high debt might get away with this ratio, so two companies with similar operating ratios can have different capital structures.
- The ratio doesn’t make much sense if seen in isolation. Viewing and comparing the Cost of Goods Sold with its peers or monitoring it across a period to check for trends is important.
Conclusion
So, the operating ratio can be a very useful tool to measure the efficiency of a company when compared to peers or insights that can be drawn when monitored over a period of time to see how well the company management is performing.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Operating Ratio. Here we discuss calculation using its formula with examples and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –