What are the Options Trading Strategies?
Investors use options trading strategies like long and short calls to predict when stock prices will go up and make money by selling the options they hold.
You only have to do this one thing if you want to earn money. It’s the one thing some of the richest people on the Earth have done and are doing. This thing is also mentioned in ancient literature and cultures. But most people will fear doing it! John D. Rockefeller did it since his childhood, and he became a billionaire. Andrew Carnegie did it, too, and he became a tycoon. What is the greatest money-making secret in the history of humanity? What is the one thing that works for everyone? And the answer is……
GIVE AWAY MONEY!
That’s right. Give it away.
Now, you must be thinking that I have completely gone Crazy. But trust me, it works. But I do agree that to give away money, you need to have the same in the first place. There are some of the weirdest money-making ways available on the internet. But for those interested in making money through trading, we have various ways of Stock trading, Hedge funds, Options, etc. In this article, I will discuss some option trading strategies and numerical examples to help you achieve this goal. Before actually bombarding you with the option trading strategies, let me first explain to you what exactly the meaning of trading an option is.
An Option gives you the right to buy or sell an asset at a certain price and by a certain date. Let’s say you want to buy a guitar from your friend. And your friend wants $1500 for it. If you don’t have the money to buy it right now, you can tell your friend that you will pay $500 if he holds the guitar for you for a month. But if you don’t come up with $1500 by then, your friend can keep the $500 and do whatever he wants with the guitar.
In this case, the guitar is the asset, and your right to buy it under those terms is an option. But if your friend realizes that the guitar is worth $ 5,000, he will still have to sell it to you for $ 1,500 because you have that right, and thus you’ll make a profit. If the guitar breaks, you probably won’t want to spend $1500 entirely to buy it, but you’ll lose the $500 you used to believe that option. This is how options trading strategies work, but it’s complicated and risky. This article will show you how to start with various options trading strategies.
Strategy 1: LONG CALL
Buying calls can be an excellent way to capture the upside potential with limited downside risk. This is one of the options trading strategies for aggressive investors who are very bullish about a stock or an index. It is the most basic of all options trading strategies. It is comparatively an easy strategy to understand. Buying means you are bullish on a stock or an index and expect to rise in the future.
| Best time to Use: | When you are very bullish on the stock or index. |
| Risk: | Risk is limited to the Premium. (There is a maximum loss if the market expires at or below the option strike price). |
| Reward: | Reward is Unlimited |
| Breakeven: | (Strike Price + Premium) |
Example
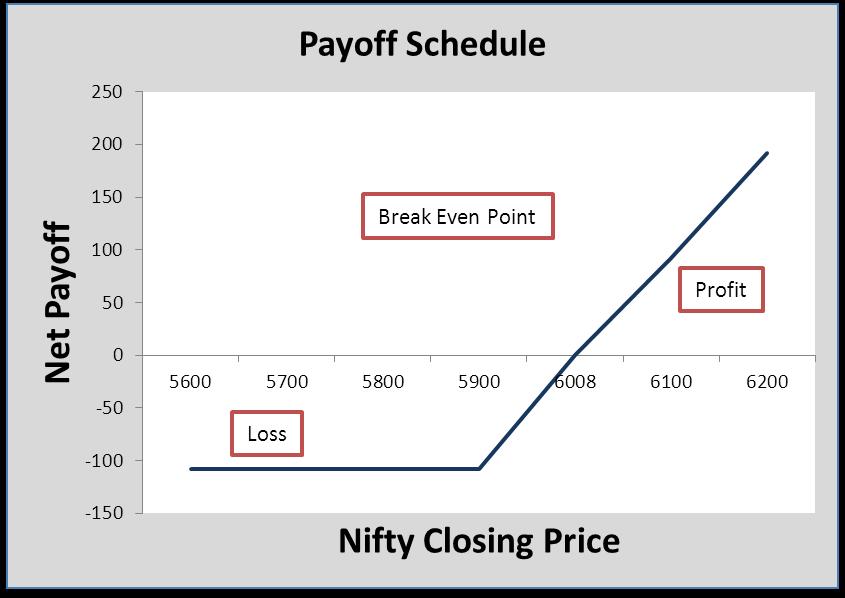
John is bullish on Nifty. On 25th May, the Nifty was at 5943.55. John buys a call option with a strike price of Rs. 5900 and a premium of Rs. 108, which expires on 31st July. If the Nifty goes above 6008 (5900+108), Mr. John will make a net profit (after deducting the premium) on exercising the option. If the Nifty stays at or falls below 5900, he can forego the opportunity (it will expire worthless) with a maximum loss of the premium.
The Input table gives you the price, premium, and Breakeven point data, whereas the Output table gives the data on the payoffs. Payoff means the profit or loss incurred in the transaction.
Input
| Strategy: Buy call Option | ||
| Current Nifty Index |
5943.55 |
|
| Call Option | Strike Price (Rs.) |
5900 |
| Mr. John Pays | Premium (Rs.) |
108 |
| Break Even Point (Rs | (Strike price + premium) |
6008 |
| The Payoff Schedule | |
| On expiry, Nifty Closes at | Net payoff |
|
5600 |
-108 |
|
5700 |
-108 |
|
5800 |
-108.00 |
|
5900 |
-108.00 |
|
6008 |
0 |
|
6100 |
92 |
|
6200 |
192 |
ANALYSIS: It limits the downside risk to the extent of the premium (Rs. 108) paid by Mr. John. But if there is a rise in Nifty, then the potential return is unlimited. This is one of the option trading strategies that will offer you the simplest way to benefit. And that is why it is the most common choice among first-time investors in Options.
Strategy 2: SHORT CALL
In the strategy we discussed above, we were hoping that the stock would rise in the future, so we adopted a strategy of LONG CALL there. But this strategy of SHORT CALL is the opposite of that. When you expect the underlying stock to fall, you adopt this strategy. An investor can sell Call options when he is very bearish about a stock/index and expects the prices to fall. This is a position that offers limited profit potential. Investors can incur large losses if the underlying price increases instead of decreases. Though this strategy is easy to execute, it can be quite risky since the seller of the Call is exposed to unlimited risk.
| Best time to Use: | When you are very bearish on the stock or index. |
| Risk: | The risk here becomes Unlimited |
| Reward: | The reward is limited to the amount of premium |
| Breakeven: | Strike Price+ Premium |
Example
Matt is bearish about Nifty and expects it to fall. Matt sells a Call option with a strike price of Rs. 5900 at a premium of Rs. 108 when the current Nifty is 5943.55. If the Nifty stays at 5900 or below, the buyer of the Call will not exercise the Call option, and Matt can retain the entire premium of Rs.154.
Input
| Strategy: Sell call Option | ||
| Current Nifty Index |
5943.55 |
|
| Call Option | Strike Price (Rs.) |
5900 |
| Mr. Matt receives | Premium (Rs.) |
108 |
| Break Even Point (Rs.) = (Strike price + premium) |
6008 |
|
Output
| The Payoff Schedule | |
| On expiry, Nifty Closes at | Net payoff |
|
5600 |
108 |
|
5700 |
108 |
|
5800 |
108 |
|
5900 |
108 |
|
6008 |
0 |
|
6100 |
-92 |
|
6200 |
-192 |
ANALYSIS: This strategy is useful when an investor strongly expects the price to fall. This is a risky strategy. As the stock prices rise, the short call loses money more quickly. This strategy is called a Short Naked Call since the investor does not own the underlying stock he is shorting.
Strategy 3: LONG PUT
Long Put is different from Long Call. You must understand that buying a Put is the opposite of buying a Call. When bullish about the stock/index, you buy a Call. But when you are bearish, you can buy a Put option. A Put Option gives the buyer of the Put a right to sell the stock (to the Put seller) at a pre-specified price. He thereby limits his risk. Thus, the Long Put here becomes a Bearish strategy. You can buy Put options to take advantage of a falling market as an investor.
| Best time to Use: | When the investor is bearish about the stock /index. |
| Risk: | Risk is limited to the amount of Premium paid. |
| Reward: | Unlimited |
| Breakeven: | Stock Price – Premium |
Example
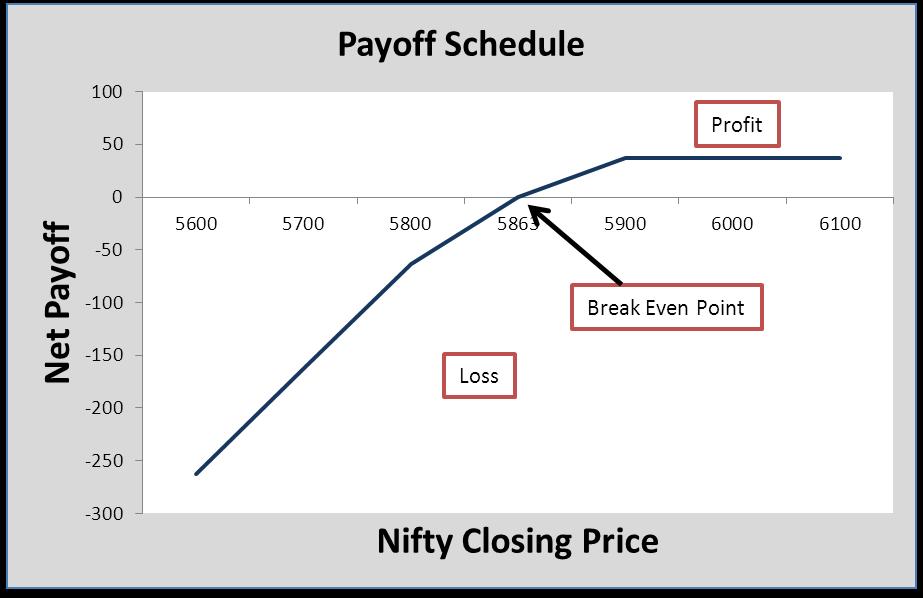
Jacob is bearish on the Nifty on 24th April, when the Nifty was at 5943.55. He buys a Put option with a strike price of Rs. 5900 at a premium of Rs. 37, expiring on 31st May. Jacob will profit from exercising the option if the Nifty exceeds 5863 (5900-52). If the Nifty rises above 5900, he can give up the option (it will expire worthless) with a maximum loss of the premium.
Input
| Strategy: Buy Put Option | ||
| Current Nifty Index |
5943.55 |
|
| Put Option | Strike Price (Rs.) |
5900 |
| Mr. Jacob pays | Premium (Rs.) |
37 |
| Break Even Point (Rs.) = (Strike price – premium) |
5863 |
|
Output
| The Payoff Schedule | |
| On expiry, Nifty Closes at | Net payoff |
|
5600 |
263 |
|
5700 |
163 |
|
5800 |
63 |
|
5863 |
0 |
|
5900 |
-37 |
|
6000 |
-37 |
|
6100 |
-37 |
ANALYSIS: If you are bearish, you can profit from the declining stock prices by buying Puts. You can limit your risk to the amount of premium paid, but your profit potential remains unlimited. This is a widely used option for trading strategy when an investor is bearish.
Strategy 4: SHORT PUT
In Long Put, we saw that when the investor is bearish on a stock, he buys Put. But selling a Put is the opposite of buying a Put. An investor will generally sell the Put when he is Bullish about the stock. In this case, the investor expects the stock price to rise. When an investor sells a Put, he earns a Premium (from the buyer of the Put). Here, the investor has sold someone the right to sell him the stock at the strike price. If the stock price increases above the strike price, this strategy will profit the seller since the buyer will not exercise the Put. But, if the stock price decreases below the strike price, more than the premium amount, the Put seller will start losing money. The potential loss is unlimited here.
| Best time to Use: | When the investor is very Bullish on the stock or the index. |
| Risk: | Put Strike Price –Put Premium. |
| Reward: | It is limited to the amount of Premium. |
| Breakeven: | Stock Price – Premium |
Example
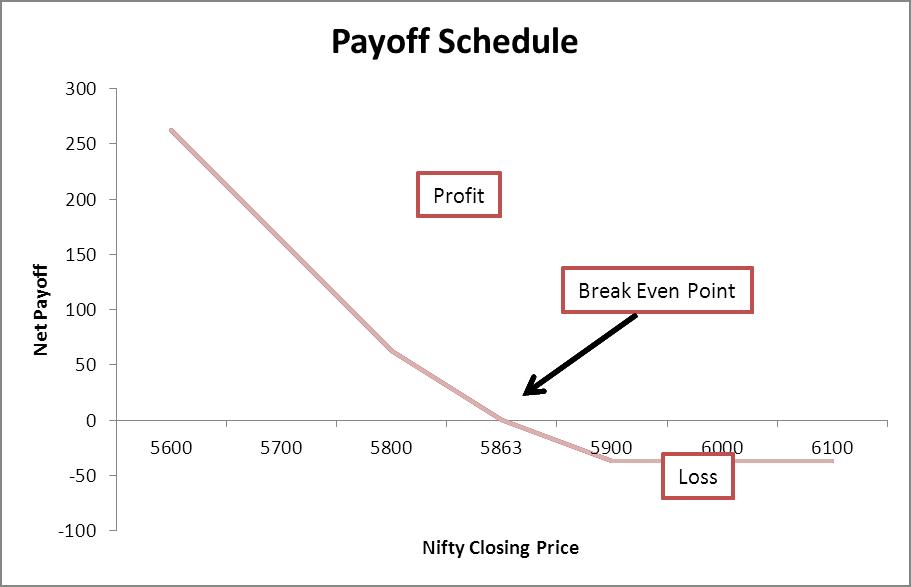
Richard is bullish on the Nifty when it is at 5943.55. Richard sells a Put option with a strike price of Rs. 5900 at a premium of Rs. 37 expiring on 31st July. If the Nifty index stays above 5900, he will gain the premium as the Put buyer won’t exercise his option. If the Nifty falls below 5900, the Put buyer will exercise the option, and Richard will start losing money. If the Nifty falls below 5863, which is the breakeven point, Richard will lose the premium and more depending on the extent of the fall in Nifty.
Input
| Strategy: Sell Put Option | ||
| Current Nifty Index |
5943.55 |
|
| Put Option | Strike Price (Rs.) |
5900 |
| Mr. Richard receives | Premium (Rs.) |
37 |
| Break Even Point (Rs.) | = (Strike price – premium) |
5863 |
Output
| The Payoff Schedule | |
| On expiry, Nifty Closes at | Net payoff |
|
5600 |
-263 |
|
5700 |
-163 |
|
5800 |
-63 |
|
5863 |
0 |
|
5900 |
37 |
|
6000 |
37 |
|
6100 |
37 |
ANALYSIS: Selling Puts can lead to regular income, but it should be done carefully since the potential losses can be significant. This strategy is income-generating.
Strategy 5: LONG STRADDLE
The long straddle strategy is also known as buy straddle or simply “straddle”. It is one of the neutral options trading strategies that involve simultaneously buying a put and a call of the same underlying stock. The strike price and expiration date are the same. This strategy can achieve large profits regardless of the underlying stock price by having long positions in both call and put options. But the move has to be strong enough.
| Best time to Use: | When the investor thinks that the underlying stock/index will experience significant volatility in the near term. |
| Risk: | Limited to the initial premium paid. |
| Reward: | The reward here is Unlimited |
| Breakeven: |
|
Example
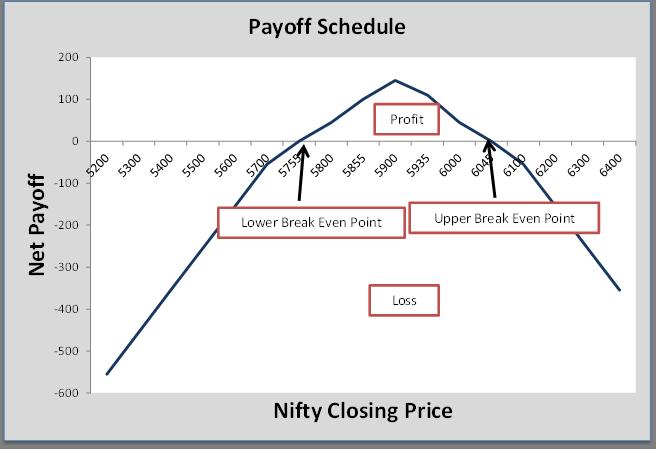
Mr. Harrison goes to the NSE website. He fetches the data for the Current Nifty Index, Strike Price (Rs.), and Premium (Rs.). He then selects the index derivative. In instrument type, Harrison selects index options. In symbol, he selects nifty, the expiry date is 31 January 2013, the option type will be a Call, and the Strike price is 5900. Call Premium paid is RS 108. Now, in the option type he selects Put, the Strike price is the same as above i.e. 5900. So The premium paid is 37.
The data for our input table is as follows:
The current nifty index is 5943.55
The strike price is 5900
The total premium paid is 108+37, which equals 145.
The upper Breakeven point is calculated as 5900+145, which comes to 6045
The lower Breakeven point is calculated as 5900-145, which comes to 5755
We will assume Nifty Closes as on expiry Nifty Closes at 5200,5300,5400,5500, and so on.
Input
| Strategy: Buy Put + Buy Call | ||
| Current Nifty Index |
5943.55 |
|
| Call and Put Option | Strike Price (Rs.) |
5900 |
| Call Premium (Rs.) |
108 |
|
| Mr. Harrison pays | Put Premium (Rs.) |
37 |
| Total Premium (Rs) |
145 |
|
| Break Even Point (Rs.) |
6045 |
|
| Break Even Point (Rs.) |
5755 |
|
Output
| The Payoff Schedule | |||
| On expiry, Nifty Closes at | Net payoff from Put Purchased (Rs.) | Net payoff from call Purchased (Rs.) | Net Payoff (Rs.) |
|
5200 |
663 |
-108 |
555 |
|
5300 |
563 |
-108 |
455 |
|
5400 |
463 |
-108 |
355 |
|
5500 |
363 |
-108 |
255 |
|
5600 |
263 |
-108 |
155 |
|
5700 |
163 |
-108 |
55 |
|
5755 |
108 |
-108 |
0 |
|
5800 |
63 |
-108 |
-45 |
|
5875 |
-12 |
-108 |
-120 |
|
5900 |
-37 |
-108 |
-145 |
|
5945 |
-37 |
-63 |
-100 |
|
6000 |
-37 |
-8 |
-45 |
|
6045 |
-37 |
37 |
0 |
|
6100 |
-37 |
92 |
55 |
|
6200 |
-37 |
192 |
155 |
|
6300 |
-37 |
292 |
255 |
|
6400 |
-37 |
392 |
355 |
|
6500 |
-37 |
492 |
455 |
|
6600 |
-37 |
592 |
555 |
Strategy 6: SHORT STRADDLE
A Short Straddle is exactly the opposite of a Long Straddle. An investor can adopt this strategy when he feels the market will not move much. He sells a Call and a Put on the same stock/index for the same maturity and strike price. It creates a net income for the investor. If the stock/index does not move much in either direction, the investor retains the Premium, as neither the Call nor the Put will be exercised.
| Best time to Use: | When the investor thinks that the underlying stock will experience very little volatility in the near term. |
| Risk: | Unlimited |
| Reward: | Limited to the premium received |
| Breakeven: |
|
Example
Mr. Buffey goes to the NSE website and fetches the data for the Current Nifty Index, Strike Price (Rs.), and Premium (Rs.). He then selects the index derivative. In instrument type, he selects index options. In symbol, he selects nifty, the expiry date is 31 January 2013, the option type will be a Call, and the Strike price is 5900. Call Premium paid is RS 108. Now, in the option type, he selects Put. The strike price is the same as above i.e. 5900. So the Put premium paid is 37.
Input
| Strategy: Sell Put + Sell Call | ||
| Current Nifty Index |
5943.55 |
|
| Call and Put Option | Strike Price (Rs.) |
5900 |
| Call Premium (Rs.) |
108 |
|
| Put Premium (Rs.) |
37 |
|
| Mr. Buffey receives | Total Premium (Rs) |
145 |
| Break Even Point (Rs.) |
6045 |
|
| Break Even Point (Rs.) |
5755 |
|
Output
| The Payoff Schedule | |||
| On expiry, Nifty Closes at | Net payoff from Put Sold (Rs.) | Net payoff from call Sold (Rs.) | Net Payoff (Rs.) |
|
5200 |
-663 |
108 |
-555 |
|
5300 |
-563 |
108 |
-455 |
|
5400 |
-463 |
108 |
-355 |
|
5500 |
-363 |
108 |
-255 |
|
5600 |
-263 |
108 |
-155 |
|
5700 |
-163 |
108 |
-55 |
|
5755 |
-108 |
108 |
0 |
|
5800 |
-63 |
108 |
45 |
|
5855 |
-8 |
108 |
100 |
|
5900 |
37 |
108 |
145 |
|
5935 |
37 |
73 |
110 |
|
6000 |
37 |
8 |
45 |
|
6045 |
37 |
-37 |
0 |
|
6100 |
37 |
-92 |
-55 |
|
6200 |
37 |
-192 |
-155 |
|
6300 |
37 |
-292 |
-255 |
|
6400 |
37 |
-392 |
-355 |
ANALYSIS: If the stock moves up or down significantly, the investor’s losses can be significant. This is a risky strategy. It should be carefully adopted only when the expected volatility in the market is limited.
Options Trading Strategies Infographics
Learn the Juice of this article in a minute through Options Trading Strategies Infographics.