Introduction to Overloading and Overriding in C++
Let’s begin this by having the basic definitions for Overloading and Overriding in C++.
Overloading: The function name is the same but the parameters and returns type changes. Since we will get to know the difference between the overloaded functions during compile time, it is also called Compile time polymorphism.
Overriding: This is a feature of Object-Oriented Programming language where the function of the child class has the same name as the parent’s class function. As the overriding functionality comes into the picture once the object is declared and the functions are accessed using the objects; that is during the execution of code, this concept of overriding is also called run time polymorphism.
We have their syntax and their programming ways in the later sections.
Syntax of Overloading and Overriding
Here is the syntax of the overloading and overriding given below.
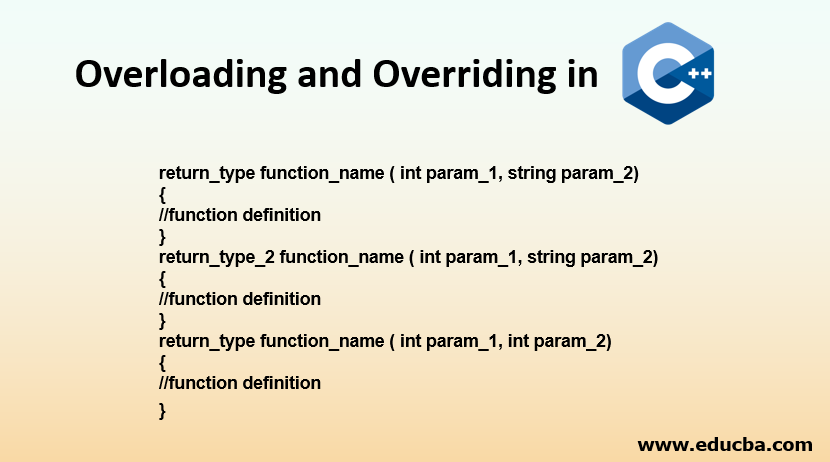
Overloading Syntax:
return_type function_name ( int param_1, string param_2)
{
//function definition
}
return_type_2 function_name ( int param_1, string param_2)
{
//function definition
}
return_type function_name ( int param_1, int param_2)
{
//function definition
}All three of them together can form an example of the concept of Overloading.
Overriding Syntax:
Class A
{
Public:
void function_name ( int param_1, int param_2)
{
//function definition
}
};Class B : Class A
{
Public:
void function_name ( int param_1 , int param_2)
{
//function definition
}
};The above is the syntax for the overriding functionality. The main output can be inferred once we declare an object and call those same methods from Class A and Class B. In the functionality of overriding the “Object” plays an important role.
Now let us see an example each for getting to know their functionality better.
Examples of Overloading and Overriding in C++
Here are the examples of Overloading and Overriding in C++ with the output given below:
Example #1 – Overloading
Let’s begin with a simple program.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int calc(int);
float calc(float);
int calc(int, float);
int main()
{
int a = 10;
float b = 11.2;
calc(a);
calc(b);
calc(a,b);
}
int calc(int a)
{
int tot=a*a;
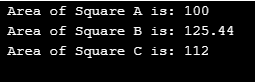
cout << " Area of Square A is: " << tot<<endl;
}
float calc(float b)
{
float tot = b*b;
cout << " Area of Square B is: " << tot <<endl;
}
int calc(int a, float b)
{
int tot = a*b;
cout << " Area of Square C is: " << tot << endl;
}Output:
Now, what if I give the wrong data type values for the variables a, b?
Code:
int main()
{
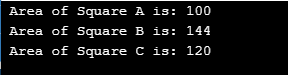
int a = 10.8;
float b = 12;
calc(a);
calc(b);
calc(a,b);
}I have only changed the main part from the above program, so here goes the output.
Output:
It gives us the output as it is going to convert the float value to int data type and gives us the output.
Now as an exercise can you try changing the function return type and parameters and play around with them.
Example #2 – Overriding
Below we can have an example for an overriding functionality in C++.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class First
{
public:
virtual void Calc( int a , float b)
{
int tot= a*b;
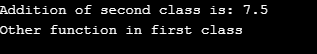
cout << "Square of First class is: "<< tot <<endl;
}
void Other()
{
cout<<"Other function in first class"<<endl;
}
};
class Second : public First
{
public:
// Overriding method
void Calc(int a ,float b)
{
float tot = a+b;
cout << "Addition of second class is: " <<tot<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
int a= 5;
float b=2.5;
Second s;
First &f1 = s;
f1.Calc(a,b);
s.Other();
}Output:
Through the above code, we can find that when the reference of the first-class object is assigned to the object created with respect to our second class. And then when we accessed the override method using the object of the base class, we can clearly notice that the derived class output has been displayed. This concept is called overriding. The first and Second classes are the Base and Derived Class respectively. The output of the above is a below:
As an exercise can you try overriding and overloading a function together and check if it is possible or check how the output turns out to be?
How Does it Work?
Let us know how it works.
Overloading: Here, there is no special point that we can have a note of. We need to make sure that the return type or the parameters inside the function vary. If we look above at the programming structure, the functions are declared first and their implementation is given.
Overriding: The syntax of Inheritance and implementation of functions are the key points to be noticed here. In the example above we can notice that the declaration of function with public keyword is quite different.
And in C++, the class definition is ended by a semi-colon (;) and if we need to inherit the base class to the child class, we use the colon (:) symbol. The main functionality of overriding is observed when objects are declared and initialized for the class. After the calling of functions using the objects, we can then clearly understand the concept of overriding.
Advantages
Following are the advantages mentioned below.
- The one main advantage of these overriding and overloading is time-saving.
- Save memory space.
- The readability of the code is increased.
- Here, for function overloading concept, we can use different same function names for different operations eliminating the use of different function names.
- Flexibility and maintainability of code become easier.
- In the case of overriding, the child class can have functions of parent class and can even have its own implementation of that function.
- The objects can be referenced and the functions of both the parent class and child class can be accessed by the child class.
Conclusion
We have now clearly understood the concepts of both overloading and overriding. In overloading, we have to make sure the difference in the overloaded functions exists either based on return type or the parameters, though the function definition inside them is the same or different.
And in the case of overriding, since it is an object-oriented programming concept, we can only utilize in the form of classes using the functionality of inheritance.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Overloading and Overriding in C++. Here we discuss the introduction, how does it works, examples, and advantages of overloading and Overriding in C++ with code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –