Updated July 13, 2023

Definition of Period Cost
Period cost refers to the fixed costs which are incurred & presented in the financial statements of the relevant year, irrespective of the actual production in the company, which is not based on any variable factor of production but is the same essential for the continuation of the normal operations of the company. In this topic, we are going to see different examples of Period Cost.
Explanation
- As the name suggests, the company has to incur “period” costs specific to a particular period. Some people refer to this cost as fixed cost.
- These costs have no reference to the actual production units of the company. These are normally capacity-driven costs.
- The company accounts for these costs in the year they are incurred.
- Period costs are not associated with any specific product. These are unavoidable costs & thus, are not included in the inventory valuation. On the other hand, product costs are associated with the particular products & are included in the normal production valuation.
- Fixed costs are also called time costs.
- Examples of period costs include depreciation of factory premises, fixed salary expense, company administration costs, allocated costs from head office, etc.
Examples of Period Cost
Let us look at the below examples of the Period Cost with calculations:
Example #1
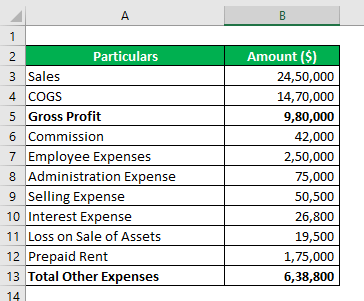
The company is a manufacturer of mousepads. It has provided a summary of the income statement. Our job is to identify whether the same is a period cost.
Solution:
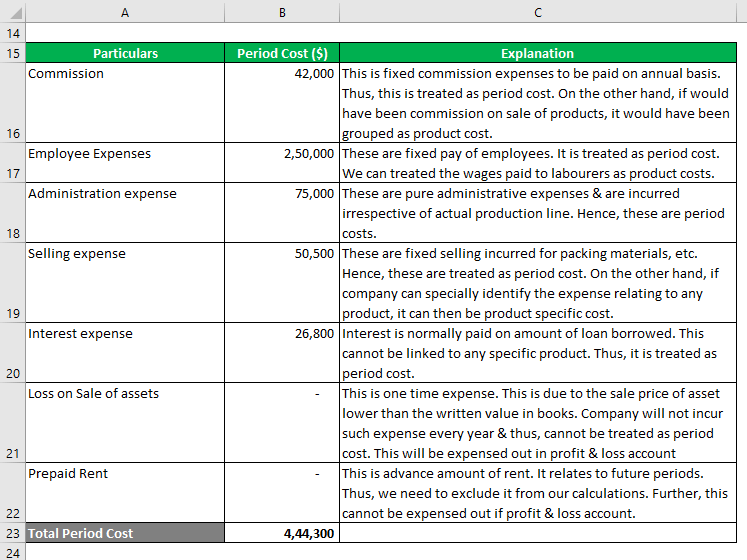
Sales & COGS are product-related amounts. We will start with commission expenses. By period cost, we mean the cost related to a period & not to any product.
Of $ 6,38,800 expenses, only $ 4,44,300 can be treated as period cost.
Example #2
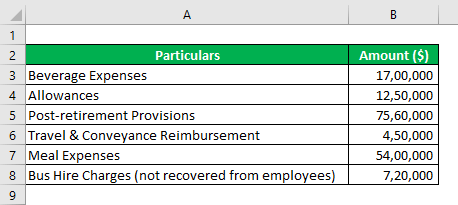
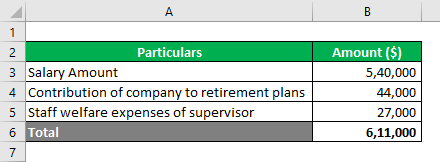
The company is engaged in business process outsourcing services. It has around 15000 employees overall units in the country. Since the employees are the revenue-generating resources for the company, it cares a lot for their convenience & welfare. Over the years, it has been incurring handsome amounts of expenses for the employees. The company wants to understand whether these can be treated as product costs.
Solution:
Explanation:
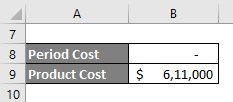
All such expenses are incurred in the period in which they are incurred. The company may believe that these expenses increase the efficiency of the employees & improve the quality of their performance. We accept that employees are revenue-generating resources of the company. However, these cannot be linked to the company’s end product. The company will incur these expenses even if the services are stopped. Hence, such expenses are shown as period costs.
Example #3
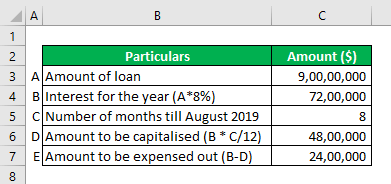
The company manufactures calculators. It wishes to expand its operations. Thus, on 1st January 2019, it decided to purchase new machinery costing $ 90 million through a loan carrying an interest rate of 8%. The company wishes to treat the interest expense as a product-related cost since the machinery will increase production efficiency by 20%. However, the machinery required installation & many formalities at the time of purchase; the company could put the machine to use only at the end of August 2019.
Solution:
Explanation:
The company’s contention to treat the interest amount as product cost just because the efficiency increases by 20% is inappropriate. As per accounting standards, the company needs to capitalize on the amount of interest till the date the asset is used. Thus, $ 4.8 million needs to be capitalized & the balance to be shown as an expense in the profit & loss account. Therefore, $ 2.4 million is the amount of the period cost. The interest expense will be treated as a period cost even in future years.
Example #4
The company hires a supervisor to guide and direct the laborers in manufacturing products and pays the supervisor the following expenses. The company has clubbed these expenses as “Other Expenses” in the statement of profit & loss account & treated the same as a period cost since the pay is fixed.
Solution:
Explanation:
The cost of a supervisor is directly linked to the manufacturing of products. His directions are helpful for the production chain. His absence will disrupt the quality of the units. Thus, all expenses incurred for the supervisors are treated as product costs & added to the cost of goods sold. The expense cannot be treated as a period cost because he is paid a fixed monthly amount.
Example #5
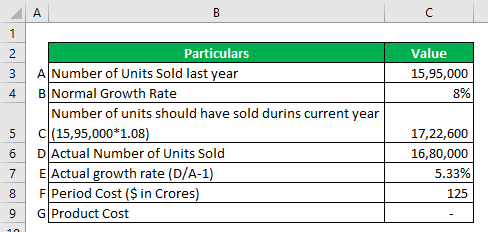
The sale of cold drinks was 15,95,000 units in the last year. The company has incurred an overall advertisement cost of $ 125 crores this year. The total sales at the end of the current year are 16,80,000 units. The normal growth of the company product line is 8% every year. The company intends to treat $ 125 crore as a product cost seeing the rise in demand.
Solution:
Explanation:
The growth % achieved in the current year is unrelated to the advertisement cost. This means the company is expecting a reduction in demand for cold drinks. Many factors may contribute to the increase or decrease in demand, but this cannot be correlated to advertisement costs. Hence, advertisement cost is to be treated as period cost.
Example #6
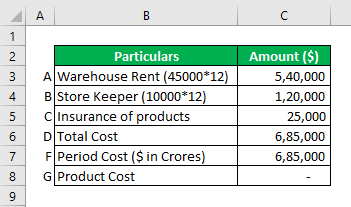
The company required a separate space for the storage of its finished goods. Therefore, it contracted with a vendor for a warehouse to be taken on rent for $ 45,000 per annum. Also, as per the agreement company needs to hire a new employee as a storekeeper for $ 10,000 per month & also has to pay an insurance cost of $ 25,000 for its products in the said warehouse. The company intends to treat this cost as product cost.
Solution:
Explanation:
The company will have to incur these costs irrespective of actual production. This is because these expenses are close to the products, but the production of units is not affected by incurring these costs. Hence, all such expenses are treated as period costs & expenses in the statement of profit & loss.
Conclusion
On a concluding thought, we can summarise that period costs are presented in the year’s financial statements, in which they have been paid for. In some cases, such as prepaid expenses, only that part of the incurred cost is shown as period cost. The company cannot avoid these costs unless it wants to discontinue a few operations. These costs are inbuilt into the company’s normal operations since these are majorly made for administrative purposes. During the COVID-19 pandemic, companies have managed to reduce the period cost by negotiating rental expenses for the factory, minimization of administrative use of office, lower traveling expenses, reduction in out-of-pocket costs, etc.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Period Cost Examples. Here we discuss the overview and top 6 practical Period Cost Examples, a detailed explanation, and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –