Table of Contents
Components of Point of Sale
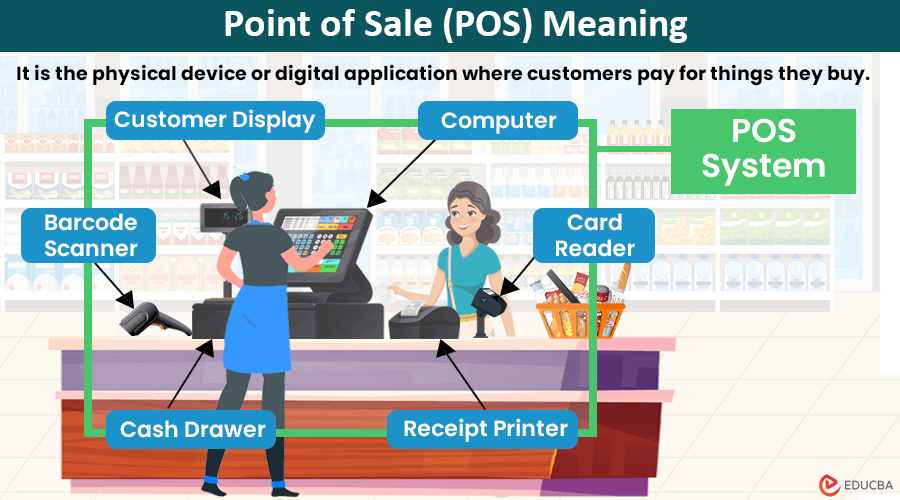
POS systems consist of the following hardware and software components.
Software:
- Desktop Software: It is a software that handles accounting, records the payment details, tracks inventory, generates reports, etc. However, the POS system will record all details in the single device that has this software. Thus, it is useful for businesses that have a single cash counter.
- Cloud-Based Software: It works like desktop software, but apart from that, it also syncs data across multiple devices. Large businesses prefer this as it helps them efficiently manage huge amounts of data.
Hardware:
- Computer/Tablet/Smartphone: It displays the user interface of POS software where the staff inputs purchase data during payment processing.
- Barcode Scanner: Barcode scanners or readers are machines that scan the product’s barcode. It speeds up the checkout process by quickly and accurately identifying items.
- Card Reader (Debit/Credit): A card reader reads debit and credit card details for contactless payment.
- Cash Drawer: The cash drawer is usually present below the computer system. It stores cash, coins, and checks collected during transactions. They are connected to the POS system and can open and close electronically.
- Customer Display: Some systems come with customer-facing display units. This display shows transaction details and pricing to the customer during checkout.
- Receipt Printer: Receipt printers produce physical or digital prints of receipts for customers after they complete a transaction. With technological advances, some printers directly send receipts to customers’ email or contact numbers.
How Does a POS System Work?
A POS system works in the following manner.
1. Scanning the Product
The customer selects an item and brings it to the checkout counter. Here, the cashier uses the “Barcode Scanner” connected to the POS system to scan the item. Sometimes, it is done manually by entering product codes or selecting items from a menu interface on the computer.
2. Recording Data and Calculating the Payable Amount
The system records the item details, including the item name, quantity of the same items, price, etc. Then, it calculates the total amount payable by the customer, including taxes and discounts. The “Customer Display” unit will also display the information for customers to see.
3. Processing the Payment
The customer can choose a payment method, such as cash, cards, mobile payment, or gift card, to process the payment.
If customers choose a cash payment method, the salesperson will keep the cash in the “Cash Drawer.” If the customer wants to pay using a card (debit or credit), the cashier would use a “Card Reader.”
For mobile payment, the customer has to hold their phone over the POS card terminal. The system’s card reader processes the payment after the customer’s bank authorizes it.
4. Printing a Receipt
After successful payment, the system generates a receipt using the “Receipt Printer” mentioning the details of the purchased items. Depending upon the retail POS setup, it may also send a digital receipt to the customer’s email or contact number.
5. Updating Inventory Levels
In addition to processing transactions, these systems often include inventory management features. Thus, when you sell an item, the system automatically updates the inventory levels to reflect the stock changes. It helps businesses track their inventory in real-time and prevent stockouts or overstocking.
6. Generating Reports
POS systems generate analytical reports that provide insights into sales trends, inventory levels, and customer behavior. Businesses can use this information to make decisions about pricing, inventory purchasing, and marketing strategies.
Point of Sales Example
Let’s say that a customer, Andrew, wants to purchase a list of items from your clothing store. Here are the steps on how the POS system will help you with the checkout process.
- Andrew selects a bunch of outfits, comes to the cash register, and sets down his items.
- You first use a barcode scanner to scan the items. The scanner transfers the details about the clothes to the POS system.
- From there, the system calculates the total purchase amount and displays it on the customer display.
- The system simultaneously also manages inventory count considering the items purchased.
- Suppose Andrew chooses to pay by credit card. Then, you will use the card reader to complete the transaction.
- The card reader charges the cardholder’s bank, and the purchase goes through.
- Once paid, you can generate a receipt for the customer using the POS system.
Types of POS systems
- Traditional: It is when the POS software is installed on a desktop computer. Apart from the single computer, there are other devices like cash drawer, barcode scanner, receipt printer, etc.
- Mobile/Handheld POS: It is when the POS system runs on mobile devices like tablets or smartphones. They are popular for businesses that need flexibility, like food trucks.
- Cloud-Based: These systems store data online rather than on local servers. They offer real-time access to data from anywhere with an internet connection. They are popular among businesses with multiple locations.
- Self-Service Kiosk: These systems allow customers to complete transactions themselves without assistance from staff. They are common in the hospitality and fast-food industries.
- Open-Source POS: This is when the developer uses open-source software or code to build the POS system. It lets businesses customize the system to their specific needs, offering flexibility.
- Multichannel POS: It allows customers to buy goods/services from multiple platforms, like online and offline stores. However, each channel operates independently. It means a product available online may not be available in an offline store, and vice versa.
- Omnichannel POS: It is similar to multichannel POS but has one key difference: all the multiple channels are interconnected. It means customers can browse the online shop, pick a product, and then buy it hassle-free at a physical store.
Features
The features of the point of sale are as follows.
1. Transaction Processing
POS systems facilitate quick and secure payment processing. It allows payments through various methods, including cash, debit cards, credit cards, mobile payments, and digital wallets. For example, a Global Payments POS system will ensure seamless, secure, and uninterrupted transactions for both businesses and customers. Thus, the POS system helps enhance transaction efficiency and business operations.
2. Inventory Management
POS systems help businesses track stock levels, manage inventory, and automate reorder processes. For example, a gym can use a gym POS system to monitor fitness equipment, supplements, and apparel, ensuring real-time data on product availability, reducing instances of stockouts, and preventing overstocking.
3. Sales Reporting and Analytics
Point-of-sale systems generate detailed reports providing valuable information about sales trends, specific product sales periods, and best-selling items. It also provides insight into employee and team performance.
4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Some POS systems include CRM features, allowing companies to store customer information, like purchase histories, product preferences, and contact information. This information helps build personalized interactions and a strong customer relationship, like implementing customized market campaigns.
5. Employee or Staff Management
POS systems help businesses manage employee schedules, track hours worked, and monitor employee performance. The information assists in providing commission and processing the payroll of staff members.
6. Integration Capabilities
These systems have the ability to integrate with other tools and software applications. It includes accounting software, e-commerce platforms, and marketing automation tools. It improves overall business efficiency.
7. Customization Options
POS systems allow businesses to tailor the user interface and report format to their needs. In addition, businesses can also customize POS with menus and update prices according to their specific requirements.
8. Security Features
POS systems have data security features that comply with industry standards such as PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry-Data Security Standard). This feature encrypts sensitive data by implementing security measures like tokenization. It protects customer’s sensitive information and prevents unauthorized access.
Advantages of Point of Sales System
- Saves Time: The POS features save the time that you spend on administrative activities. For instance, a POS system provides instant inventory reports, allowing you to monitor stock levels without hassle.
- Multi-Store Systems: It can be challenging to provide the same level of service to every store if you operate multiple ones. Thus, using a POS system, you can handle several stores with the same degree of effectiveness.
- Increased Sales: Some POS systems provide actionable insights into your sales trends. Therefore, you may identify areas where change is required and boost your revenue.
Disadvantages of Point of Sale system
- Expensive: POS systems can be slightly expensive since they offer many more features than a standard cash register. It can also be pricey and time-consuming to fix or replace if something goes wrong.
- Security Risks: A point-of-sale system, like any other internet-based system, can be vulnerable to flaws or viruses. It can cause malfunction, which can disrupt operations.
- Frequent Upgrades: POS system suppliers regularly release changes to the system. It means you will need to frequently pay for upgrades, new licenses, and software.
Final Thoughts
As the article outlines, choosing the right POS system can greatly enhance the efficiency and profitability of any business. For restaurants, a specialized restaurant POS system is an invaluable tool. It integrates order management, payment processing, and inventory tracking into one unified platform, streamlining operations and ensuring a seamless experience for both staff and customers. With features like real-time reporting and customer data analytics, this POS system can help restaurant owners make informed decisions that drive growth and improve service quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Who uses point-of-sale systems?
Answer: Although every small and large business has a point of sale system, they are more common among retail businesses, service providers, and restaurants.
Q2. How do you choose the best point-of-sale system?
Answer: There is no right or wrong way to choose a POS system. The best system for you depends on your business’s needs and capabilities. Firstly, identify the essential features required for your business and choose a system suitable for your business type (Retail, restaurant, or service-based).
Make sure the interface is user-friendly, and the system is compatible with your existing hardware. Also, consider both upfront costs and ongoing fees. Additionally, look for a system with robust security measures and seamless integration capabilities. Finally, read reviews and get recommendations.
Q3. What are some best point-of-sale systems for small businesses?
Answer: Purchasing a POS system for your small business has never been simpler. Here are the top 12 point-of-sale systems for small businesses.
- Lightspeed POS
- Square POS
- Clover
- eHopper POS
- KORONA POS
- Revel Systems
- Shopify
- Erply
- PayPal
- TouchBistro
- Toast
- Aloha Cloud
Recommended Articles
We hope you found this comprehensive article on point of sale informative and easy to understand. To learn similar concepts, read the following recommended articles,

