Updated September 6, 2023
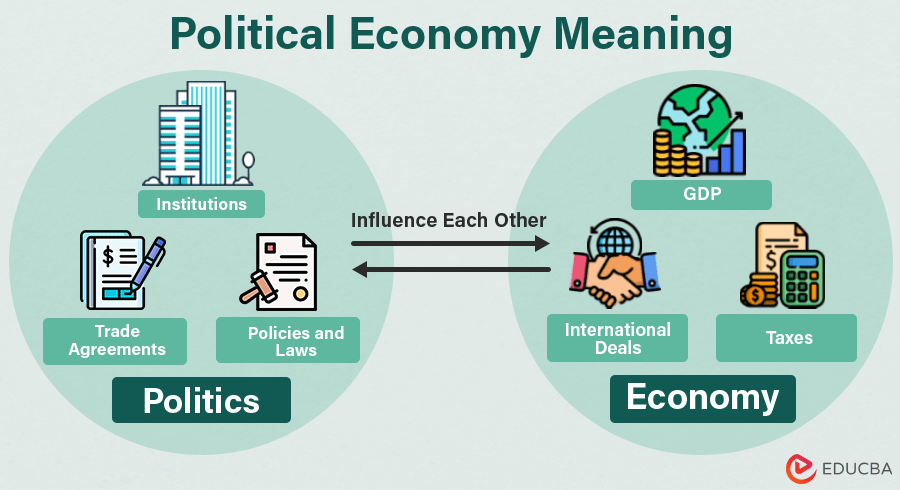
What is Political Economy?
Political economy examines how governments, policymakers, and political leaders make decisions about matters like taxation, trade, monetary policy, etc., and how these decisions impact citizens, markets, and society.
It studies how politics and economics affect each other in the real world through government laws and policies. In addition, it also studies the distribution of power and resources in society and how this affects economic development, resource allocation, decision-making, and globalization.
For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the government decided to impose lockdowns and ban drug exports, leading to a decline in the world economy. This is how the political economy works.
Table of Contents
Key Highlights
- Political economy is a field that studies economics and political science as well as how politics and economic factors affect each other.
- The three types are capitalism, socialism, and communalism.
- The ideologies that influence it are economic nationalism, Marxism, and liberalism.
- It helps governments and world leaders understand how their policies affect the world so they can make better and more informed decisions.
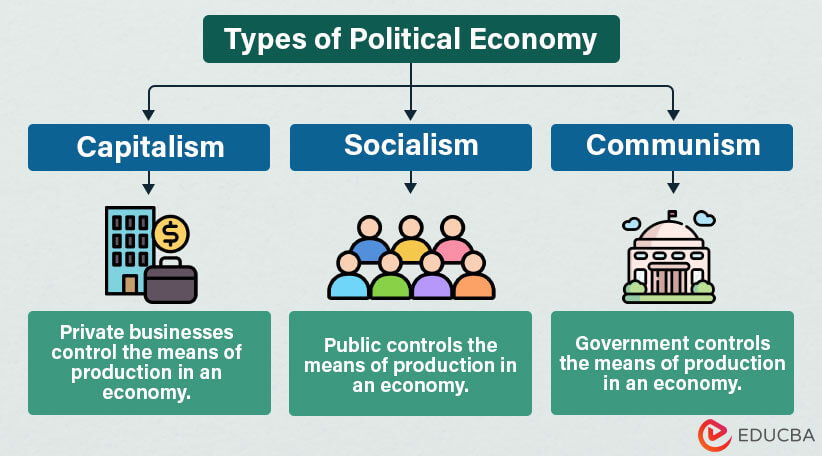
Types
The following are three political economy types, each representing a particular economic organization and governance approach.
1. Capitalism
- Capitalism promotes the theory that private owners or businesses control every means of production.
- It gives the right to produce, distribute, and determine the prices of goods and services to the private owners.
- Thus, there is limited government influence in capitalism.
2. Socialism
- Socialism emphasizes the idea that society (public ownership) controls the production and distribution of goods and services.
- There is no involvement of a particular group, but the government can make certain decisions.
- It involves equal redistribution of wealth and resources among society to reduce economic inequality.
3. Communism
- In communism, there is no capitalism, and the government entirely oversees the production, distribution, and prices of goods and services.
- Communism aims to eliminate private ownership and class discrimination.
- Therefore, it ensures a strong community where individuals contribute and receive according to their needs.
Theories
The political economy includes the following ideologies:
1. Economic Nationalism:
It states that the government owns and controls the production and distribution of resources, and the individuals have no part in the decision-making process. The aim is to improve a nation’s economic well-being and self-sufficiency.
2. Marxism:
According to Marxism theory, private ownership or capitalism creates a class conflict, i.e., discrimination between rich and poor, leading to inequality. Thus, it suggests that everyone is equal and a nation can generate more capital if communities work together.
3. Liberalism:
Liberalism believes that less government interference can improve and promote individual rights. It states that a community or society can improve its living standard by using the economy wisely.
Examples
Let’s look at some examples of political economy.
#1: International Trade Agreements:
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) aims to reduce trade barriers between the United States, Canada, and Mexico. This promotes industrial growth and economic cooperation among these countries.
#2: Monetary Policy:
In the 2008 financial crisis, the U.S. Federal Reserve enacted quantitative easing and near-zero interest rates to stabilize the economy and prevent recession. These decisions faced political issues and debate.
#3: Taxation Policies:
Sometimes, the ruling political parties may lower taxes or give tax cuts when elections are near to win more votes. They believe that cutting taxes can help the economy grow, give people and businesses more money, and increase their chances of keeping their position in power.
Components
The components of political economy are as follows:
- Interdisciplinary Studies: Interdisciplinary studies help us understand the relationship between multiple fields, such as economics, political science, and sociology, in the real world.
- New Political Economy: It combines the ideology of classical and advanced economic theories and proposes that we must challenge existing policies and implement improvements.
- International Political Economy: It is a branch that studies how politics and economics work together globally, concentrating on international trade, investment, law, and policies.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The below table lists the advantages and disadvantages of political economy.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Provides a deep understanding of how politics and economics interact. | The interdisciplinary nature can be complex to understand. |
| Offers practical insights to make effective policies to address real-world challenges. | Policymakers’ biases and ideologies can influence policy decisions. |
| Consider traditional or historical factors, patterns, and data. | Gathering correct data is challenging, leading to inaccurate analysis. |
| Provides insights into global trade, finance, and governance. | Controversial debates may arise due to politics. |
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What are the principles of political economy?
Answer: The principles of political economy that influence economic decisions are the production, distribution, exchange of goods/services, and government intervention. These principles encompass how resources are produced, distributed, and traded, as well as how government policies such as taxation and infrastructure spending impact the lives of individuals. Understanding these principles can help to achieve a balanced economic status.
Q2. What does comparative political economy mean?
Answer: Comparative political economy is a branch of political science that studies the impact of political systems and economic policies on different countries or regions. It includes the study of government market inventions, income distribution, economic policies, and how all this impacts a country’s monetary policy.
Q3. Why is political economy important?
Answer: Political economy is important because it helps us understand how politics and the economy are connected. It looks at how changes in one can affect the other. For instance, how culture, GDP, supply and demand, and resource distribution can influence government policies.
Recommended Article
This article on political economy focuses on the meaning of political economy, its types, theories, and components, along with examples. For more details on economics-related topics, please refer to the following articles: