Updated March 6, 2023

Definition of PowerShell Open File
PowerShell open file commands are meant to open the file using the PowerShell cmdlet or using the .Net Namespace and once the file is opened it can be used for reading the contents from the file by reading a single line or the whole content, writing the content to the file and then close the file end the running process of the opened file and these files can be various types like TEXT, JSON, XML, etc.
Syntax:
Using Get-Content to open and read file.
Get-Content
[-ReadCount <Int64>]
[-TotalCount <Int64>]
[-Tail <Int32>]
[-Path] <String[]>
[-Filter <String>]
[-Include <String[]>]
[-Exclude <String[]>]
[-Force]
[-Credential <PSCredential>]
[-Delimiter <String>]
[-Wait]
[-Raw]
[-Encoding <Encoding>]
[-AsByteStream]
[-Stream <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Get-Content
[-ReadCount <Int64>]
[-TotalCount <Int64>]
[-Tail <Int32>]
-LiteralPath <String[]>
[-Filter <String>]
[-Include <String[]>]
[-Exclude <String[]>]
[-Force]
[-Credential <PSCredential>]
[-Delimiter <String>]
[-Wait]
[-Raw]
[-Encoding <Encoding>]
[-AsByteStream]
[-Stream <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Using File.Open method
a. Open(String, FileMode)
Opens the file from the specified path with the various FileModes, explained later.
b. Open(String, FileMode, FileAccess)
Opens the file from the specified path with the various file modes and file access method.
c. Open(String, FileMode, FileAccess, FileShare)
Opens the file from the path specified with the specified file mode, file access rights, and the specified sharing option.
Using File StreamReader class.
System.IO.StreamReader(“FilePath”)
How does the open file command work in PowerShell?
When we use the Get-Content method, we can read the file from the path we specify, and when we read the file by default PowerShell command opens up a file and read the content of the file.
Get-Content C:\Temp\Servers.txt
While using the System.IO namespace with PowerShell, we can use its class File and its methods Open() as shown in the syntax.
a. Open(String, FileMode)
String: It is the path of the file to open its content.
FileMode: Below is the file modes used by the File System.
- Append: Opens a file if exists or creates a new file. This requires to append permission FileMode.Append and can only be used with FileAccess.Write.
- Create: Specifies that the Operating system will create a new file and if exists it will overwrite the file and should be used with the FileMode.Create permission.
- CreateNew: Specifies that the Operating System will create a new file and if exists it will throw an exception.
- Open: Specifies that the Operating System will open a file if exist, otherwise it will throw an exception.
- OpenOrCreate: Specifies if the operating system should open a file. If the file exists, it will open a new file otherwise it will create a new file.
- Truncate: Specifies that the operating system should open an existing file. When the file is truncated so that its size should be zero bytes.
b. Open(String, FileMode, FileAccess)
String: Path of the file to open.
FileMode: As explained in the previous syntax.
FileAccess: Below are the FileAccess methods.
- Read: Read Access to the file. Data can be read from the file.
- ReadWrite: Read and write access to the file. Data can be written and read from the file.
- Write: Write access to the file. Data can be written to the file.
C . Open(String, FileMode, FileAccess, FileShare)
String, FileMode, and FileAccess is explained earlier. We will provide description about FileShare here.
Below are the supported fields.
- Delete: Allows deleting of a file.
- Inheritable: Makes the files are inheritable. This is not supported by Win32 system.
- None: Rejects the file sharing.
- Read: Allows the opening file for the reading until the file is closed.
- ReadWrite Allows the opening file for reading and writing until the file is closed.
- Write: Allows the opening file for the writing until the file is closed.
Examples
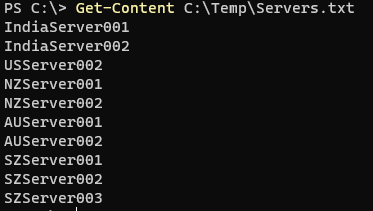
Example #1: Use the Get-Content to open and read the file.
Get-Content C:\Temp\Servers.txt
Output:
When you type this command, it opens the file for the reading and when file read is successful, it closes the file.
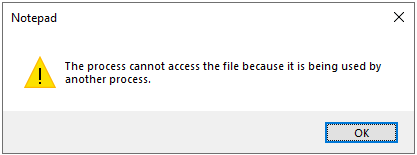
When you add the content to the file, the file is first opens and then data is written to the file. For example, if the Servers.txt file is in use the server name “AusServer001” can’t be added to the file.
"AUSServer001" | Add-Content -Path C:\Temp\Servers.txt -Force
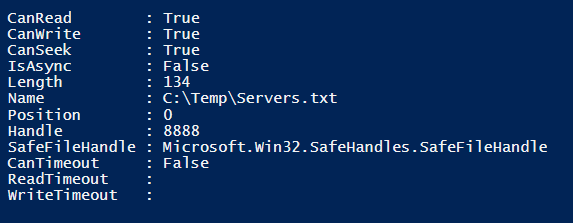
Example #2: Open the file with System.IO namespace.
To open the file for the operation, we can use the below command. We have the file to open is Servers.txt from the C:\temp location.
[System.IO.File]::Open("C:\Temp\Servers.txt", [System.IO.FileMode]::Open)
Output:
So when the file is open and when you try to open or edit the file it will show the below error message.
To close the open file once the operation completes, use the close() method.
$file = [System.IO.File]::Open("C:\Temp\Servers.txt", [System.IO.FileMode]::Open)
$file.Close()
As shown in the above syntax, instead of Open, you can use various methods like Create, CreateNew, Truncate, etc.
For example, below command, will open Servers.txt if it is exist otherwise it will Create a new file.
[System.IO.File]::Open("C:\Temp\Servers.txt", [System.IO.FileMode]::OpenOrCreate)
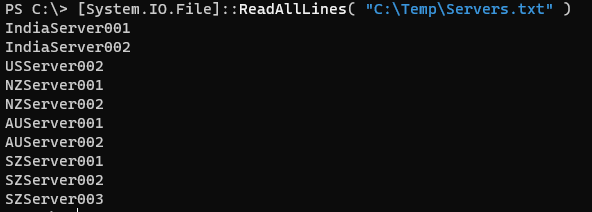
Another method to open and read file with the System.IO.File namespace is by using the ReadAllLines() command.
[System.IO.File]::ReadAllLines( "C:\Temp\Servers.txt" )
Output:
Example #3: Using File StreamRead to open and read the file.
Using the filestream method, we first need to create the FileStream .Net namespace as shown below.
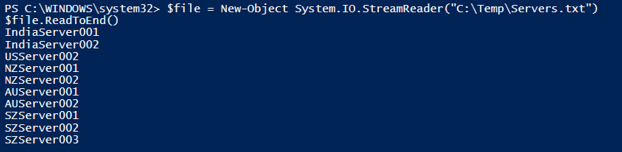
$file = New-Object System.IO.StreamReader("C:\Temp\Servers.txt")
You can read the file with the method ReadToEnd() method.
$file.ReadToEnd()
Output:
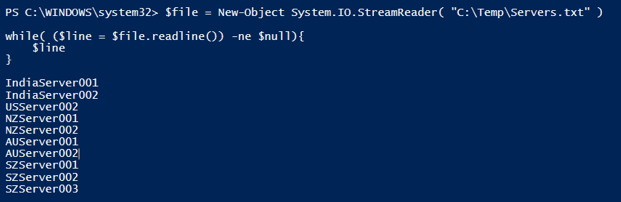
We can also use the ReadLine() method to read the file but this command read one line at a time so we need to use the loop to read the entire file as shown below.
$file = New-Object System.IO.StreamReader( "C:\Temp\Servers.txt" )
while( ($line = $file.readline()) -ne $null){
$line
}
Output:
Conclusion
While writing a script sometimes we need to work with files. The above cmdlets and the .Net commands in PowerShell mentioned are useful in opening the file and reading and writing the content of the file using the script and this approach is helpful when we write a script to store logs or events.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Open File. Here we discuss Introduction, syntax, parameters, How does the open file command work in PowerShell?. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –