Updated July 25, 2023
Introduction to Predetermined Overhead Rate
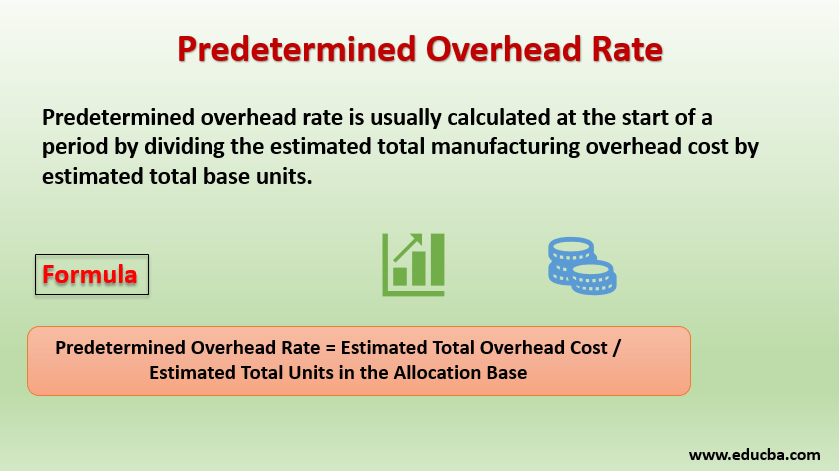
At the start of a period, organizations typically calculate the predetermined overhead rate by dividing the estimated total manufacturing overhead cost by the estimated total base units.
They then utilize this predetermined overhead rate for product pricing, contract bidding, and resource allocation within the organization based on each department’s utilization of resources.
Components of Predetermined Overhead Rate
The components are given below:
1. Overheads Estimation
The first step is to identify the total overheads identification for the target period. The total overheads are a combination of fixed, variable, and semi-variable overheads. A detailed analysis of past expenses and anticipation of upcoming new expenses helps inaccurate estimation of overheads.
2. Base Allocation
Once the total overheads are estimated, the organization needs to identify the base unit used for allocating overheads. The base unit can be the number of units produced; labor hours worked, machine hours utilized, or any other base depending on the type of business. The base unit identification is critical for the accurate allocation, which ultimately helps identify the department-wise performance and any issues.
3. Purpose
It is very important to understand the purpose for which the predetermined overhead is being used. If we prepare the cost sheet for a year or a longer period, it is appropriate to include the fixed cost in overhead allocation. However, if we have to submit a quote for a one-time order which is not recurring and the organizations have already recovered the Fixed cost from the current contribution. In this case, we might consider only the variable and incremental costs.
4. Analysis
The predetermined overhead rate helps prepare budgeted costs for each department. After the actual numbers are out, comparing actual and budgeted numbers helps identify variances and the factors driving them. This analysis is one of the most important aspects of cost accounting in any organization, as it accurately identifies the reason for the change.
5. Accounting
It is part of Cost Accounting which focuses on identifying critical costs and tries to reduce them by implementing best practices and new techniques. Standard cost is an example of a predetermined overhead rate used extensively to identify price variance, material variance, usage variance, and various other variances needed by an organization.
Example of Predetermined Overhead Rate
Formula:
Some of the Examples are :
Example #1
Let’s say there is a company, ABC Ltd., which uses Labour Hours as the base for allocating Overheads. In the coming year, the company expects the total overheads to be $150,000 and expects that there will be 3,000 direct labor hours worked.
Predetermined Overhead Rate = Estimated Total Overhead Cost / Estimated total units in the allocation base
Predetermined Overhead Rate = $150,000/3,000 = $50 per direct labor hour.
Example #2
Let’s say a company XYZ Ltd., uses Machine Hours as the base for allocating Overheads. In the coming year, the company expects the total overheads to be $100,000 and expects that there will be 25,000 machine hours worked.
Predetermined Overhead Rate = Estimated Total Overhead Cost / Estimated total units in the allocation base
Predetermined Overhead Rate = $100,000/25,000 = $4 per machine hour.
Example #3
Calculation of under and over-absorption of Overheads: It is very important to understand the application of a predetermined overhead rate. We learned how to calculate the it in the above examples. Now let’s consider the data in example 1 for analysis in which the predetermined overhead rate is $50 per direct labor as expected and prepared by the management. By the end of the period, the total labor hours worked was 3,200, which is 200 more than expected. Calculating the overhead based on the predetermined overhead rate, the actual overhead comes to $50*3200 = $160,000. In this case, the organization has incurred $10,000 ($160,000 – $150,000) more cost than anticipated. So, the organization here has over-absorbed its overhead cost by $10,000.
Suppose we consider that by the end of the period, the total labor hours worked was 2,900, which is 100 less than expected. Calculating the overhead based on the predetermined overhead rate, the actual overhead comes to $50*2900 = $145,000. In this case, the organization has incurred $5,000 ($150,000 – $145,000) less cost than anticipated. So, the organization here has under-absorbed its overhead cost by $5,000.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Let us take a look over the advantages and disadvantages mentioned below
Advantages
Some of the advantages are :
- It helps in the quick calculation of the expected cost for each department
- It is a useful tool for the calculation of over or under-absorption of overheads in each department
- It helps in performance tracking
- Useful in preparing a budget
- An important aspect of an organization involved in manufacturing activities
- Useful in finalizing the cost and selling price of products
- Helps invariance analysis of budgeted Versace actual numbers
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages are :
- It is a time-consuming process
- Many organizations find it difficult to implement
- It is not always easy to track all future expenses accurately
Points to Note
The predetermined overhead rate is based on anticipation and certain historical data. The person involved in preparing and finalizing overhead rates must have an eye for detail and an in-depth understanding of products and the manufacturing process within the organization. Then only he/she will be able to accurately track the expenses. Also, any change in the product line, raw material, or any deviation from previous processes must be taken into consideration before the finalization of predetermined overhead rates.
Conclusion
With increasing globalization and cut-throat competition in today’s world, the manufacturing process of any organization must meet global standards to stay in the game. So, predetermined overhead rates are an important tool for the organization to assess their performances quickly and take corrective measures. These rates help exactly track each department’s expense and resource utilization, which helps the higher management fix any issues quickly before it goes out of hand.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Predetermined Overhead Rate. Here we discuss Components and Examples along with Advantages and Disadvantages. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –