Updated July 21, 2023

Definition of Price to Earnings Ratio
The term “P/E ratio,” which is the acronym for price-to-earnings ratio, refers to the price an investor pays for the earnings the company generates. This ratio is also known as the earnings multiple or price multiple.
The formula for the P/E ratio is expressed as the subject company’s share price or market value divided by its earnings per share. Mathematically, it is represented as below,
Example of Price to Earnings Ratio (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
P/E Ratio – Example #1
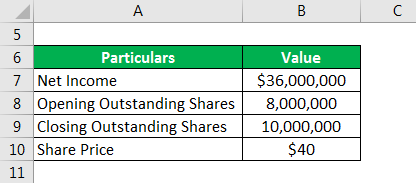
Let us take the example of a company in Wheeling, Illinois (US), to illustrate the calculation of the P/E ratio. In 2019, the company recognized a Net Income of $36.0 million. The company had 8.0 million Common Stocks at the start of 2019 and ended the year with 10 million common stocks. Calculate the company’s P/E ratio for 2019 if the company stock currently trades at $40 per share.
Solution:
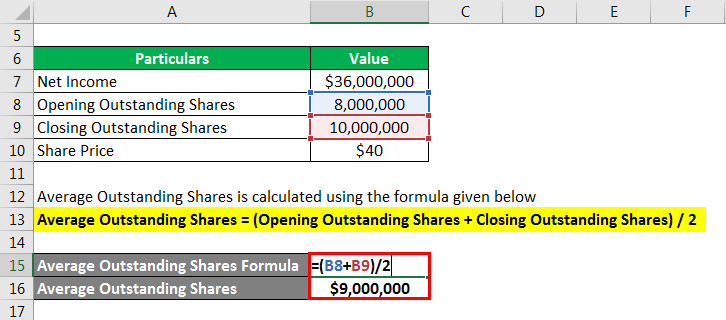
Average Outstanding Shares are calculated using the formula given below
Average Outstanding Shares = (Opening Outstanding Shares + Closing Outstanding Shares) / 2
- Average Outstanding Shares = (8,000,000 + 10,000,000) / 2
- Average Outstanding Shares = $9,000,000
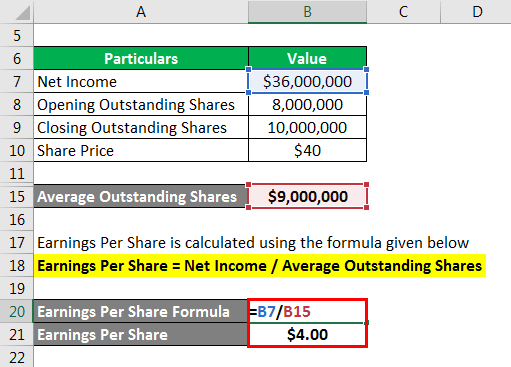
Earnings Per share are calculated using the formula given below
Earnings Per share = Net Income / Average Outstanding Shares
- Earnings Per Share = $36,000,000 / $9,000,000
- Earnings Per share = $4.00 per share
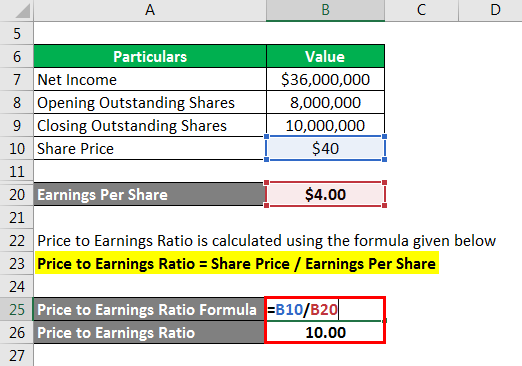
P/E Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
P/E Ratio= Share Price / Earnings Per Share
- Price to Earnings Ratio = $40 per share / $4.00 per share
- Price to Earnings Ratio = 10.00x
Therefore, the company’s stock is currently trading at a P/E ratio of 10.0x.
P/E Ratio – Example #2
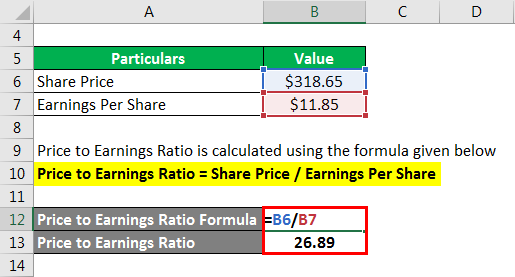
Let us take the latest available market information about Apple Inc. to illustrate the calculation of the P/E ratio. As of 17th January 2019, the stocks of Apple Inc. were trading at $318.65 per share with earnings per share of $11.85. Calculate the current P/E ratio of Apple Inc. based on the given information.
Solution:
P/E Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
P/E Ratio= Share Price / Earnings Per Share
- Price to Earnings Ratio = $318.65 per share / $11.85 per share
- Price to Earnings Ratio = 26.89x
Therefore, Apple Inc.’s stock is trading at a P/E ratio of 26.89x.
Source Link: Apple Inc. Balance Sheet
Explanation
The formula for P/E Ratio can be calculated by using the following points:
Although the P/E ratio is mathematically reciprocal to return on investment, it is an indicator of the same. As the ratio relates the company’s share price to its earnings per share, it shows how much money an investor needs to pay as a share price for each dollar of revenue generated by the company.
How Does P/E Ratio Work?
The formula for the P/E ratio can be derived by using the following steps:
Step 1: Firstly, determine the share price of the subject company. It is the price at which the company’s stock is currently trading in the stock market.
Step 2: Next, determine the company’s net income generated during the period.
Step 3: Next, determine the outstanding number of shares available across the period, which is the average of the outstanding number of shares at the start (opening) and the end (closing) of the given period.
Average Outstanding Shares = (Opening Outstanding Shares + Closing Outstanding Shares) / 2
Step 4: Next, compute the company’s earnings per share by dividing the net income (step 2) by the average outstanding shares (step 3).
Earnings Per share = Net Income / Average Outstanding Shares
Step 5: Finally, the formula for the P/E ratio can be derived by dividing the company’s share price (step 1) by its earnings per share (step 4), as shown below.
P/E Ratio = Share Price / Earnings per Share
Importance of Price to Earnings Ratio
The P/E ratio is a critical financial metric for stock valuation that investors usually use. Typically, a higher P/E ratio indicates that the investors expect the company’s earnings to grow faster than the other companies with a lower P/E ratio. On the other hand, a company with a lower P/E ratio may indicate that it is currently undervalued, or it may be doing exceptionally well compared to its past trends. A Higher P/E ratio means the stock price is high and vice versa.
Difference Between P/E Ratio vs P/B Ratio
The significant differences between the P/E ratio vs P/B ratio are as follows:
- The P/E ratio shows the relationship between the company’s stock price and earnings recognized during the given period. The P/B ratio demonstrates the relationship between the market value and the company’s book value.
- The P/E ratio can be associated with return on investment such that the lower P/E ratio indicates a better return. On the other hand, the P/B ratio gives a fair idea about a company’s solvency, such that a lower P/B ratio is more favorable because the market value is close to the book value.
Advantages and Disadvantages of P/E Ratio
Following are the points that explain the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
The significant advantages are as follows:
- It is easier to understand and use for assessment of the stock valuation.
- It helps to compare the performance of different company stocks.
- It can also be used to track the performance of a company stock across the period.
Disadvantages
The major disadvantages are as follows:
- This ratio is not relevant for growth stocks.
- It should only be compared with companies operating in the same industry.
- It can be misleading in case of exceptional gains or losses captured under net income.
Conclusion
So, the P/E ratio is a significant financial metric that is used for stock valuation, and it shows how more or less expensive is a stock price relative to the earnings generated by it.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Price to Earnings Ratio. Here we discuss how to calculate along with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –