Price War Meaning
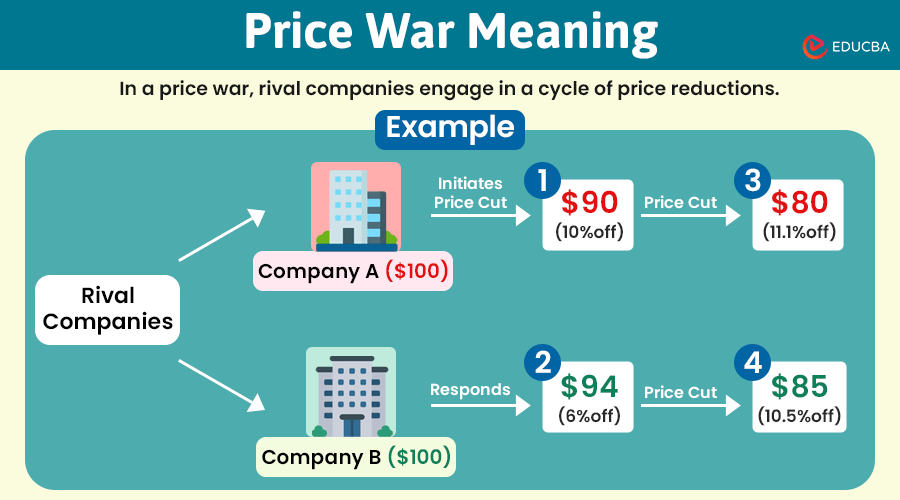
In a price war, rival companies engage in a cycle of continually lowering their prices on products to attract customers and gain a larger market share.
It may be a short-term tactic to gain an advantage or a long-term strategy to dominate the market entirely. When businesses engage in a pricing war, they may not initially see significant profits and could even lose money.
When one competitor lowers their price, it compels others to do the same to remain profitable and competitive. Small enterprises can suffer greatly from this battle because they cannot afford to operate at a loss or with minimal earnings. Therefore, only businesses that can sustain operations after lowering their prices can control or initiate a pricing war.
Table of Contents
What Happens in the Price War?
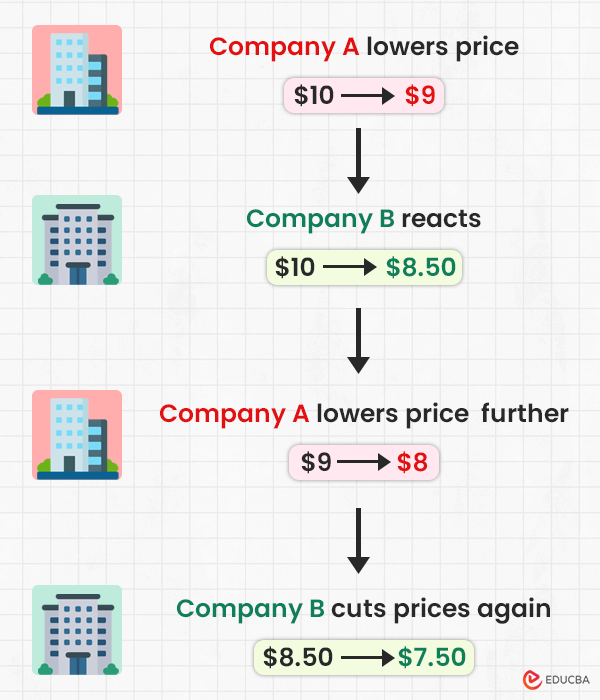
A price war often starts with one company lowering its prices to attract more customers, prompting its competitor to respond.
Let’s understand the steps involved with an example of two rival companies: Company A and Company B.
- Company A lowers the price of its product from $100 to $90 to attract more customers.
- Company B reacts by reducing its prices from $100 to $85.
- Company A further lowers its prices to $80 in response to Company B’s actions.
- Company B continues the cycle by cutting prices even more, down to $75.
- Both companies may experience increased sales volume but reduced profit margins due to the lower prices.
- Customers are drawn to the lower prices, increasing market competition.
- Both companies assess how long they can sustain reduced prices without incurring losses.
- Eventually, one or both companies may find the price cuts unsustainable and raise prices back to $90, stabilizing the market.
Examples
Here are three examples of companies engaging in price wars:
#1. Amazon Vs. Walmart
In recent years, Amazon and Walmart have been engaging in a fierce pricing war to dominate the e-commerce market. Both companies frequently lower prices on many products, be it on Amazon’s Prime Day or Walmart’s competing sales events.
#2. Uber Vs. Lyft
Uber and Lyft have been in a continuous price war, offering discounts, promotions, and lower fare prices to attract riders. This competition has been especially intense in major cities where both services operate.
#3. Coca-Cola Vs. Pepsi
Coca-Cola and PepsiCo have a long-standing rivalry, but recent price wars have been evident in promotions and discounts offered in retail stores and through direct-to-consumer channels. Both companies use aggressive pricing strategies to capture market share, especially during major holidays and events.
How to Survive a Price War?
Some key measures to help businesses survive a price war are as follows:
1. Analyze Competitor Actions
To survive a pricing war, businesses should analyze competitor actions carefully. Such wars often start because companies misinterpret their rivals’ actions or intentions. A hasty response can lead to a downward pricing spiral that could hurt profitability. Thus, businesses should avoid knee-jerk reactions.
2. Communicate Your Strategy Clearly
Next, it’s crucial to communicate your strategy clearly but selectively. Companies should avoid predatory pricing and only share pricing strategies when necessary to prevent it.
3. Understand Customer Price Sensitivity
Understanding customer price sensitivity is another vital strategy. Knowing how sensitive your target market is to price changes helps tailor your pricing strategy to maintain customer loyalty and deter new competitors.
4. Be Reliable and Prompt in Your Responses
Competitors will act aggressively if they believe they will benefit. Therefore, you must respond quickly to aggressive pricing to minimize their advantage and maintain a consistent approach to discourage ongoing aggressive tactics.
5. Manage Business Capacity
Industry overcapacity is the primary cause of pricing wars. Once there is overcapacity, everyone is competing to maintain critical mass, making pricing wars almost impossible to avoid. Align production and inventory levels with realistic demand forecasts.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Customers benefit from lower product prices. | Hurts the company’s financial performance, clients, and the market. |
| Businesses can increase sales volume, | Small businesses may shut down due to unsustainable competition. |
| Can quickly gain market share for the business. | Leading firms may raise prices after capturing market share, hurting consumers in the long run. |
| Increases short-term customer acquisition. | Eliminates healthy market competition. |
| Drives operational efficiency and cost reduction. | Decreased pricing can result in lower employee wages and reduced overtime pay, leading to fewer job opportunities. |
Final Thoughts
A price war can only occur when products are equivalent in terms of similar attributes. Customers will always choose the best product if it offers more value. Instead of lowering prices and starting a pricing war, differentiating the products and making them unique is always preferable.
While a healthy rivalry in the market is necessary, it can also result in long-term issues for both the customers and the company if it escalates into a pricing war. A short-term approach that benefits both clients and businesses is ideal, as it promotes healthy competition without compromising long-term value.
Therefore, to remain competitive in the market for a longer period, every company must have a unique selling proposition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How can you win a price battle?
Answer: Focusing on product quality, letting the competitors see your firm’s or strategy’s business so that they know what they lose if they lower their pricing, and being strategic in cutting expenses are all ways to win a price war.
Q2. How does a price war affect consumers?
Answer: A price war affects consumers in several ways:
- Consumers can save money due to lower costs.
- They gain more options as competition increases.
- Quality improvements may occur as companies strive to attract customers.
Q3. How can you stop a price war?
Answer: To prevent a price war, businesses can take these steps:
- Don’t pressure competitors to drop prices.
- Focus on value competition, not just price.
- Serve specific market areas well and understand market changes.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on “Price Wars” helped you understand how competitive pricing impacts markets. For more price and market-related insights, refer to the below posts.