Updated June 19, 2023

Introduction to Prime Number in JavaScript
A prime number is a whole number more significant than one that can be fully divisible by two numbers, including the same number. It’s a positive number divided by the numbers less than it will not divide perfectly. Writing a program to check if a number is prime or not is a very common question asked in programming. It can be implemented on the front end using JavaScript so that the client machine will be used for calculation. In this article, we will see how we can check if the number is prime or not in JavaScript.
Logic
We can divide the input number by all the numbers between 1 and the numbers less than itself and check the remainder; if the remainder comes as zero, in any case, the number is fully divisible and is not prime.
Examples of Prime Numbers in JavaScript
Below are examples of prime numbers in JavaScript:
Example #1: Using for loop
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
Prime Number Check in JavaScript
</title>
<style>
.results {
border : green 1px solid;
background-color : aliceblue;
text-align : left;
padding-left : 20px;
height : 150px;
width : 95%;
}
.resultText {
font-size : 20px;
font-style : normal;
color : blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class = "results">
<h2> Enter the Number </h2>
Number: <input type = "number" name = "number" id = "number" required>
<button type = "button" onclick = "checkForPrime()" > Submit </button>
<div class = "resultText">
<p id = "result"> </p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function checkForPrime() {
num = document.getElementById("number").value;
if(num == '' || num < 1) {
document.getElementById("result").style.color = "red";
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = "Please Enter a Valid Number";
return;
}
var i;
var flag = true;
if (num == 1) {
flag = false;
} else {
for(i = 2; i < num-1; i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag == true) {
document.getElementById("result").style.color = "blue";
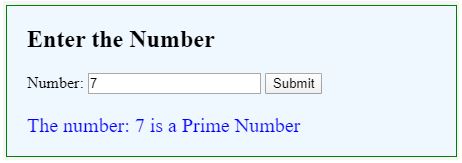
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = "The number: " + num + " is a Prime Number";
} else {
document.getElementById("result").style.color = "red";
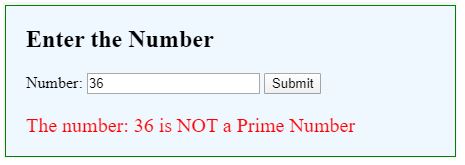
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = "The number: " + num + " is NOT a Prime Number";
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>We have called the function checkForPrime() upon submitting the value. First, we have checked if the user has entered valid input. The input should not be blank or negative, as prime numbers cannot be negative. Then, we used one flag to indicate if, in the process of dividing the number by numbers from 2 to n-1, we get the remainder as zero. If we get the zero in between, that means the number is not prime, and we will immediately change the flag’s status, break the loop, and then declare that number as not prime. If the flag status is not changed, we didn’t get zero as the remainder in the process, so that we will declare that number as prime.
Output:
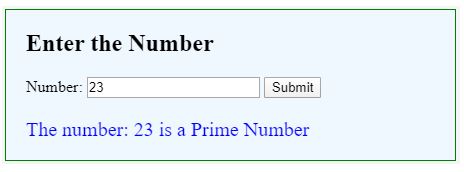
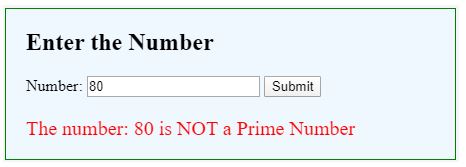
For a valid Prime number:
For Not Prime number:
Example #2: Using while loop
This example here is to showcase another way of implementation in JavaScript.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
Prime Number Check in JavaScript
</title>
<style>
.results {
border : green 1px solid;
background-color : aliceblue;
text-align : left;
padding-left : 20px;
height : 150px;
width : 95%;
}
.resultText {
font-size : 20px;
font-style : normal;
color : blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class = "results">
<h2> Enter the Number </h2>
Number: <input type = "number" name = "number" id = "number" required>
<button type = "button" onclick = "checkForPrime()" > Submit </button>
<div class = "resultText">
<p id = "result"> </p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function checkForPrime() {
num = document.getElementById("number").value;
// valid input checking
var i;
var flag = true;
if (num == 1) {
flag = false;
} else {
i = 2;
while (i < num/2) {
if(num % i == 0) {
flag = false;
break;
}
i++;
}
}
if(flag == true) {
document.getElementById("result").style.color = "blue";
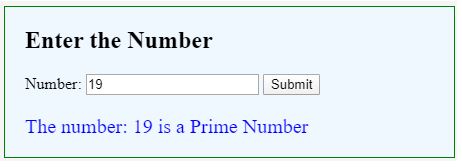
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = "The number: " + num + " is a Prime Number";
} else {
document.getElementById("result").style.color = "red";
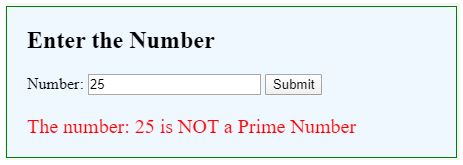
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = "The number: " + num + " is NOT a Prime Number";
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Here, we have used a while loop for diving the number; note that we are checking divisibility up to n/2 only here. Because of mathematical property, the number cannot be perfectly divisible by the numbers greater than half of that number. This will improve the performance as multiple divisions will be reduced here.
Output:
For a valid Prime number:
For an invalid Prime number:
Example #3: Using Recursion
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
Prime Number Check in JavaScript
</title>
<style>
.results {
border : green 1px solid;
background-color : aliceblue;
text-align : left;
padding-left : 20px;
height : 150px;
width : 95%;
}
.resultText {
font-size : 20px;
font-style : normal;
color : blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class = "results">
<h2> Enter the Number </h2>
Number: <input type = "number" name = "number" id = "number" required>
<button type = "button" onclick = "checkForPrime()" > Submit </button>
<div class = "resultText">
<p id = "result"> </p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function checkForPrime() {
num = document.getElementById("number").value;
if(num == '' || num < 1) {
document.getElementById("result").style.color = "red";
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = "Please Enter a Valid Number";
return;
}
var i = 2;
var flag = isPrime(num, i);
if(flag == true) {
document.getElementById("result").style.color = "blue";
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = "The number: " + num + " is a Prime Number";
} else {
document.getElementById("result").style.color = "red";
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = "The number: " + num + " is NOT a Prime Number";
}
}
// new recursive function
function isPrime( num, i) {
if(num < 2) {
return false;
}
if(num == 2) {
return true;
}
if(i > num/2) {
return true;
} else {
if( num % i == 0) {
return false;
} else {
return isPrime(num , i+1);
}
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
For a valid Prime number:
For an invalid Prime number:
Here, we have added one new function, which calls itself recursively. We have base cases per the logic; the function will call itself until it reaches out to base cases. It will divide the number by the dividing numbers, i.e., 2 to n-1, and return the value based on the remainder.
Conclusion
We have seen the property number as prime and implemented logic accordingly in JavaScript. We can use multiple types of loops to implement the same.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Prime Number in JavaScript. Here we discuss the basic concept, logic, and different examples of prime numbers in JavaScript. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –