Introduction to Principles of Procurement
Procurement is important to any organization, ensuring the acquisition of goods and services needed for smooth operations. To maintain a fair and efficient procurement process, several fundamental principles of procurement guide the way. This article will explore these principles of procurement in simple language to help you understand the key elements that make procurement effective.
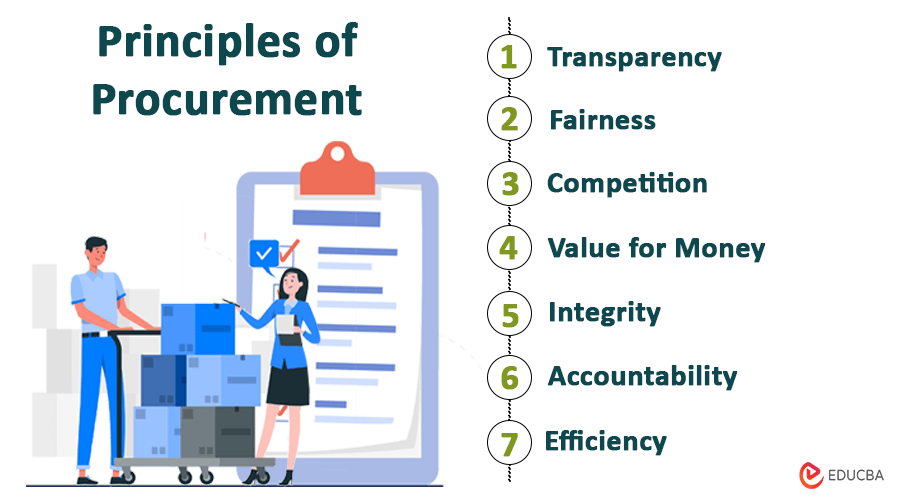
7 Principles of Procurement
Several principles guide effective procurement practices, which may vary slightly depending on the source or context; here are seven commonly recognized principles of procurement:
1. Transparency: It is important in procurement processes. It is like a window into the procurement process. It means openly communicating the requirements, procedures, and decision-making processes. Transparency builds trust and helps stakeholders understand how and why certain choices are made.
2. Fairness: It is an important quality of a procurement system. It means treating all suppliers equally and without bias. Every supplier should have an equal chance to participate, and decisions should be based on merit rather than personal preferences. Fairness ensures that opportunities are distributed equitably, fostering a level playing field for all involved.
3. Competition: It is the driving force behind effective procurement. It encourages suppliers to offer their best in terms of quality and price. When there is healthy competition, organizations can choose from various options, leading to better value for money and improved overall quality of goods and services.
4. Value for money: Getting value for money means obtaining the best possible outcome with available resources. It is about balancing cost with quality and performance. A focus on value for money ensures that the chosen goods or services provide the most significant benefit to the organization.
5. Integrity: It is the moral compass of procurement. It involves conducting business with honesty, integrity, and adherence to ethical standards. This principle ensures that all transactions are above board, preventing corruption and promoting a culture of trust and credibility in the procurement process.
6. Accountability: It ensures that those responsible for procurement decisions are answerable for their actions. It includes being transparent about choices, taking responsibility for outcomes, and learning from mistakes. Accountability helps maintain a sense of responsibility throughout the procurement process.
7. Efficiency: It is about doing things most effectively and timely. Streamlining processes, minimizing waste, and utilizing resources wisely are key components of an efficient procurement system. Efficiency saves time and money and contributes to the organization’s overall effectiveness.
Case Study
Suppose XYZ Corporation, a medium-sized company, recognized the need to improve its procurement practices.
Challenges Faced by XYZ Corporation:
- Lack of transparency: The procurement process at XYZ Corporation lacked transparency. Stakeholders were unclear about the criteria used for supplier selection, leading to distrust and speculation.
- Inefficiencies: Lengthy procurement cycles and repetitious paperwork resulted in inefficiencies. It not only delayed projects but also increased operational costs.
- Limited Competition: XYZ Corporation often relied on a handful of suppliers, limiting competition. It slowed the company’s ability to secure the best value for money and quality.
Implementation of Principles of Procurement:
1. Transparency
XYZ Corporation implemented a transparent communication system. All procurement guidelines, criteria, and decision-making processes were documented by the procurement team and shared with stakeholders. It increased understanding and trust among employees, suppliers, and management.
2. Efficiency
The company streamlined its procurement procedures by adopting a digital procurement platform. It automated many manual tasks, reducing processing time and minimizing errors. Employees could now focus on strategic aspects of procurement rather than administrative tasks.
3. Competition
XYZ Corporation expanded its supplier base by actively seeking new vendors to foster healthy competition. The company also introduced a fair and objective evaluation system for supplier performance, encouraging suppliers to improve and compete on merit consistently.
4. Value for Money
XYZ Corporation implemented a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis for each procurement decision. It involved considering the initial cost and evaluating long-term benefits and the overall impact on the company’s objectives. This shift in perspective ensured that the chosen goods and services provided true value for money.
5. Integrity and Ethics
The company strengthened its code of conduct, emphasizing ethical behavior in all aspects of procurement. Employees underwent training to raise awareness of potential ethical challenges, and the procurement team established a whistleblowing mechanism to encourage reporting of any unethical practices.
6. Accountability
XYZ Corporation implemented a clear accountability framework. Roles and responsibilities were defined, and regular audits were conducted to ensure adherence to the established guidelines. Procurement decisions were documented and made accessible for internal and external scrutiny.
Results:
Streamlining the procurement process led to significant cost savings. The company could negotiate better deals, and the reduced processing time resulted in lower administrative costs. Moreover, the expanded supplier base increased competition among vendors. This improved the quality of goods and services and provided the company with more negotiating leverage.
Transparency and adherence to ethical standards built trust among stakeholders. Employees felt more confident in the fairness of the procurement process, and suppliers appreciated the equal opportunities provided. Additionally, adopting a digital procurement platform significantly reduced processing time and errors. The procurement team could now focus on strategic decision-making, improving overall operational efficiency.
Therefore, by aligning its procurement practices with the key principles of transparency, fairness, competition, value for money, integrity and ethics, accountability, and efficiency, XYZ overcame its procurement challenges and achieved substantial improvements in cost-effectiveness, stakeholder trust, and overall operational efficiency. This case study demonstrates the transformative power of embracing these principles to enhance an organization’s procurement excellence.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on principles of procurement was informative. For similar articles, refer to the following.

