Meaning of Procurement
Procurement is the process companies go through while buying goods or services that they need to run their business, from finding suppliers to making payments.
For instance, if you run a bakery, you need ingredients like flour and sugar. Suppose instead of growing them yourself, you buy them from suppliers. Procurement is finding the right suppliers, purchasing, and keeping track of everything.
Purchasing teams handle procurement. They procure external resources from suppliers and ensure smooth supply chain management. In addition, they have to maintain quality standards and acquire resources timely.
Table of Contents
How Procurement Works?
Procurement involves multiple activities that are interconnected and is not a simple single process. It includes finding potential suppliers, negotiating prices and terms, selecting the best suppliers, buying, and building relationships with suppliers. To achieve this, all departments, including finance, legal, IT, and supply chain management, play a crucial role.
Types
Companies engage in different types of procurement, depending on business requirements and primary objectives.
1. Direct
It means purchasing goods that directly contribute to the production of a company’s core product or service.
Examples:
- Raw materials
- Components
- Machinery
- Other inputs that are directly related to manufacturing
Objective: It is important for a business’s operational and production aspects.
2. Indirect
It means buying goods that are not directly used in producing the final product but are essential for the day-to-day operations of a business.
Examples:
- Office Supplies
- Utilities
- Maintenance services
- Other overhead expenses
Objective: It supports the smooth functioning of the business but does not directly contribute to the core product or service.
3. Goods
It focuses on acquiring physical, tangible products or materials that an organization needs for its operations or resale.
Examples:
- Finished goods
- Inventory
- Equipment
Objective: The primary goal is to ensure a reliable and cost-effective supply of physical items required for business activities.
4. Services
It involves acquiring intangible products, expertise, or labor to fulfill specific business needs.
Examples:
- Consulting services
- Legal services
- Maintenance contracts
- Other service-oriented agreements
Objective: Services procurement aims to secure the necessary expertise and support to enhance business processes and functions.
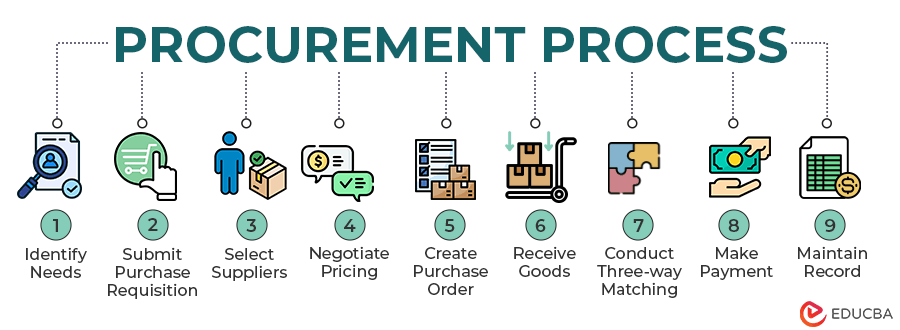
Procurement Process in Stages
The procurement process has several steps that aim to acquire necessary items that meet an organization’s requirements. These steps are divided into three stages:
1. Sourcing Stage
Step #1: Identify Needs: Recognize the goods, services, or work requirements you need and establish detailed specifications and requirements for these items.
Step #2: Create Purchase Requisition: Document the identified needs and start the procurement process.
Step #3: Select Suppliers: Conduct market research to explore available supplier options and select potential suppliers based on capability, reliability, and cost criteria.
2. Purchasing Stage
Step #4: Negotiate Terms: Negotiate terms and conditions with the selected supplier and settle details such as price, payment terms, and delivery schedules.
Step #5: Create Orders: Generating purchase orders that outline the procurement details, including quantities, prices, and delivery terms.
Step #6: Receive and Inspect Goods/Services: Receive the delivered goods or services and inspect them to make sure they meet the identified requirements.
3. Payment Stage
Step #7: Conduct Three-Way Matching: Match the supplier’s invoice with the corresponding purchase order and receipt of goods or services to ensure consistency.
Step #8: Approve Invoice and Make Payment: Verify the accuracy of the invoice, approve it for payment, and arrange for the payment to the supplier.
Step #9: Keep Records: Maintaining detailed records of the procurement process, including purchase orders, invoices, payment receipts, and any related correspondence.
Procurement Case Study
Let’s consider ABC Ltd. is buying wood (raw material) for its production of doors. This is how the process would go:
Step #1: The company finds that they need tons of wood for production.
Step #2: The employee creates a purchase requisition listing the requirement of 200 tons of wood.
Step #3: The company finds 3 suppliers that match their criteria.
Step #4: After some negotiation, the supplier agrees to sell one ton at $60.
Step #5: ABC Ltd then generates purchase orders with all the necessary details.
Step #6: Once they receive the wood, they perform checks to see if the quality is good.
Step #7: The company then matches their purchase order with the supplier’s invoice and the receipt.
Step #8: Once approved, the company makes the required payment.
Step #9: Finally, ABC Ltd., records the procurement transaction in their accounting books.
Three Components of Procurement
The procurement process has three key components: people, process, and paperwork. Let’s take a look at each of these components in detail.
1. People
Procurement professionals ensure organizations get the necessary goods and services. They work with stakeholders who have an interest or are affected by the procurement process to ensure everyone’s needs are met.
2. Process
The procurement process involves several steps. You can refer to the “Procurement Process in Stages” section to understand the entire process easily.
3. Paper
In the procurement process, various documents, such as requests for proposals, purchase orders, contracts, and invoices, are created and managed. These documents help organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements. Accurate records of all involved transactions must be maintained to ensure compliance and transparency.
Final Thoughts
Procurement is quicker and more efficient thanks to AI and data analytics. It leads to better predictions, smoother supplier relations, and better risk management. To drive innovation and value in the supply chain, all departments need to work together, and procurement professionals need to keep up-to-date with new technology and trends. If you want to learn more about procurement, these procurement courses can help you.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on procurement was informative. For similar articles, refer to the following.