Updated July 7, 2023
What is Product Cost?
Product cost refers to the total amount of money a business spends on resources and the efforts needed to make a product during production. It includes direct expenses incurred in making the product (such as raw materials and labor) and indirect expenses (such as utilities, factory overhead).
However, it does not include the costs associated with selling the product or the administrative expenses of the business, as these expenses are not directly related to the production process. Simply put, it involves all the financial aspects helpful in bringing a product to life beyond just the visible direct expenses.
Imagine you want to bake a loaf of bread. The costs for it will include direct expenses, such as the ingredients like flour, yeast, and salt, and indirect expenses, like the electricity used to operate the oven and the overall costs of maintaining your kitchen. In this case, the product cost is the total money spent to bring your bread idea to reality.
Formula
The formula for calculating the cost of producing the product is,
We can also calculate the cost per unit, as it can help us set a suitable selling price for the final product. The formula to calculate cost per unit is,
Types
As per the formula, we have to add direct labor, direct materials, and overhead to find the cost of the product. Let us see what each of them means.
1. Direct Labor: Direct labor is the effort of employees to create the product or deliver the service. It includes:
- Employees’ salaries
- Medical or meal allowance benefits.
Example: A carpenter’s salary for creating a table from wood can come under the cost of direct labor.
2. Direct Material: Raw material or inventory used to create the final product can come under this category.
Example: The cost of wood and nails needed to create the table will come under direct material cost.
3. Factory Overhead: It refers to the costs that a company incurs for space, facilities, and support staff required to create a product. These costs come under indirect expenses. There is a formula to calculate this. It is,
Example: Overhead costs can include electricity costs or the salary of guard/security staff.
Product Costs on Financial Statements
Below we discuss the ways in which firms add the cost of the product to the three financial statements using the example of Apple Inc.
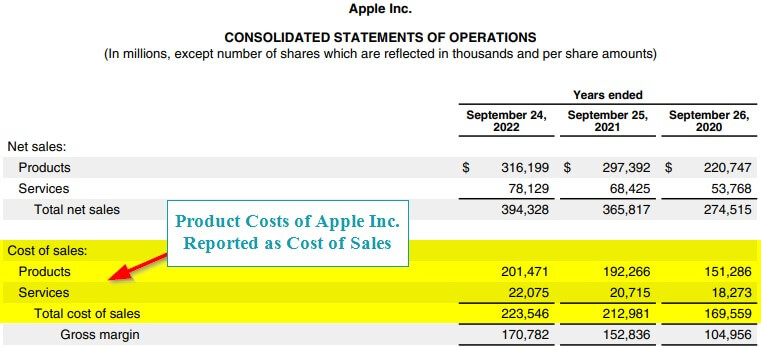
1. Income Statement
Businesses typically add the cost of the product on their income statement as a part of their cost of goods sold (COGS) or cost of sales. It includes the cost of materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. We can then reduce the costs from the revenue to find the gross profit.
(Image Source: Apple Annual Report 2022 )
2. Balance Sheet
We include the cost of producing the product on the balance sheet as a part of the inventory. Inventory represents the cost of unfinished goods, raw materials, and finished products. As we sell the products, we move the product costs from inventory (balance sheet) to cost of goods sold (COGS) on the income statement.
(Image Source: Apple Annual Report 2022 )
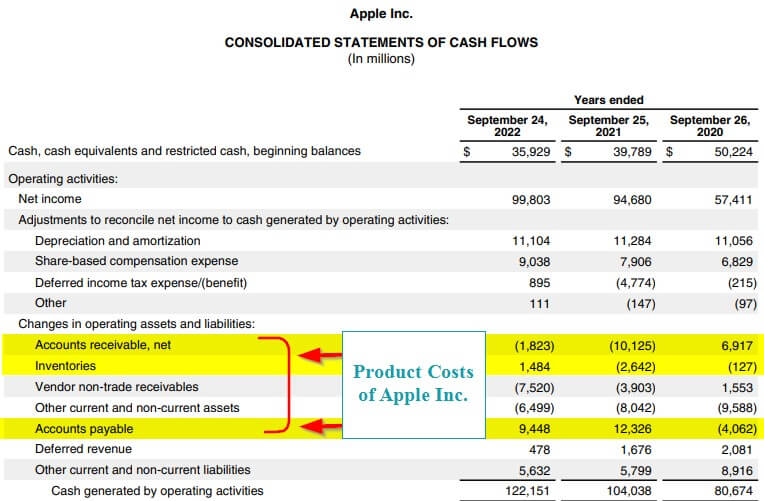
3. Cash Flow Statement
We do not enter the product costs directly in the cash flow statement. However, the cost of producing the product affects the working capital. As we add changes in working capital to the cash flow statement, we indirectly add the product cost to the cash flow statement.
So, when a company incurs product costs, the changes in working capital include changes in the accounts payable (due to purchases made), inventory levels (due to additions of product stock), and accounts receivable (pending payments from consumers). We add these in the operating activities section of the cash flow statement.
(Image Source: Apple Annual Report 2022 )
How to Calculate Product Cost?
Step 1: Determine the direct materials cost (add up the cost of all materials used to produce the product).
Step 2: Calculate the direct labor cost (multiply the hours of labor required to make the product by the labor rate per hour).
Step 3: Include the manufacturing overhead cost (calculate the overhead expenses such as rent, utilities, and equipment depreciation).
Step 4: Sum up the direct materials, direct labor, and overhead costs to get the total product cost.
Excel Examples
Example #1
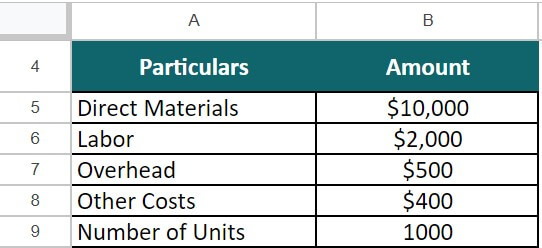
Let’s say, Jack, a carpenter, has received a firm’s orders to prepare 1000 tables. To manufacture the tables, he must have raw materials, hours, and other equipment. Below are the prices of all the costs, and we need to calculate the product cost for the carpenter.
- Direct materials =$10,000
- Labor = $2,000
- Overhead = $500
- Other costs =$400
Given,
Solution:
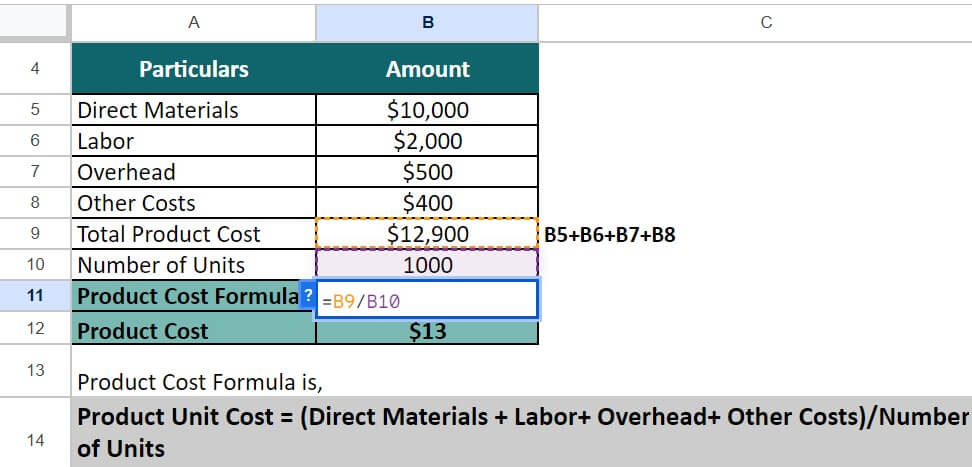
To determine the product cost, you have two options. First, you can calculate the product cost separately using the dedicated formula (Direct Labor + Direct Materials + Factory Overhead). Then, to find the cost per unit, you can use another formula (Total product cost / Number of producing units).
Alternatively, we have combined these two formulas into a single concise formula in this example. The formula is:
= $10,000 + $2,000 + $500 + $400 / 1,000
= $12,900 / 1,000
= $13
Hence, the total cost for creating 1,000 tables is $12,900, while the per-unit cost is $13.
Example #2
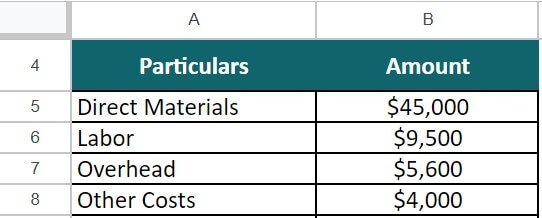
Macate bag manufacturing company produces a specific type of backpack. The company uses various materials and incurs direct labor and manufacturing overhead costs in the production process. Calculate the product cost for 6000 backpacks for the company based on the following information:
- Direct materials = $45,000
- Labor = $9,500
- Overhead = $5,600
- Other Costs = $4,000
Given,
Solution:
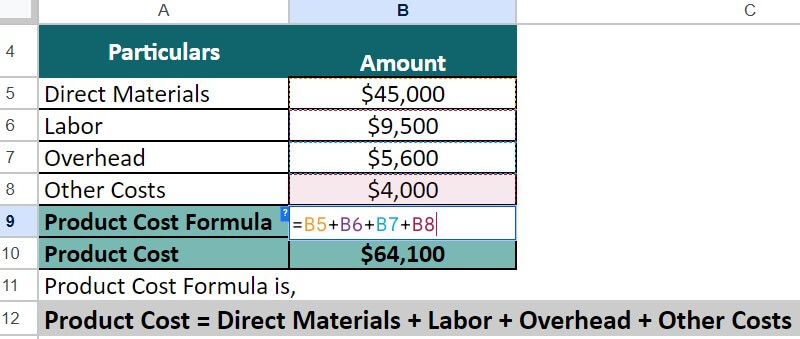
1. As we already have the direct material, labor, and overhead values, let us use the cost per unit formula directly.
= $45,000 + $9,500 + $5,600 + $4000 = $64,100
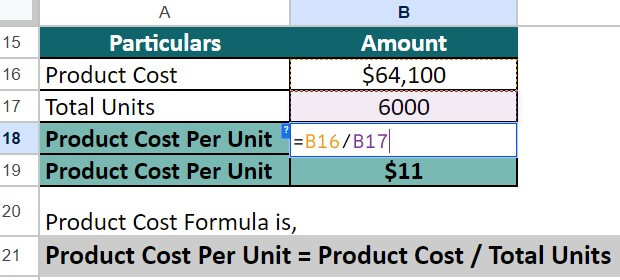
2. We calculate the product cost per unit using the following formula:
= $64,100 / 6,000 = $11
Therefore, the cost per backpack for the bag manufacturing company is $11.
Example #3
Baking Heaven is a bakery famous for making muffins. The bakery uses various raw materials and ingredients to bake the muffins, which require hours of labor. As per the bakery, the employees take 1 hour to bake and pack one packet of muffins. The employees get $15 per hour as wages. Thus, calculate the labor cost to produce 5 packets of muffins. Also, given below are all the necessary details, and we have to find the product cost with them:
- Flour = 5 kg = cost per kilo = $10;
- Cost for Flour = 5 x $10 = $50
- Sugar = 3kg = cost per kilo = $13;
- Cost for Sugar = 3 x $39
- Others = $20
- Additional Costs = $200
Solution:
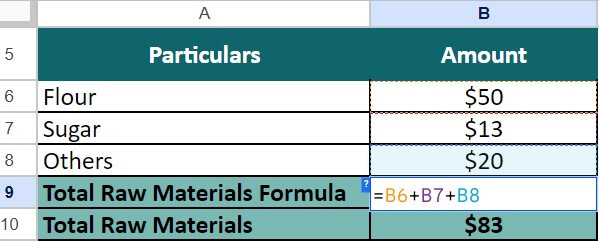
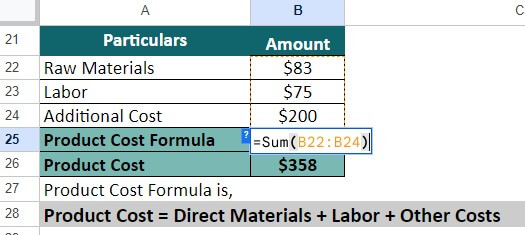
Step 1: First, we will calculate the raw materials cost using the following information:
- Flour = $50
- Sugar = $13
- Others = $20
Total Raw Materials = $50 + $13 + $20 = $83
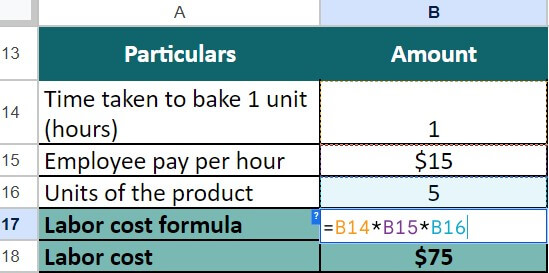
Step 2: Now, let’s calculate the labor cost using the following information:
- Time taken to bake a packet of muffins = 1 hour
- Employee pay per hour = $15
- Units of muffins = 5
Labor cost of 5 muffins = $15 x 5 = $75
Step 3: Now that we have all the necessary details, let’s calculate the product’s cost.
=$83 + $75 + $200 = $358
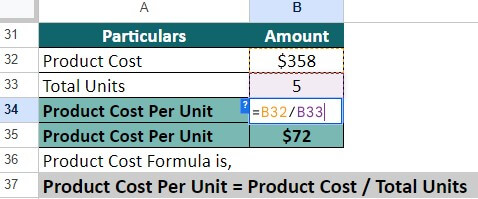
Step 4: Now, let us use the cost that we found to calculate the cost per unit. We can use the below formula for the same:
= $358 / 5 = $72
Thus, the per unit cost of the product is $72.
Product Cost Calculator
Use the following calculator for product cost calculations.
| Direct Labor | |
| Direct Materials | |
| Factory Overhead | |
| Product Cost = | |
| Product Cost = | Direct Labor + Direct Materials + Factory Overhead |
| = | 0 + 0 + 0 = 0 |
Advantages & Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It helps businesses set a profitable as well as affordable selling price for their products. | The calculator can be complicated and inaccurate in some cases. |
| Companies can use it to know how much profit each product or product line makes. | Paying more attention to this formula can reduce the profitability of your business. |
| It helps businesses identify areas where they can lower or optimize costs. | As this formula only uses internal costs, it provides a limited perspective on the cost of production. |
Product Vs. Period Cost
| Particulars | Product Cost | Period Cost |
| Definition | It is the total money the company spends on producing goods/ services. | It is the total money that the company incurs in a specific period of time, such as a year or a month. |
| Examples | It includes raw materials, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, packaging costs, etc. | It includes salaries of administrative staff, rent, utilities, advertising costs, accounting expenses, etc. |
| Timing | It considers the costs that are incurred during the production process. | It focuses on a specific period of time, regardless of production. |
| Recording | Companies record it as inventory at the beginning, and after selling the goods, they record it as costs of goods sold. | Firms record these as expenses on the income statement. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Why is calculating product cost important?
Answer: Calculating product cost is essential for:
- Determining the profitability of a product
- Making informed pricing decisions
- Understanding the expenses associated with the production
- Implementing cost control and budgeting.
Q2. What factors can affect product cost?
Answer: Several factors can influence product cost, such as:
- Fluctuations in raw material prices
- Changes in labor rates
- Variations in overhead expenses
- Economies of scale
- Production efficiency
- Technological advancements
Q3. What is the difference between product cost and period cost?
Answer: Product cost refers to the expenses incurred in producing a specific product and is assigned to the inventory. On the other hand, period cost includes non-production expenses (e.g., sales and marketing expenses, administrative costs) incurred and recorded during the period they occur.
Q4. How to reduce product costs in a business?
Answer: To reduce product costs, you can explore options such as:
- Negotiating better prices with suppliers
- Improving production efficiency
- Optimizing resource utilization
- Adopting cost-effective manufacturing processes
- Implementing lean practices
Recommended Articles
We presented you with the guide to Product Cost. Here we explored its definition, formula, and advantages and disadvantages. Moreover, you can have a look at some more relatable articles: