Introduction to Product Development Process
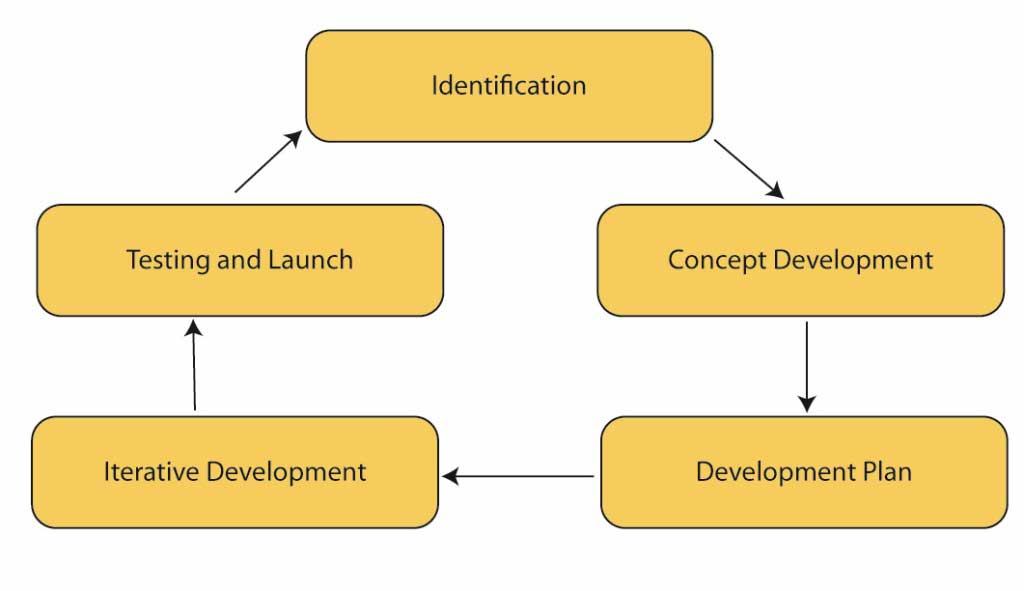
The Internet has brought a new height of suppleness to product development. Among many digital companies, two strong beliefs are prevalent – “Learn as you go” and “Sense and Respond.” The Internet has given rise to a new height of forms of products and services. A flexible product development process is envisaged upon collaborative work and a modular action, which promises an ultimate design formation until the last achievable instant. Digitally, a streamlined product development process includes five steps below:
Product Development Process over Digital Platform
But before we go further, we need to shed some light on some basic building blocks that define a product’s three significant sides.
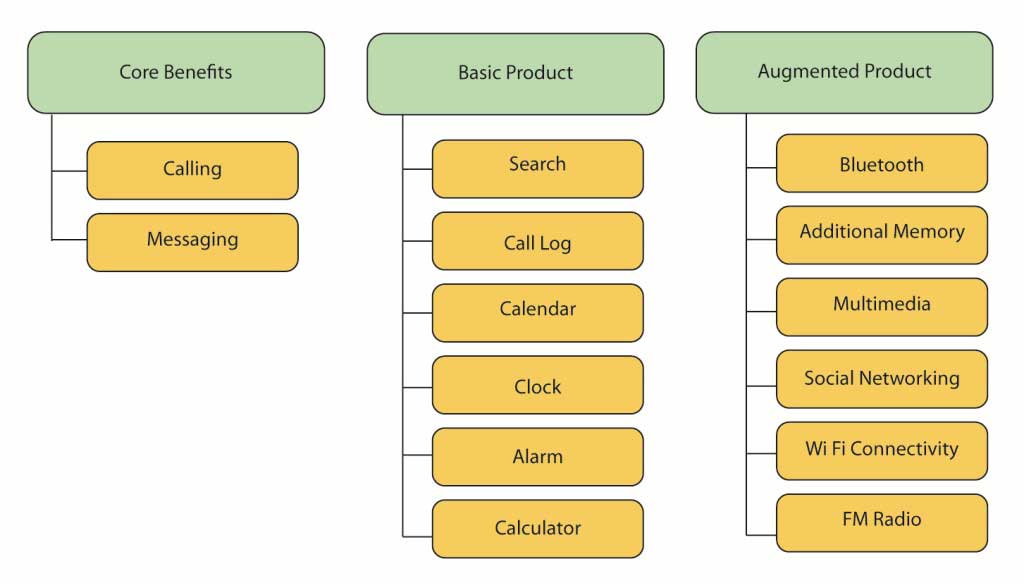
- Core Benefit: The core benefit is the product’s most basic or principal value. This is often the category of product that a product development company would create in an attempt to develop an MVP or minimum-viable product. Regarding a mobile phone, the core benefit is communication which includes calling and sending text messages. Nevertheless, the core benefit differs from the point of differentiation a buyer uses to differentiate between the products.
- Primary Product: By essential product, minimum product offerings are meant. For a mobile phone, calling, sending messages, searching, calling logs, calendars, clocks, alarms, and calculators are basic product functionalities. Primary products are different from each other by how well they cater to different customer needs.
- Augmented Product: This goes beyond the minimum expectations of buyers. Through augmentation, a product is differentiated from the competitors’ products. Customer expectations predominantly distinguish between the augmented and essential products subject to a particular market and sometimes upon the country. In the case of mobile, Bluetooth, additional memory, Multimedia, Social Networking, Wi-Fi connectivity, FM Radio, Camera, and Mobile Apps are all examples of augmented product features; each one improvises the value of the main product (i.e., mobile).
Several factors are considered while creating a product augmentation strategy. Price is deemed the first aspect; for every augmentation to the primary outcome, an additional cost is added.
In today’s digital landscape, businesses can further enhance product value using an interactive product experience platform. Such a platform immerses customers in a hands-on, engaging product journey — allowing them to explore core, primary, and augmented features seamlessly. This not only differentiates the product but also empowers customers to understand the added value, fostering stronger emotional connections and driving more informed purchasing decisions.
Product Value Hierarchies
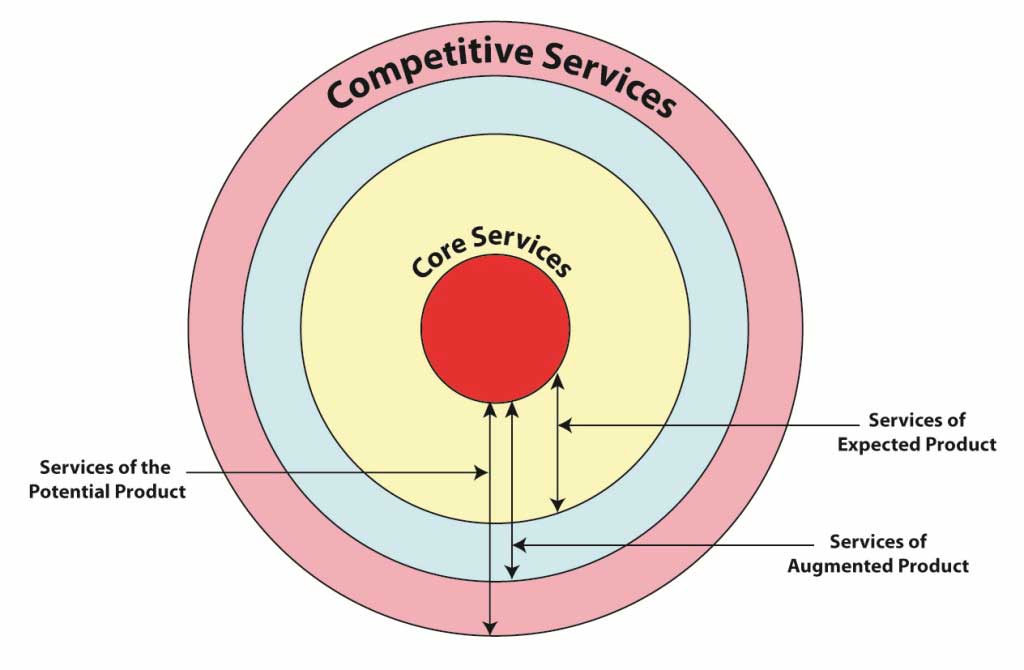
Product Development Career Model
The product encompasses tangible goods, services, ideas, people, and places. All of these can be marketed on the Internet. The product development career model is explained in the given diagram below. At the center, the core and essential services exist. Outside of this, there is a competitive service provided by the manufacturer. This is equally applicable and important for services, e.g., travel services, etc.
1. Perfect Model Product on the Web
For instance, eBay’s business model can be explained
Create and maintain a person-to-person business community in which
- Buyers and sellers can promptly and uninterruptedly trade information and goods.
- Act as a facilitator that supports trading
- Create aggressive trading surrounding with conviction and security programs, economic and suitable services, and sturdy community similarity.
Spin around three profit centers: Domestic business, international trade, and payments.
2. Properties
Product augmentation on the Web can happen in various ways and at different times. Amazon e-tailor provides proposals, electronic coupons, complementary product sales, and information.
Whenever a customer logs in to any e-commerce site, so many uncalled and unpaid services are given to him to enrich his buying experience. And consumers are getting those accompanying services and are used to them without paying for them. So, vendors find it challenging in cases where customers have begun to look forward to getting those services by default on any product purchase.
Gradually, many augmented products have become the primary product today since the extra services that customers use with the augmented products are available during the immediate product development process. For example, before buying any mobile phone, customers first judge through e-tailor the relevant competitive advantages of purchasing a specific mobile phone. And every company tries to add extra functionalities, expecting to be reckoned unique in the brand game. Infinite qualities are available with each of these mobiles, and the notion of the potential product development process is changing daily.
To be effectively competitive, online e-tailers should present a host of services that go with the product development process, and ultimately these added features constitute the final product. But only some companies are equally viable regarding human resources, technology, and cost. Some products perform well compared to other products.
3. Branding
In this connection, it is imperative to mention the branding exercises. The brand is an image when seen from the outside. A brand is your strength, reliability, and your reputation. A brand is neither a name nor a positioning statement. It is not even a marketing message. It is a promise or proposition a company poses for its target audience, and that company should maintain it. The success of a brand solely depends on the consumer perception of identifying it as unique. And this would help the company differentiate itself from other brands. Online branding is building that personal niche in the customers’ psyche. It is the total effect that creates a special uniqueness.
4. Brand Relationship Power
The organizational viewpoint is establishing the branding in the online atmosphere in the following ways: web page message capability, combining branding and marketing communications across diverse online channels, setting up of company value propositions, using brands as search key strings, connecting and improving the brand positions and globalization, and increasingly involve public sector with the branding.
Some key themes are operational in this case: customer control, customization, customer rapports, self-help qualities of the medium, emphasis on experience, and the chance given by m-commerce to modernize the branding experience.
The following stages of the online brand development strategy are relevant:
- The brand context
- The brand objectives and message
- The brand specification
- Brand design
- The websites and other communications utilizing the brand
- The brand promotion
- The brand experience
- Brand evaluation and review
The achievement of Google, Yahoo, and MSN shows how a new and online product can utilize internet properties and build a successful brand. A brand is not just a trade name or logo but the emotional attachment of the customers to the brand; in the proper product development process, this factor has to be understood very well, and an intelligent marketer must strike this note in the beginning during the product development process.
The Internet has impacted the following areas of the digital product development process:
- Constant Consumer Interaction: Every product development career phase must combine an in-depth plan to encourage customer feedback because it is the benefit that every company sells, not the product. So, all products, irrespective of different turns, such as market conditions, customer expectations, and business ups and downs, should be well-thought regarding the existing and potential customer needs and continue to garner consistent customer feedback. The Internet is the only medium for this ongoing communication as it is instant, cheap, and interactive.
- Product Design and Communication Devices: Given the massive progress in Internet technology, rapid product development occurs through Internet tools, such as 3D presentations and video conferencing.
- Testing of Products: Companies can benefit from concurrent market data through the advent of computer-supported design, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and other sophisticated technologies. For product testing, digital surveys are beneficial. One can quickly test the actual efficacy of the product by conducting an online consumer survey; most marketing experiments can take place.
Customer Assisted Product Design
The products must be able to satisfy customer needs and give them delight in every way they can. So, a product must have the relevant qualities to help customers solve their problems (if any). But for that, information on customer needs and desires is paramount.
We all know customers are a product’s final release point (i.e., they are the ultimate users of the product). On the other hand, a customer knows the downside and shortcomings in the product design. It is the customer who can give honest feedback (if properly asked) regarding a product; the product features can be improved to meet the customer needs if we heed what all the potential customers add to a product.
Real-life Examples
So many companies involve their target prospects and seek advice while evaluating the products.
Microsoft and many other software companies encourage the user to report bugs in the software. This would help them develop software with no or most minor bugs. Both the company and the customers would heave a sigh of relief – the customer would have a perpetual reliance on the product, increasing the brand equity, and the company will be able to start testing the next phase of the product development career. How does such a liaison between customer and company take place? The answer is primarily online. Dell computers also get customers engaged in times of new product development careers and in cases where they test the performance of a newly-launched product.
Some distinctive product variants are as follows:
- Bundling: In some cases, companies give customers various combinations or bundles of products. Bundling is a simple way to appeal to and serve different customer segments. For example, a laptop targeted to the student category, sold with the pre-installed operating system (OS) and MS Office or bundled with a pen drive, is a perfect example of bundling. Bundling is very common in different supermarkets and malls.
- Complementary Products: Some products are of very little use unless complementary products are available with them; these are complementary products. Complementary products include basic functionality, added features, tools, and other augmentation that enhance the primary product value, for instance, Mobile and SIM cards, laptops and Anti Virus or OS, etc. IBM, Wipro, HCL, and Dell add complementary products in the software area so that the users favor the software and choose the hardware. Consumers can get information about complementary products and existing offers over the Internet.
- Aggregated Product Demand: In the digital age, marketing products with limited profitability, if marketed to restricted geographic areas or through distributing channels needing greater volume, has become lucrative as the Internet is spread across the globe.
New Product Offering
So many new concepts are being developed in the digital world, such as YouTube, MySpace, Facebook, and Twitter. These were primarily used for social networking, now majorly for creating different marketing strategies. Companies, big, small, and start-ups, are utilizing the open access of these social networking sites to establish their brimming marketing needs and reach the target prospects. They spend millions on these social platforms.
Other examples are V blogs (video blogs). People use these effective mediums to present new and modified product attributes.
Third-Party Offerings
Different companies seek the expertise of veteran marketing professionals, and this consulting service is called third-party marketing. Also defined as third-party distributors, these firms hire knowledgeable marketing and sales professionals. These professionals work with the client’s employees to raise the assets within the distribution channels. These experts include organizational bankers, brokers, dealers, investment platforms, fiscal advisors, and high-network individuals. Generally, on a commission basis, they work for the clients, but depending on their expertise, some charge a moderate fee out of the total value of the assets raised. The proper evaluation of third-party offerings is done through whether they can increase the holdings as per what they targeted.
In the e-mail marketing process, the third-party offering mainly ensures delivering the e-mails. Having a good relationship with all the major ISPs, the third-party offering whitelisted the releasing IP addresses. Still, there are cases when the recipients spam the e-mails, and IP addresses can be blacklisted. Here, the third-party marketers can quickly turn around sending IPs to ensure the e-mails are delivered and contact the ISP to bring back the spammed IP addresses on the allowlist.
Conclusion
So, we see how the Internet has created a new dimension to form products and services. After identifying the market prospect and value proposition, with the help of several factors, the product is being developed to reach the end customers. Online access makes it possible for all kinds of experimentation and product research. Open-eyed marketers always take the chance on this situation and product development process that effectively serves the customers.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Product Development Process” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.