Updated October 10, 2023
Profit Taking Meaning
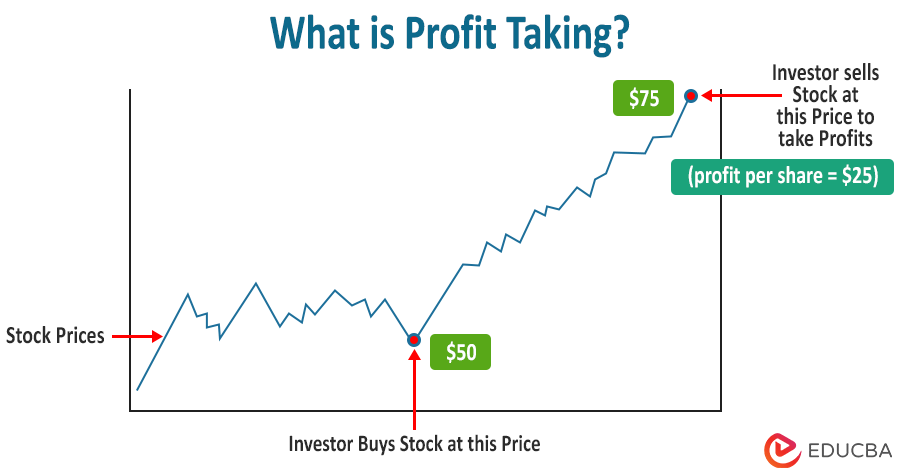
Profit taking is when investors sell their investments, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, once it reaches the expected price level to earn a profit.
It is a fundamental aspect of investment and trading strategies. All investors invest to earn a maximum profit. They understand that the stock markets constantly experience fluctuations, i.e., rise and fall. Thus, many investors buy and hold securities until they reach a desired price level, and after that, they sell those securities to make profits.
Table of Contents
Key Highlights
- Profit-taking involves selling assets to make profits when their prices have increased significantly.
- Implementing these strategies can help preserve capital, manage risk, and reduce the influence of emotions in investment decisions.
- Types include sector-specific (selling within a specific industry) and marketwide (selling across all investments).
Types
There are two types of profit-taking: Sector-Specific and Marketwide.
1. Sector-Specific Profit Taking
This strategy involves selling investments within a specific industry or sector when you believe that sector has reached its peak or is overvalued.
Example: Let’s say you invested in a technology stock that has seen significant gains over the past year. You noticed that technology stocks have been performing exceptionally well. Still, you believe the sector may be vulnerable to a downturn due to factors like high valuations and regulatory concerns. In this case, you decide to take profits by selling some or all of your technology stock holdings to lock in your gains.
2. Marketwide Profit Taking
This strategy involves selling your investments when you believe that the broader stock market is already at a high point and prices may start falling.
Example: Suppose you have a diversified investment portfolio that includes stocks, bonds, and real estate. Over the past few years, the stock market has experienced a significant bull run, and your portfolio has grown substantially. However, the overall market’s condition shows the possibility of a market downturn. In this scenario, you decide to rebalance your portfolio by selling some of your stock holdings and reallocating those funds into safer assets like bonds or cash, thereby taking profit from the overall market.
Example
Let us take a look at a detailed example of how profit-taking works.
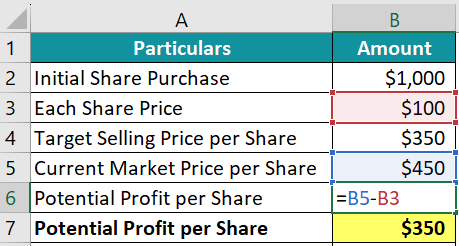
Suppose Theo, an investor, purchased 1000 shares of XYZ Inc. at $100 each on April 1, 2022. He wishes to hold these shares until they reach the price of $350 per share.
XYZ Inc. is a company in the business of manufacturing reusable bags. On August 15, 2023, the government introduced a policy change mandating reusable bags and an immediate ban on all other types of bags. This policy change profoundly impacted XYZ Inc. and caused the price per share to surge to $450 per share, a sudden increase of $350 per share.
At this stage, Theo decides to take profits by selling his share at a higher market price.
Let’s calculate the following:
- Profit per share
- Total profit
- Total extra gain
Given:
Solution:
1) Profit Per Share
=$450 – $100 = $350
Theo stands to earn a profit of $350 per share. Let’s see how much total profit he can earn.
2) Total Profit
= $1000 x $350
= $350,000
3) Total Extra Gain
= $100 x $1000
= $100,000
Result:
Theo’s strategic decision to hold onto his shares until the target price of $350 per share was not only met but exceeded significantly due to favorable government policy changes in the reusable bag industry. As a result, he was able to capitalize on this unexpected surge in share price and secure a substantial additional profit.
Profit Taking Strategies
Here are some effective profit-taking strategies:
- Time-Based: It includes setting a predefined holding period for your investments. For instance, you might decide to sell after holding a stock for six months, regardless of price movements.
- Trailing Stop Orders: In trailing stop orders, you increase your stop-loss level as the price moves in your favor. However, if the price starts to reverse, the stop order stays at the last highest price level. This lets you make a profit and limit potential losses.
- Fixed Profit Target: You can set a specific percentage gain or price level you aim to achieve on your investment or trade. Once the price reaches this target, you can sell the investment to secure profits. For example, if you set a 20% profit target and your investment appreciates by 20%, sell to lock in gains.
- Trend Following Exits: The basic strategy is to exit the investment when you think that the upward-moving price trend is over. You can check this using various methods, like following the moving average lines.
- Fundamental Exits: When a major announcement or news can affect the financial market, and you think it can cause a downfall in stock prices, you must exit the market.
- Opposite Signal: Imagine you used a signal that showed the market was going up, and you started trading. But when the signal changes and shows the market is going down, it’s the opposite of what you followed to get in. So, you should get out of the market at that point.
- Scale-Out: It involves gradually selling portions of your stock investment as it increases. This allows you to secure profits while you still have a chance to make further gains with the remaining stocks. For instance, if you hold 100 shares of a stock, you could sell 25 shares when it reaches a specific profit level, then sell more as the price continues to rise.
How to Take Profits?
You can practice profit-taking using the following steps:
Step 1: Set Clear Goals
Determine your financial objectives, i.e., the percentage gain or specific price level at which you want to take profits.
Step 2: Use Stop Order or Alert
Consider setting up stop orders or price alerts with your brokerage platform. This allows you to automate the profit-taking process by triggering a sale when the asset reaches your target price.
Step 3: Monitor Market Conditions
Continuously assess your profit-taking strategy based on your evolving financial goals and market conditions. Monitor news, economic events, and technical indicators that might affect your investment. Adjust your approach as needed to optimize your investment results.
Step 4: Consider Partial Profit Taking
Instead of selling your entire position, think about partial profits. This involves selling some of your holdings while keeping some for potential future gains. It allows you to secure profits while maintaining exposure to the potential upside.
Importance
Profit-taking holds significant importance for several reasons:
- Market Correction: It is crucial for maintaining the health of the financial market. It helps correct the prices of securities in the open market, preventing them from becoming artificially inflated or overvalued due to excessive buying pressure.
- Short-Term Return: Implementing a profit-taking strategy can give short-term investors attractive returns.
- Long-Term Investments: By consistently delivering profits to short-term investors, a company can cultivate a positive image and reputation. This positive perception may lead some investors to consider long-term investments in the company, further bolstering its stability and growth prospects.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Profit-taking allows investors to secure profits from their investments, reducing the risk of losing those gains if the market reverses. | Selling too early may result in missing out on potential future profits if the asset continues to appreciate. |
| Taking profits can help preserve capital, providing funds for future investments or financial goals. | Frequent profit-taking can lead to higher transaction costs, such as commissions and taxes, which can eat into overall returns. |
| It can prevent emotional decision-making and reduce the influence of fear and greed. | Depending on tax regulations, selling assets for profit may trigger capital gains taxes, reducing the net return. |
Conclusion
Profit-taking is a strategy that enables investors and traders to safeguard their gains and manage risk effectively. It can help achieve financial goals while minimizing potential losses when executed wisely. However, it’s essential to strike a balance between realizing profits and staying invested for long-term growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Are there tax implications to profit-taking?
Answer: Yes, profit-taking may trigger capital gain taxes, depending on your jurisdiction and the length of time you held the asset.
Q2. Should I reinvest profits or take them as cash?
Answer: Whether to reinvest profits or take them as cash depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategy. Diversifying investments is often a sensible approach.
Q3. Can you automate profit-taking?
Answer: Yes, you can automate profit-taking using stop orders, trailing stops, or other trading tools offered by brokerage platforms.
Q4. What is the difference between profit-taking and day trading?
Answer: Profit-taking can be a part of various trading strategies, including day trading. Day trading involves buying and selling assets within the same trading day, while profit-taking is a broader strategy used to lock in gains at any time horizon.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to profit taking where we discuss its types and strategies in detail. You can also go through our related articles to learn more: