
Brief on Project Management Tools and Techniques
In the present scenario, in spite of having advanced technology & plenty of resources, projects were not delivered in line with the expectations of stakeholders (i.e. delivering the project in a stipulated time frame & available budget). Here where the need for project management arises, it is a strategic initiative that directs the project towards the specified goals by structuring the whole project in initiating, planning, executing, controlling/monitoring & completing the project. In this topic, we are going to learn about Project Management Tools and Techniques.
Project Management Flow
Project Management flows in the following phase-wise manner:
a. Initiation Phase
This is the primary project management phase for any project; in this phase, the initial requirements are identified and established as follows:
- With respect to project requirements, a suitable team is identified & brought on board
- The project’s scope and goals are defined clearly, and all stakeholder expectations are clearly discussed with the team.
- The team is assigned to their respective job roles & responsibilities.
- Procedures & formats for posting project information and updates to stakeholders are provided to the team.
- Internal & cross communicational protocols and respective hierarchies are disclosed to all stakeholders.
- Apt tools that are required for project management are identified & provided to the team.
b. Project Planning
After Initiation, here comes the major & crucial phase of the project, which is a way ahead route map for the project management:
- Detailed project scope, feasibility is defined.
- All the activities of the project are listed down, and their respective WBS (Work breakdown structure) is prepared. WBS is nothing but breaking down the major event into a set of activities (For ex. Event: Planting a tree Activity: Procuring tree, 2. Digging a pit, 3. Planting tree)
- After preparing WBS, a budgeting exercise is carried out where the quantum of all the activities are estimated & competitive rates are being derived, and a preliminary estimate of the project is prepared for further approval (where necessary amendments are done based on any additional cost incurred during the project)
- Risk identification is done by self-interpretation or comparing the project with other competitive projects, and necessary mitigation plans are prepared to prevent potential risks.
- With respect to the requirement of stakeholders, the master schedule is prepared by sequencing all the listed activities in order to derive the baseline (ideal/preliminary) duration of the project. There are majorly 4 types of sequencing SS – Start to Start, SF – Start to Finish, FS – Finish to Start, FF – Finish to Finish.
c. Project Execution & Monitoring phase
- The project manager initiates the execution of the project with respect to the baseline plan prepared in the planning phase.
- Procurement/deployment of required resources and ensure that the project is on schedule within prescribed quality standards.
- Project progress is tracked/monitored against the baseline plan using different tools (Gantt chart, PERT, etc.)
- Due to some unavoidable circumstances project may have time or cost overruns, where the baseline schedule or estimate shall be modified accordingly if required.
- Project status is maintained in prescribed formats provided in the initiation phase, and the same is updated & circulated on a timely basis to stakeholders of the project.
d. Project closure/completion
- This is the final stage of project management where a project team achieves the destined goal within valid timelines, stipulated budget & quality.
- All the necessary closure records & reconciliations are completed and disclosed to stakeholders.
- Based on the project experience, various reports like project learning reports, customer satisfaction reports, etc., are prepared as a reference for future projects.
- Finally, the project is handed over to the customer by ensuring there is no stone unturned by closing all checklist points or by attending to snags raised by the customer.
The project management techniques discussed above shall structure the project and enable the project team to ensure the following:
- Delivery of specified goals with respect to stakeholder requirements.
- Develop baseline schedules.
- Estimating & Budgeting costs for the project in line with the baseline schedule.
- Breaking of events into work breakdown structure.
- Risk assessment & mitigation.
- Project controlling / monitoring.
Project Management Tools
Project management is a technique that has a wide variety of tools to assist in accomplishing tasks and executing responsibilities. There are both manual & automated tools in project management. Some of the most widely used techniques are:
- PERT – Project Evaluation & Review Technique
- CPM – Critical Path Method
a. PERT – Project Evaluation & Review Technique
PERT is a statistical tool used in project management, which was designed to represent & analyze the tasks involved in the completion of a project. This is a probabilistic model that is time-driven.
PERT planning involves the following steps:
- All the events/milestones are further classified into activities & necessary sequencing is done.
- Preparing a network diagram based on the activity sequence where events/milestones are represented in circles & flow of activities from one to other is denoted with arrows.
- Further estimation of time required for each activity is done in terms of Hours, Days, Weeks or Months as per project requirement.
- A differential feature of PERT is dealing with the uncertainty of completion timelines. Therefore, PERT model usually includes three types of time estimates:
- Optimistic time – Best possible time for completion of the activity.
- Most likely time – Highest probabilistic time for completion of the activity.
- Pessimistic time – Longest time for completion of the activity.
Finally, the weighted average is calculated by the following formula:
Expected Time = (Optimistic + 4 x Most Likely + Pessimistic) / 6
b. CPM (Critical path Method)
- The longest duration for the completion of the project is the critical path of the project. The critical path determines the total duration required for the completion of the project. The amount of time that activity can be delayed without delaying the project is called slack time & the activity is called Non-Critical activity. Thus, CPM is a deterministic model that is both time & cost-driven.
The critical path of the project determines the following four parameters for each activity, which are calculated using the expected time for relevant activities:
ES – Earliest Start, EF – Earliest Finish, LS – Latest Start & LF – Latest Finish
- With the forward working of the network, the earliest start and finish time of each activity is determined with reference to predecessor activities in the network.
- By working in a backward approach through the network, we can determine the latest start & latest finish time, which means the time where an activity can start and finish without any delay in the project.
Slack = Latest Start – Earliest start (or) Latest Finish – Earliest finish
Example:
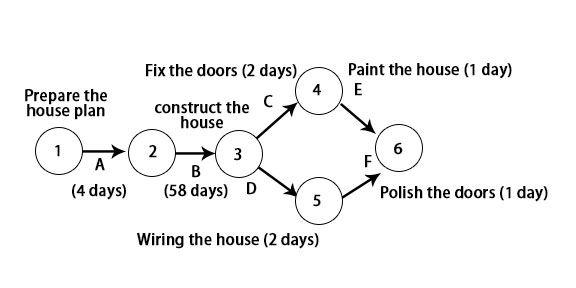
Network diagram for PERT & CPM
PERT & CPM shall help in arriving at the simplified way of project completion by:
- Identification of critical activities.
- Resource requirement & deployment in the project.
- Establishing project completion timelines.
- Defining activities with slack time (i.e. noncritical activities).
- Deriving interdependencies & Resource limitations.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Project Management Tools and Techniques. Here we discuss the project management flow and project management tools to assist in accomplishing tasks. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –

