Updated March 10, 2023

Introduction to Properties Class in Java
A properties class in Java is a class with a special object present in the properties class, which holds the persistent data set related to the object for streaming. Properties class is a subclass of Hashtable and is used to maintain the entire series of data in the form of the key as a string and its value in the form of a string. A very good characteristic of this class is that it will return the value that does not satisfy the values provided with a key. The multiple threading concept also gets satisfied easily with properties class.
Constructors
There are two types of constructors in the Properties class, which are as follows:
# Properties() as a constructor
Properties() constructor is a constructor used to create properties object with no default values.
# Properties(Properties Default) as a constructor
Properties(Properties Default) creates an object that uses its default values as propDefault. But in any case, whether it is Properties() as a constructor or Properties() as a constructor, the property list will be empty only.
Methods
Java Properties is a type of class which includes the following methods within it:
- String getProperty(String Key)
- String getProperty(String key, String defaultProperty)
- voidList(PrintStream streamOut)
- voidList(PrintWriter streamOut)
- voidload(InputStream streamIn) throws IO Exception
- Enumeration propertyNames()
- ObjectSetProerty(String key, StringValue)
- void store(Output Stream streamOut, String Description)
# Object setProperty(String key, String value)
A value is associated with the key, which returns the previous value linked with the key or returns null if there is no association between the key and value pair.
# void load (InputStream streamIn) throws IO Exception
Streamln, as a parameter passed, is linked with the input stream and gets an input with a list of the property lists.
# Enumeration propertyNames()
An enumeration and description of the defined keys get returned, including those keys that also comprise the property list with its content and explanation.
# String getProperty(Key)
Constructor passed should be a key with the associated value as a string, and if in case a null object gets returned, then either the keys are not present in the list or not even present in any property list as default.
# String getProperty(StringKey, String defaultProperty)
Behavior is the same as String getProperty besides the fact it also returns default Property. It doesn’t care whether the key is present in the property or default list.
# void list(PrintStream, streamOut)
Parameter streamOut is linked with the Output stream and returns the value as soon as the property list is sent.
# void list(PrintWriter streamOut)
Parameter streamOut linked with the Output stream returns as soon as property list is passed, which means its behavior is the same as Print stream with little more privileges
# void store(OutputStream streamOut, Description)
streamOut linked with the outputStream writes the property list; that string will write with the specified description once written.
Examples of Properties Class in Java
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
Program to demonstrate the methods and constructors associated with the Properties class.
import java.util.*;
public class PropertiesExmpl
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Properties ex = new Properties();
Set url;
String str;
ex.put("ide", "ide.educba.org");
ex.put("contribution", "contribution.educba.org");
ex.put("articles", "articles.contribution.educba.org");
url = ex.keySet();
Iterator itr = url.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext())
{
str = (String)itr.next();
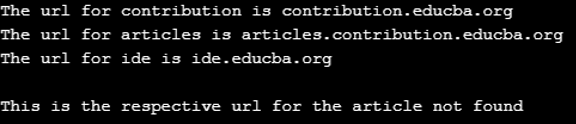
System.out.println("The url for " + str +
" is " + ex.getProperty(str));
}
System.out.println();
str = ex.getProperty("article", "not found");
System.out.println("This is the respective url for the article " + str);
}
}Output:
Example #2
Program to demonstrate the list method associated with the Properties list.
import java.util.*;
public class PropertiesList
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Properties ex = new Properties();
Set url;
String str;
ex.put("ide", "ide.educba.org");
ex.put("contribution", "contribution.educba.org");
ex.put("article", "article.educba.org");
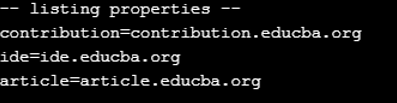
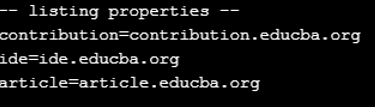
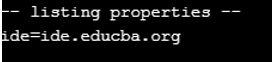
ex.list(System.out);
}
}Output:
Example #3
Program to use PrintWriter method present in properties list method of properties class.
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.*;
public class PropertiesDem1
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Properties ex = new Properties();
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(System.out);
ex.put("ide", "ide.educba.org");
ex.put("contribution", "contribution.educba.org");
ex.put("article", "article.educba.org");
ex.list(writer);
writer.flush();
}
}Output:
Example #4
Program to enumerate and demonstrate the values present in the properties list.
import java.util.*;
public class PropertiesDem2
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Properties exmpl = new Properties();
Set str;
String s;
exmpl.put("ide", "ide.educba.org");
exmpl.put("contribution", "contribution.educba.org");
exmpl.put("artcle", "article.educba.org");
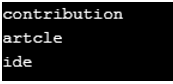
Enumeration name = exmpl.propertyNames();
System.out.println(name.nextElement());
System.out.println(name.nextElement());
System.out.println(name.nextElement());
}
}Output:
Example #5
Program to set the value with the properties object of properties class.
import java.util.*;
public class PropertiesDem4
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Properties exmpl3 = new Properties();
exmpl3.put("ide", "ide.educba.org");
exmpl3.put("contribute", "contribute.educba.org");
exmpl3.setProperty("article", "article.educba.org");
System.out.println(exmpl3);
}
}Output:
Example #6
Program to demonstrate the properties class method of loading the data set.
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
public class PropertiesDem8
{
public static void main(String arg[]) throws IOException
{
Properties exmpl4 = new Properties();
String s = "ide = ide.educba.org";
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("properties.txt");
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("properties.txt");
out.write(s.getBytes());
exmpl4.load(in);
exmpl4.list(System.out);
}
}Output:
Example #7
Program to demonstrate the Properties class associated with the object of the properties class and then load the values within the properties class.
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.util.*;
public class PropertiesDem9
{
public static void main(String arg[]) throws IOException
{
Properties ex = new Properties();
String s = "ide = ide.educba.org";
StringReader reader = new StringReader(s);
ex.load(reader);
ex.list(System.out);
}
}Output:
Example #8
The program stores the properties’ objects and key values in the properties class.
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.util.*;
public class PropertiesDem5
{
public static void main(String arg[]) throws IOException
{
Properties ex = new Properties();
ex.put("ide", "ide.educba.org");
ex.put("contribution", "contribution.educba.org");
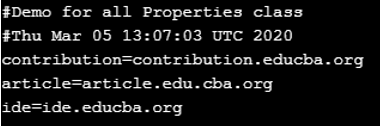
ex.put("article", "article.edu.cba.org");
ex.store(System.out, "Demo for all Properties class");
}
}Output:
Advantages of Properties class in Java:
- It is easier for end-users to get the maintained form of a list specifying the required value and associated key.
- Return of default value is a very good property for specification and kind of notification if the key and value pair don’t get matched, it will return the null or default value associated.
- There is no need for external synchronization in multi-threading, which shares object properties within the property class.
Conclusion – Properties Class in Java
The properties class has an instance variable within the object of the properties class, which is used to get the return value and to get the associated default value with the streaming also associated with it. Therefore, the properties class in Java is pivotal in the methods and constructors present.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Properties Class in Java. Here we discuss the Methods and Examples of Properties Class in Java and the Advantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –