Updated March 30, 2023

Definition of Python 3 Dictionary
Python 3 dictionary values data type replicated, however, keys cannot be copied and must be immutable. Keys of the dictionary is case-sensitive. With simply two curly braces, an empty dictionary with no objects can be written Values may or may not be unique within a dictionary. The keys of a dictionary must be immutable data types like texts, numbers, or tuples, whereas the contents can be of any kind.
Creating Python 3 Dictionary
Unlike other Data Types, which can only carry elements of a single value, Dictionary can hold key-value pairs. This means that even if the name is the same, different cases of Key will be interpreted differently.
The below example shows creating python 3 dictionaries are as follows.
1) In the below example we have created python 3 dictionaries with integer and mixed keys.
Code:
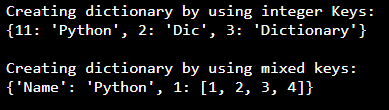
# Creating dictionary by using integer Keys
Dic = {11: 'Python', 2: 'Dic', 3: 'Dictionary'}
print("\nCreating dictionary by using integer Keys: ")
print(Dic)
# Creating dictionary by using mixed keys
Dic = {'Name': 'Python', 1: [1, 2, 3, 4]}
print("\nCreating dictionary by using mixed keys: ")
print(Dic)Output:
2) In the below example we are creating an empty dictionary and also creating a dictionary by using dict() method.
Code:
# Creating empty Dictionary by using dict method.
Dict = {}
print ("Creating Empty Dictionary: ")
print (Dict)
# Creating dictionary by using dict method.
Dict = dict ({1: 'Python', 2: 'dict', 3:'dictionary'})
print (Dict)Output:
In the above example we have created an empty dictionary without passing any values of keys and pairs.
3) In the below example we are creating a nested dictionary are as follows.
Code:
# Example to create a Nested Dictionary by using python 3.
Dict = {1: 'Python', 2: 'Dictionary',
3:{'A' : 'Welcome', 'B' : 'To', 'C' : 'Python'}}
print (Dict)Output:
Python 3 dictionary access
To get to the things in a dictionary, look up the key name. Inside square brackets, the key can be utilized.
1) In the below example we are accessing elements by using keys are as follows.
Code:
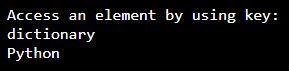
# Create dictionary by using python 3
Dict = {1: 'Python', 'name': 'dictionary', 3: 'dict'}
# accessing an element from dictionary by using key
print ("Access an element by using key:")
print (Dict ['name'])
print (Dict [1])Output:
2) In the below example we are accessing elements from the python 3 dictionaries by using the get method are as follows.
Code:
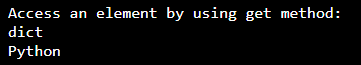
# Create dictionary by using python 3
Dict = {1: 'Python', 'name': 'dictionary', 3: 'dict'}
# accessing an element from dictionary by using get method
print ("Access an element by using get method:")
print (Dict.get (3))
print (Dict.get (1))Output:
3) In the below example we are accessing elements from python 3 by using a nested dictionary are as follows.
Code:
# Create dictionary by using python 3
Dic = {'Dic1': {1: 'Python'},
'Dic2': {'Name': 'Dictionary'}}
# accessing an element from dictionary by using key
print (Dic ['Dic1'])
print (Dic ['Dic1'][1])
print (Dic ['Dic2']['Name'])Output:
Python 3 dictionary Elements
- The addition of elements in Python Dictionary can be accomplished in a variety of ways. By defining value together with the key, such as Dict [Key] = ‘Value,’ we can also add a single value to the python 3 dictionaries.
- The built-in update method can be used to replace an existing value in a Dictionary. An existing Dictionary can also have nested key values added.
- If the key-value pair exists, the given value is updated, otherwise, a new Key is created with the value.
- The elements of a dictionary are organized, changeable, and duplicates are not allowed. The key name can be used to refer to dictionary components that are given in key-value pairs.
- When we state that our dictionary is in order, we’re referring to the fact that the entries are in a specific sequence that will not alter. Unordered objects don’t have a set order, thus we can’t use an index to find them.
Python 3 Dictionary Functions
Below are the functions available are as follows.
1. Len
This function gives us the total length of the dictionary. The length is equal to the number of elements from the dictionary.
The below example shows len functions in python are as follows.
Code:
Dic = {'Python': 18,'dict':12,'dictionary':22,'python':25}
print ("Length : %d" % len (Dic))Output:
2. Str
This function produces the printable string are as follows.
Code:
Dic = {'Python': 18,'dict':12}
print (str (Dic))Output:
3. Type
This function returns the type of a variable is as follows.
Code:
Dic = {'Python': 18,'dict':12}
print (type (Dic))Output:
Python 3 Dictionary Method
Below is the method available as follows.
1. Copy
This method returns a shallow copy of the dictionary.
Code:
Dic = {1: 'Python', 'name': 'dictionary'}
Dic.copy()
print("copying Dictionary: ")
print(Dic)Output:
2. Clear
This method will delete all the items from the dictionary.
Code:
Dic = {1: 'Python', 'name': 'dictionary'}
Dic.clear()
print("\nDeleting Dictionary: ")
print(Dic)Output:
3. Pop
This method removes and returns element from the dictionary.
Code:
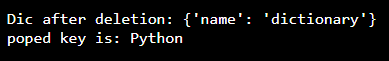
Dic = {1: 'Python', 'name': 'dictionary'}
pop_ele = Dic.pop(1)
print('\nDic after deletion: ' + str(Dic))
print('poped key is: ' + str(pop_ele))Output:
4. Popitem
This method will remove and returns the arbitrary element.
Code:
Dic = {1: 'Python', 'name': 'dictionary'}
pop_ele = Dic.popitem()
print('\nDic after deletion: ' + str(Dic))
print('poped key is: ' + str(pop_ele))Output:
5. Get
This is conventional method used to access value from the key.
Code:
Dic = {1: 'Python', 'name': 'dictionary'}
print (Dic.get (1))Output:
Conclusion
The dictionary includes key-value pairs. It can be formed in Python by enclosing a succession of entries in curly braces and separating them with a comma. The dictionary stores the pair Key and the other is the Key value pair element.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python 3 Dictionary. Here we discuss the definition, Creating Python 3 Dictionary, Python 3 dictionary access, Examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –