Updated March 31, 2023

Introduction to Python Split String
In Python, strings can be defined as an array of characters represented by Unicode character. As Python doesn’t support char data type, Python has a single character as also a string. Strings are declared either in the single quote or double-quotes. The most import function on the string is the split() method. The split () function is a function when applied to any string it returns the list of strings after recognizing the delimiter and breaks the string into substrings. This method is used to split the strings into characters. Sometimes it is required to split large strings into small chunks of characters or substring. Spit () functions work the opposite of concatenation. As the split function returns the list of strings, it can be accessed using an indexing method in which every string or character of the given string is given the index number starting with number 0 and so on. In this topic, we are going to learn about Python Split String.
How Does Python split function work?
In python, the split () function is a function to split strings using separator white space being a default separator. As we know in Python, we have a concatenation of strings which means combining strings, whereas split function is the opposite of concatenation. Therefore Python uses a built-in function called split(), which breaks down the strings into other strings.
Whenever we split strings in Python, using the split() function will always be converted into lists. In Python, data types are not declared before any variable; hence, we need to assign it to some variable whenever the split() function is used. It will then be easily accessible using advanced for a loop. So when a string assigned to any variable and after applying a split() function to that variable, it will be converted to an array or list, and this array of strings can be accessed using an index.
Syntax:
str.split(separator, maxsplit)The split () method takes two parameters, as shown in the syntax above separator and maxsplit.
The separator parameter is optional because, by default, the whitespace is taken as a separator if not specified.
Maxsplit is also an optional parameter of the split () function; this parameter defines the maximum number of splits on the given string. By default, it will take -1 as the value of maxsplit if not specified.
Examples of Python Split String
Here are the following examples are mention below:
Example #1
The below code shows the simple program which uses a split() function without the maxsplit parameter.
Code:
str = 'Python split strings article'
print(str.split())Output:
The above program uses a split function where the parameter isn’t specified, so by default, it will split the sentence given in str with space as the delimiter.
Now let us see the example for the code which uses a split function with maxsplit parameter also.
Code:
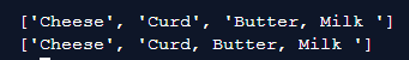
items = 'Cheese, Curd, Butter, Milk '
print(items.split(', ', 2))
print(items.split(', ', 1))Output:
In the above program, we have specified the maxsplit parameter as 2 and 1in the program. The items get split into 3 strings and 2 strings wherefrom the above it takes Cheese as 0th the string, Curd as 1st string, Butter and Milk as 2nd string.
There is another function, reverse split, which is defined as rsplit() in Python, which returns the list of string in reverse order, which means it starts from the end of the string and returns a string in a reverse way with the specified delimiter.
Syntax:
txt.rsplit(delimiter, maxsplit)The syntax is similar to the split() function and the working also, but it returns the strings in reverse order with a specified separator.
If no argument is passed to the rsplit() function, then it returns the same as the split() function.
Example #2
Code:
txt = "apple, pineapple, custardapple"
print(txt.rsplit())Output:
Using the rsplit function with maxsplit argument. This will spit the string in a set of string from the right side of the given string.
Example #3
Code:
txt = "apple, pineapple, custardapple"
print(txt.rsplit(',', 1))Output:
The above screenshot is for the above program with maxsplit argument as 1, which will split the string from back to front and it returns two strings as shown it will return first ‘custardapple’ then it takes a second string as ‘apple, pineapple’.
Another example of the rsplit() function which splits at the letter t and the provided maxsplit is 1, so it will split the string into two strings first, it splits at t so ’rings’ is one string, and the second string will be ‘Python, split, s’ is another string. The code is given below with output and screenshot.
Example #4
Code:
txt = 'Python, split, strings'
print(txt.rsplit('t', 1))Output:
There is another function similar to a split() function known as splitfields(). The earlier split() function was used with only one parameter, and the splitfields() function used two parameters. Now split() also uses two parameters; if no argument, it will take whitespace as default delimiter and splits the string and returns the string list.
Conclusion
In Python, strings can be broken and accessed using a split() function, which splits the given string according to the specified separator or by default separator as whitespace. This function returns the array of strings, so as earlier in Python array can be accessed using indexing. Similarly, these sets of strings returned after the split() function can be accessed using indexing. In this, each of string or character is given a corresponding index number starting with 0 and can be accessed using this index number.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Python Split String” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.