Updated March 23, 2023

Introduction to Python Threading Timer
The timer is a subsidiary class present in the python library named “threading”, which is generally utilized to run a code after a specified time period. Python’s threading.Timer() starts after the delay specified as an argument within the threading. Timer class itself and thus delaying the execution of the subsequent operation by the same duration of time. threading.Timer() class needs to be started explicitly by utilizing the start() function corresponding to that threading.Timer() object. It can also be stopped even before it has started execution by utilizing the cancel() function corresponding to that threading.Timer() object.
Syntax of Python Threading Timer
We need to import the python library “threading” to use the “Timer” function specified in it.
import threading as thHere we have specified a short name for the library by creating an alias for the same using the “as” keyword. In Short, Aliasing the Python library gives us the capability of utilizing this shorthand notation to call the Timer() class as:
th.Timer()instead of
threading.Timer()Timer() classed is specified with multiple arguments, out of which the “Delay Duration / Interval” and the corresponding function that needs to be delayed are quire important ones.
T = th.Timer (Delay Duration, function, args = None, kwargs = None)- Delay Durationis the time interval in seconds for which the specified function needs to be delayed.
- The function is the specified function that needs to be delayed.
- An empty list will be utilized by default if args is None.
- An empty dict will be utilized by default if kwargs is None.
Here we are creating a timer object named as “T”, which can be stated explicitly by utilizing.
T.start()It can also be stopped even before it has started execution by utilizing the cancel() function corresponding to this timer object “T” as:
T.cancel()Examples of Python Threading Timer
Following are the different examples of the python threading timer.
Example #1
Let’s try to understand its operation with the help of the below Example:
Code:
##Program to demonstrate the usage of threading.Timer() class within Python
import threading as th
## Creating a function
def prnt():
print("EDU CBA \n")
T = th.Timer(3.0, prnt)
T.start()
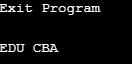
print("Exit Program\n")Output:
Case 1:
EDU CBA
Exit Program
Case 2:
Exit Program
EDU CBA
Although the “prnt” function is being called even before we are printing the text “Exit Program”, but still results may vary as it’s dependent on multiple factors.
- As we have used Timer() over here, which will call the “prnt” function after 3.0 seconds once we have explicitly started the timer object “T”.
- If the program takes more than 3.0 seconds from T.start() till print(“Exit Program\n”), then we will get the output as per Case 1.
- Otherwise, the output will be as per Case 2.
Example #2
Let’s now discuss the importance of the cancel function available in Timer class with the help of the below example:
Suppose we want to cancel the execution of this time delayed function “prnt” if in case the control reaches the end of the program before that specified delay time (3.0 seconds) itself, once the timer has been started [ T.start() ], then we can place the below statement at the end of the program.
T.cancel()Or otherwise, if the program takes more than the specified delay time (i.e. 3 seconds in this case), then the cancel statement will act as a redundant one. The reason being, the Delayed function would already have been executed until the control reached the T.cancel() function itself.
Code:
Let’s try to execute the below program:
##Program to demonstrate the usage cancel() function within Timer class
import threading as th
## Creating a function
def prnt():
print("EDU CBA \n")
T = th.Timer(3.0, prnt)
T.start()
print("Exit Program\n")
T.cancel()Output:
Case 1:
EDU CBA
Exit Program
Case 2:
Exit Program
EDU CBA
Case 3:
EDU CBA
Case 4:
Exit Program
If will think about the permutation and combinations of the outputs presented by the above program, then case 3 is not at all feasible. The reason being the below statement is not at all governed by the Timer object.
print("Exit Program\n")Case 1 is feasible when the control of the program takes more than the specified delay time (3.0 seconds) itself to reach the below statement, once the timer has been started [ T.start() ]
T.cancel()Case 2 is feasible when the control of the program takes more than the specified delay time (3.0 seconds) itself to reach the below statement but executes the print(“Exit Program\n”) before that specified delay time (3.0 seconds) once the timer has been started [ T.start() ]
T.cancel()Case 4 is feasible when the control of the program reaches and executes the cancel() function before that specified delay time (3.0 seconds) once the timer has been started [ T.start() ]
T.cancel()In this case, the Timer object will be canceled even before it has executed the “prnt” function.
Example #3
Code:
##Program to demonstrate the if cancel() function cancels the start() function or the Timer object itself
import threading as th
## Creating a function
def prnt():
print("EDU CBA \n")
T = th.Timer(3.0, prnt)
T.cancel()
T.start()
print("Exit Program\n")Output:
Case 1:
Exit Program
EDU CBA
Case 2:
Exit Program
In this example, we have placed T.cancel() even before we have explicitly called the Timer object using the below statement.
T.start()The question here is, can a canceled Timer() object “T” be called by using the start() function? What do you think? The answer is No !!! Once the object is canceled. It can not be started. Thus the output will be as per Case 2.
Conclusion
- The timer is a subsidiary class present in the python library named “threading”, which is generally utilized to run a code after a specified time period.
- Timer() class needs to be started explicitly by utilizing the start() function corresponding to that threading.Timer() object.
- It can also be stopped even before it has started execution by utilizing the cancel() function corresponding to that threading.Timer() object.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python Threading Timer. Here we discuss the Introduction to Python Threading Timer along with different examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –