Updated May 15, 2023
Difference Between Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
The following article provides an outline for Quality Assurance vs Quality Control. Quality assurance (QA) is a process to avoid mistakes/blunders and defects in a product and prevent obstacles when it is delivered to the customers. ISO 9000 defines quality assurance as “part of quality management focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled”. The complete Quality Assurance process is called the PDCA cycle or Deming cycle.
The phases of this cycle are:
- Plan: The organization should plan the process and its objectives and determine the direction that is required to deliver a high-quality product.
- Do: Developing and testing the process and making necessary modifications in the processes.
- Check: Supervise the procedure, change it as per requirements, and ensure whether it meets the predetermined objectives.
- Act: Executing steps required to improvise upon the process.
Quality control (QC) is a process by which one reviews the quality of all the factors influencing the manufacturing of a product. ISO 9000 defines quality control as “A part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements”.
This process emphasizes three facets (enshrined in standards such as ISO 9001).
- Elements such as controlling, management of the job, processes being well defined and well managed, criteria of performance and integrity, and record identification.
- Competence, e.g., degree qualified, skillset possessed knowledge base, etc.
- Soft elements, e.g., integrity, dignity, responsibility, accountability, relationship management, etc.
Head to Head Comparison Between Quality Assurance vs Quality Control (Infographics)
Below is the top 9 comparison between Quality Assurance vs Quality Control:
Key Differences
The terms “quality assurance” and “quality control” are often used as a replacement for each other to refer to various procedures of monitoring service or product quality. For example, the term “assurance” is often used as the following: Executing techniques of quality assurance in a music system software by SONY. The term “control” explains the fifth stage of the DMAIC model, which includes Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. DMAIC is based on data and is used to improvise upon business processes.
The key differences between the two are:
- QA is the execution of procedures and techniques that make sure that the final product or service will match the expected quality, while QC is the set of activities that are executed to verify the final product or service meets the set quality criteria.
- QA focuses on the improvisation of processes and techniques used to manufacture a product, but QC concentrates on the improvisation of the product by identifying hindrances.
- QA is a process of prevention that helps establish a flawless business process, whereas QC is a process of error correction.
- Quality Assurance is a process of verification, while Quality Control is a process of validation.
- The entire team is responsible for a QA process; on the other hand, QC is the responsibility of the testing team members that help locate the bugs and hindrances.
Quality assurance includes administrative and process-related activities executed in a quality-based system so that all the requirements of the end-product are fulfilled, and the final objectives are achieved. It is the system of measurement, comparison with the set standards, overviewing and supervising of the process, and a very thorough feedback procedure that ensures the prevention of error. Quality assurance consists of two components: “Fit for purpose” (the product should match the intended purpose) and “right first time” (mistakes should be identified and corrected). QA also involves the management of the quality of inventory and resources used, assemblies, important components, manufacturing services, and monitoring process. The two principles also make it very clear the background of manufacturing and producing a novice product or service. The purpose of manufacturing is making a product work once while that of QA is making it work all the time. Defining what an ultimate end-product or service based on quality is a very difficult procedure, estimated by numerous methodologies, from the subjective user-based weighted average approach with regard to quality characteristics to the value-based quality and price relationship approach.
Quality control and its major aspect include inspection; the final product is examined with an overview (or the end results of a process are examined). Product inspectors will be given a complete explanation of unacceptable deliverables and their defects like cracks, surface blemishes, etc. The quality of the deliverables is compromised if any of the aspects are either missed or not paid proper attention in any way. Therefore, there is a necessity for project managers and testing teams to check the ultimate deliverable in terms of quality and ensure that it matches the quality.
Quality Assurance vs Quality Control Comparison table
The quality of the outputs is at risk if any of these three aspects is deficient in any way.
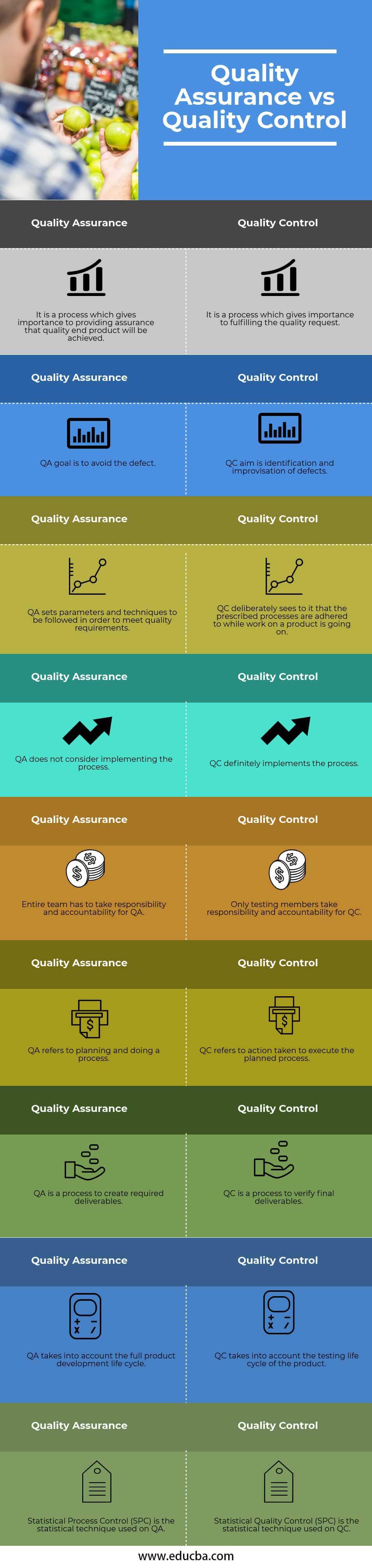
| Quality Assurance | Quality Control |
| It is a process that gives importance to providing assurance that quality end products will be achieved. | It is a process that gives importance to fulfilling the quality request. |
| QA goal is to avoid the defect. | QC aim is the identification and improvisation of defects. |
| QA sets parameters and techniques to be followed in order to meet quality requirements. | QC deliberately sees to it that the prescribed processes are adhered to while work on a product is going on. |
| QA does not consider implementing the process. | QC definitely implements the process. |
| The entire team has to take responsibility and accountability for QA. | Only testing members take responsibility and accountability for QC. |
| QA refers to planning and doing a process. | QC refers to action taken to execute the planned process. |
| QA is a process to create required deliverables. | QC is a process to verify final deliverables. |
| QA takes into account the full product development life cycle. | QC takes into account the testing life cycle of the product. |
| Statistical Process Control (SPC) is the statistical technique used on QA. | Statistical Quality Control (SPC) is the statistical technique used in QC. |
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Quality Assurance vs Quality Control. Here we have discussed the Quality Assurance vs Quality Control key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

