Updated April 17, 2023
Introduction to Radix Sort Java
Radix sort in Java is an integer sorting algorithm that uses integer keys and grouping the keys with individual digits that share the same significant position and place value. Then, elements are sorted according to increasing/ decreasing order. The main idea of Radix sort is to perform digit by digit sort starting from the least significant digit to the most significant digit. It uses counting sort as a subroutine to sort an array of numbers. Radix sort incorporates counting sort so that it can sort large and multi digits without having to decrease its efficiency by increasing the range of keys algorithm would sort over. Let’s dig deeper into Radix sort and see How Radix sort works in Java with few examples.
Syntax
Radix sort has Algorithm steps or a Flowchart on How Sorting is performed. So let’s look at the Algorithm of Radix Sort.
Algorithm of Radix Sort
Step 1: First, we need to find the largest element in the array, i.e., the max element. And let us consider X as the number of digits in the maximum element.
We need to calculate X as we need to go through the place value of a maximum element.
Step 2: Now, we need to go through each place value of the maximum element.
Step 3: We need to use any stable sorting algorithm to sort digits at each significant place value.
Step 4: Elements are now sorted based on digits at unit place value {X=0}
Step 5: Then, sort elements based on digits at tens place {X=10}
Step 6: Then, sort elements based on digits at Hundreds place {X=100}
Step 7: The above step repeats if there any more place values for elements in the array, i.e., based on X value.
How is Radix Sort Performed in Java?
Let us check on How Radix sort is implemented with some examples.
Example #1
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class radixSorting {
static int get_maxVal(int radixArr[], int arrLen) {
int maxVal = radixArr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arrLen; i++)
if (radixArr[i] > maxVal)
maxVal = radixArr[i];
return maxVal;
}
static void countSorting(int radixArr[], int arrLen, int exp) {
int resultArray[] = new int[arrLen];
int i;
int countVal[] = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(countVal,0);
for (i = 0; i < arrLen; i++)
countVal[ (radixArr[i]/exp)%10 ]++;
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
countVal[i] += countVal[i - 1];
for (i = arrLen - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
resultArray[countVal[ (radixArr[i]/exp)%10 ] - 1] = radixArr[i];
countVal[ (radixArr[i]/exp)%10 ]--;
}
for (i = 0; i < arrLen; i++)
radixArr[i] = resultArray[i];
}
static void radix_array_sort(int radixArr[], int arrLen) {
int m = get_maxVal(radixArr, arrLen);
for(int exp = 1; m/exp > 0; exp *= 10)
countSorting(radixArr, arrLen, exp);
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
int radixArr[] = {32,456,71,10,9,892,55,90,23,667};
int arrLen = radixArr.length;
System.out.println("Array after radix sort is ");
radix_array_sort(radixArr, arrLen);
for (int i=0; i<arrLen; i++)
System.out.print(radixArr[i]+" ");
}
}Output:
So here, we can see that the input array has been sorted using Radix sort along with Counting sort.
Example #2
Code:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class RadixSorting {
public static void sorting(int[] inputArray) {
RadixSorting.sorting(inputArray, 10);
}
public static void sorting(int[] inputArray, int radix) {
if (inputArray.length == 0) {
return;
}
int minVal = inputArray[0];
int maxVal = inputArray[0];
for (int i = 1; i < inputArray.length; i++) {
if (inputArray[i] < minVal) {
minVal = inputArray[i];
} else if (inputArray[i] > maxVal) {
maxVal = inputArray[i];
}
}
int exponentVal = 1;
while ((maxVal - minVal) / exponentVal >= 1) {
RadixSorting.countingSort_by_digit(inputArray, radix, exponentVal, minVal);
exponentVal *= radix;
}
}
private static void countingSort_by_digit(
int[] inputArray, int radix, int exponentVal, int minVal) {
int bucket_index;
int[] bucket = new int[radix];
int[] output = new int[inputArray.length];
for (int i = 0; i < radix; i++) {
bucket[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < inputArray.length; i++) {
bucket_index = (int)(((inputArray[i] - minVal) / exponentVal) % radix);
bucket[bucket_index]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i < radix; i++) {
bucket[i] += bucket[i - 1];
}
for (int i = inputArray.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
bucket_index = (int)(((inputArray[i] - minVal) / exponentVal) % radix);
output[--bucket[bucket_index]] = inputArray[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < inputArray.length; i++) {
inputArray[i] = output[i];
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
RadixSorting rs = new RadixSorting();
int radix_input[] = {72, 15, 30, 21, 13, 944, 417};
System.out.println("Original Input Array:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(radix_input));
rs.sorting(radix_input);
System.out.println("Sorted Array using Radix Sort:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(radix_input));
}
}Output:
So here, we are using a different logic to get the input array sorted using Radix Sort.
Now, let me explain to you or show you how Radix sort is done with a live Example,
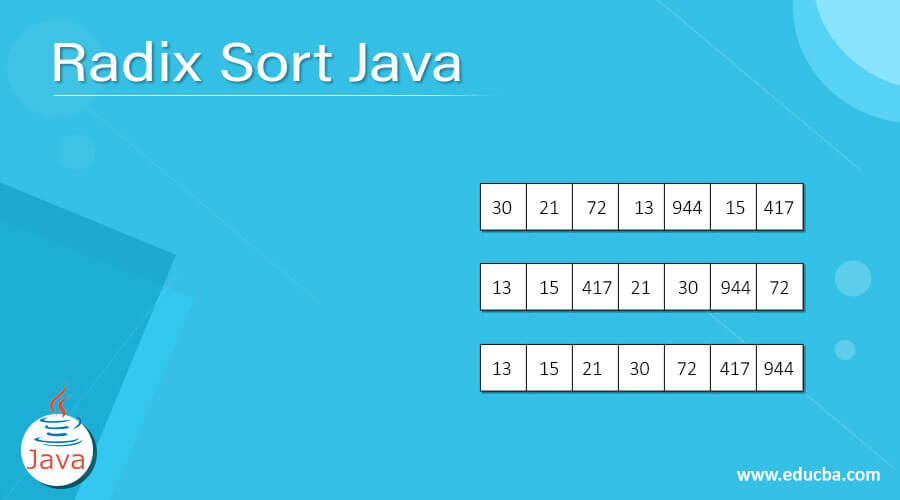
We shall take input array as [72, 15, 30, 21, 13, 944, 417]
Step 1: Get the maximum value out of the array, i.e., 944. So, now X value would be 3, i.e., X = no. of digits in Maximum element, which actually means that arrangement of the array would be done in thrice
Step 2: So, now we will try to arrange numbers on the basis of the least significant digit.
Considering the unit’s place value of all the elements will rearrange the array as below,
[30, 21, 72, 13, 944, 15, 417]Considering the tens place value of all the elements will rearrange array as below,
[13, 15, 417, 21, 30, 944, 72]Considering the Hundreds place value of all elements, if any, will rearrange array as below,
[13, 15, 21, 30, 72, 417, 944]Step 3: That’s it arrays have been sorted.
Conclusion
With this, we shall conclude the article ‘Radix sort in Java.’ We have seen what Radix sort is and how it is implemented using counting sort. It is one of the simplest forms of sorting and also is faster if the keys are short, i.e., the range of elements is less. For the past few years, sorting techniques have been extensively put into daily Algorithmic usage. However, there are also some disadvantages; Radix sort depends much on the input, i.e., letters or digits, and hence is less flexible than other sorts.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Radix Sort Java. Here we discuss the performance of Radix Sort in Java, along with an example of its code implementation and output. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


