Updated March 23, 2023
Difference Between RAID 0 vs RAID 1
RAID technology is nothing but a Redundant Array of Independent Disks storage units, which allows a balanced input/ output flow with higher performance rates. One of the primary differences between RAID 0 and RAID 1, where RAID 0 provides the basic storage facility in one target unit, and RAID 1 allows multiple storage locations. While RAID 0 enables very less or no data redundancy, RAID 1 functions as a data mirroring technique.
. Here we will discuss the top differences of RAID 0 vs RAID 1:
Head to Head Comparison Between RAID 0 vs RAID 1 (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between RAID 0 vs RAID 1:
Key Differences Between RAID 0 vs RAID 1
Let us look at the key differences between RAID 0 vs RAID 1 as below:
- RAID 0 simply means stripping of data, whereas RAID 1 is data mirroring; in RAID 0, data is stored in one place, whereas in RAID 1, it can be stored in stripes at multiple places.
- RAID 0 gives faster read and writes speed capabilities, whereas RAID 1 has less writing speed but better read capability.
- For RAID 0 minimum of 2 disks are needed (same for RAID 1) 2, but the factor that decides the speed in it is RAID controller, RAID controller processor, RAID controller Bandwidth and for RAID 1 the factors that decide speed are RAID controller, RAID controller processor, and RAID controller bandwidth.
- The visual representation of Raid 0 can be easily understood with the above-mentioned illustration. Here both the data sets have different segments associated with them, which means data is divided into stripes and placed in multiple places, whereas the visual representation of Raid 1 can be seen and understood in a very clear manner form the above-mentioned illustration. We can see similar data is placed at two places, out of which one is genuine data, whereas the other is its mirror image.
- Raid 0 has no redundancy capability because there is no parity and no mirroring facility, whereas Raid 1 has the highest redundancy possibilities; the reason for this behaviour is its mirroring behaviour.
- The rebuild criteria are worth mentioning – rebuild is to manipulate the entire system when the RAID system fails. The rebuild time and expense are comparatively less both in time and cost in Raid 0; factors affecting reliability in RAID 0 are System crashes, Bit errors, and Disk failures, whereas, for RAID 1, the rebuild time is more and higher due to mirroring. Factors affecting the reliability in RAID 1 are Uncorrectable bit errors, Hardware size and the Latest edition in comparison to RAID 0.
- RAID 0 is ideal for use at places like graphic design and video editing workstations, whereas RAID 1 is ideal for web servers or servers with small chassis where only 2 drivers can be used.
RAID 0 vs RAID 1 Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the topmost comparison between RAID 0 vs RAID 1:
| Basis of Comparison |
RAID 0 |
RAID 1 |
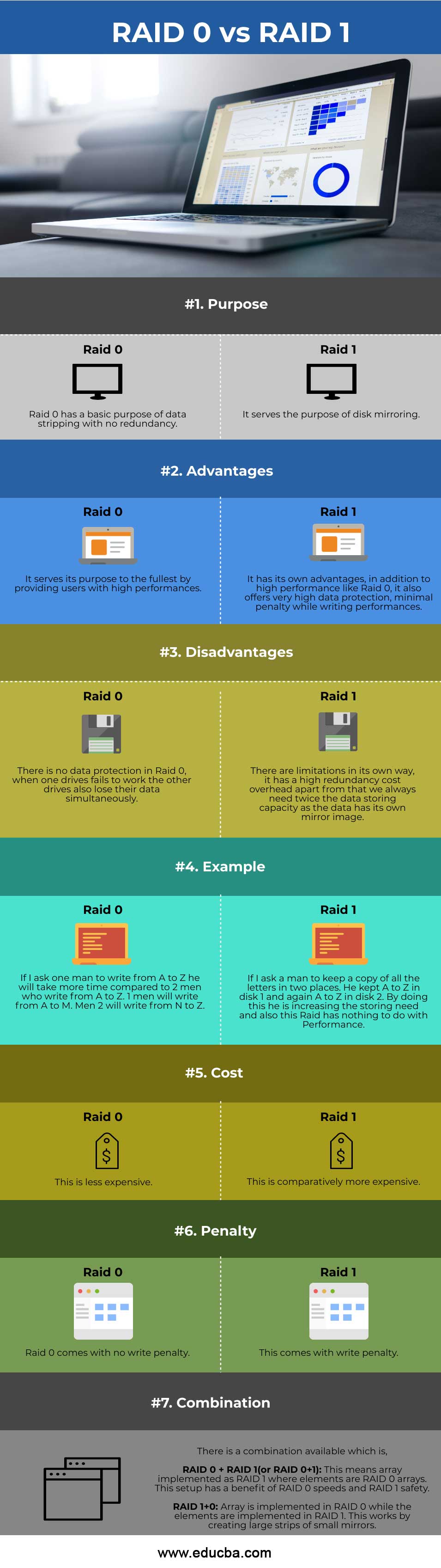
| Purpose | Raid 0 has a basic purpose of data striping with no redundancy. | Raid 1 serves the purpose of disk mirroring. |
| Advantages | Raid 0 serves its purpose to the fullest by providing users with high performances. | Raid 1 has its own advantages; in addition to high performance like Raid 0, it also offers very high data protection, minimal penalty while writing performances. |
| Disadvantages | There is no data protection in Raid 0; when one drive fails to work, the other drives also lose their data simultaneously. | Raid 1 has limitations in its own way; it has a high redundancy cost overhead; apart from that, we always need twice the data storing capacity as the data has its own mirror image. |
| Example | If I ask one man to write from A to Z, he will take more time compared to 2 men who write from A to Z. 1 men will write from A to M. Men 2 will write from N to Z. | Suppose I ask a man to keep a copy of all the letters in two places. He kept A to Z in disk 1 and Again A to Z in disk 2. By doing this, he is increasing the storing need, and also, this Raid has nothing to do with Performance. |
| Cost | This is less expensive. | This is comparatively more expensive. |
| Penalty | Raid 0 comes with no write penalty. | Raid 1 comes with a write penalty. |
Conclusion
You know there are specific reasons for choosing among any RAID levels, which depends on your need, and size of operations, better to consider these points.
- performance
- data protection
- rebuild and
- cost-effective
RAID technology is mostly used by web hosting companies apart from personal users.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to RAID 0 vs RAID 1. Here we discuss the RAID 0 vs RAID 1 introduction, key differences with infographics and comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –