Updated October 26, 2023
Raw Materials Definition
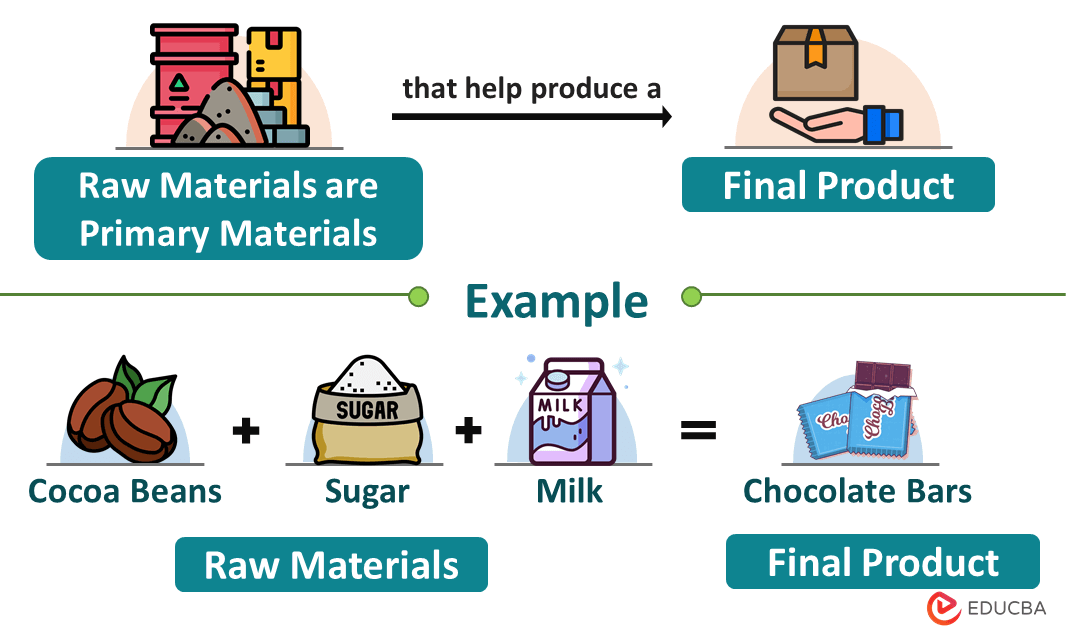
Raw materials are the primary materials or commodities that businesses use to produce goods or finished products. For instance, cocoa beans, sugar, and milk are the raw materials that we can use to make a chocolate bar.
These materials exist in their natural or unprocessed state and undergo conversion or transformation through manufacturing processes to become finished products. Moreover, manufacturers monitor, store, and source these materials to ensure a seamless production cycle. This helps in the proper management to control costs and maintain product quality.
Table of Contents
Types
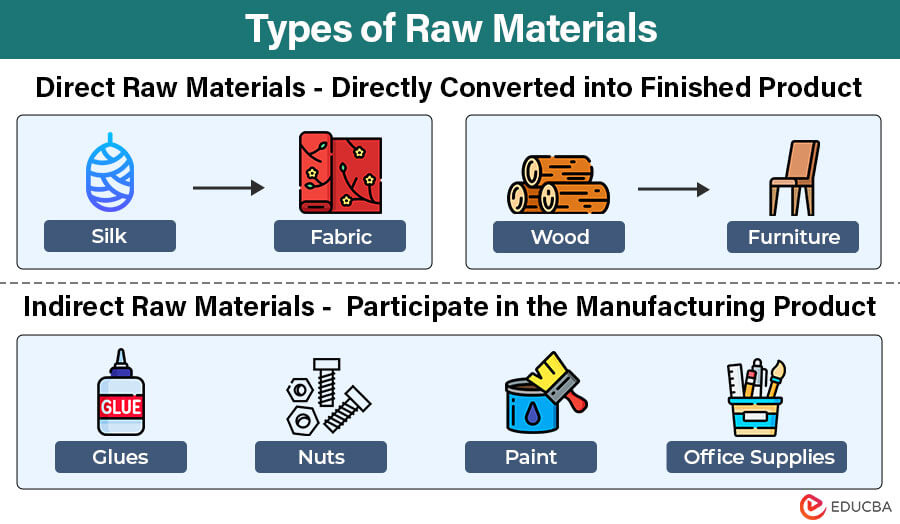
The two types of raw materials are direct and indirect.
- Direct: The primary materials that we can directly convert into finished products in the manufacturing process are called direct raw materials. For instance, leather is a direct raw material for shoes and bags, like silk is for fabrics.
- Indirect: These are materials that we cannot directly convert into final products but are still useful in manufacturing. Glue, varnish, safety equipment (like gloves and goggles), packaging materials (like cardboard), etc., are some examples of indirect materials.
Sources
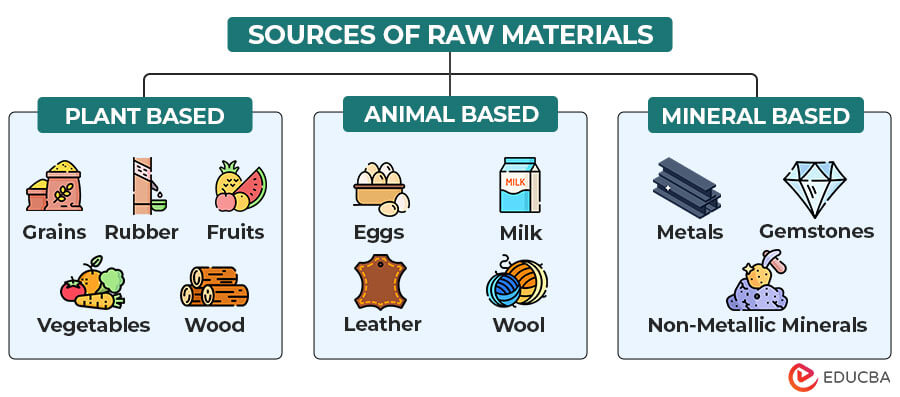
Apart from direct and indirect, we can also categorize raw materials based on their sources of origin.
1. Plant-Based
These are materials derived from various plants and crops, such as grains, oilseeds, fruits and vegetables, fiber crops, etc. It also includes natural rubber, timber, wood, and plant extracts like resins, gums, etc.
2. Animal-Based
This category includes materials sourced from animals like meat, eggs, milk, and dairy products. This also encompasses animal hides and skin (like leather), wool, and silk for textile and clothing.
3. Mineral-Based
These are materials obtained from the Earth’s mineral resources. This includes metals and ores (like iron ore, copper ore, gold, silver), gemstones (like diamonds and rubies), and non-metallic minerals (like limestone and sand).
Examples
Let us look at some hypothetical examples of raw materials.
Example #1
Suppose Mr. Jeffrey wants to start a small bicycle business for cyclists who seek racing and long-distance rides. The following are the raw materials that he can use for bicycle manufacturing.
Direct:
- Aluminum frames for the main structure.
- A lightweight and stiff carbon fiber fork to absorb road vibrations.
- Alloy wheels for speed.
- Rubber for designing high-pressure, low-resistance tires.
- Steel to make chains and gears.
- Leather for saddle (seat).
Indirect:
- Oil and grease as lubricants.
- Tools for bicycle assembly.
- Paint for visual appeal.
- Cardboard for packaging.
Example #2
Consider a business person who wants to open a poultry business. The following are some direct and indirect raw materials.
Direct:
- Chicken as the main source of egg production and meat supply.
- Feed like grains and pellets.
- Water for the chicken’s proper hydration.
- Nesting boxes to provide a place for laying eggs.
Indirect:
- Heating, lighting, and ventilation systems to maintain a comfortable bird environment.
- Vaccines and medications for chicken’s health and disease control.
Accounting
Accounting for materials is essential to running a business as it is crucial for budgeting and financial reporting. It also helps companies make informed decisions about pricing and production costs.
Here is how companies account for raw materials:
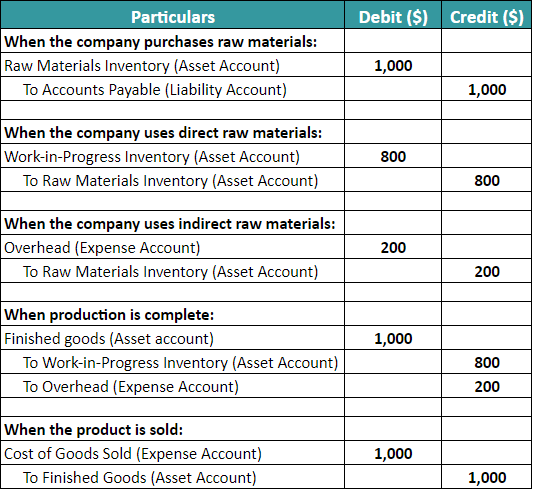
#1: When a company buys raw materials, it records the purchase in the inventory account.
- Debit the raw material inventory account.
- Credit the accounts payable account.
#2: When the company uses the direct material for manufacturing, they transfer it to the work-in-progress inventory account.
- Debit the work-in-progress account.
- Credit the raw material inventory account.
#3: When the company uses indirect raw materials, they record it in the overhead account.
- Debit the overhead account.
- Credit the raw material inventory account.
#4: Once the finished product is ready, firms move the work-in-progress inventory to the finished goods.
- Debit the finished goods inventory account.
- Credit the work-in-progress inventory and overhead account.
#5: After the manufactured products are sold, the total cost of producing and selling a product is reflected in the cost of goods sold (COGS) account.
- Debit the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) account.
- Credit the finished goods inventory account.
Importance
The importance of raw materials is as follows.
- Industries rely on these materials to manufacture goods like automobiles, buildings, and furniture.
- These materials’ extraction, processing, and distribution generate mining, agriculture, and manufacturing jobs.
- Businesses can reduce costs, minimize waste, and improve production efficiency by managing their raw material supply chain, increasing profitability.
- They are crucial in economic development, particularly in resource-rich countries. Their exports can generate revenue and support economic growth.
Final Thoughts
Raw materials are the fundamental building blocks in industries for manufacturing various goods and products. The sourcing, transportation, and pricing of these materials can significantly impact businesses, global trade, and environmental sustainability. As the world becomes more interconnected and resource-constrained, sustainable raw material management will become increasingly vital for businesses, governments, and society.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What industries are dependent on raw materials?
Answer: Many industries, including construction, manufacturing, agriculture, mining, and energy production, rely on materials.
Q2. What determines the cost of raw materials?
Answer: Supply and demand factors, market fluctuations, production costs, and global economic conditions frequently determine raw material prices.
Q3. What are some of the difficulties in obtaining and using raw materials?
Answer: Some challenges include environmental impacts, resource depletion, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions. Sustainable raw material sourcing and responsible use are increasingly important considerations for businesses and governments.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on the Raw Materials benefited you. For further guidance on accounting-related topics, EDUCBA recommends these articles: