Definition of Recourse Factoring
Recourse factoring is a kind of agreement which is entered between a client and a factor where any unpaid bills or invoices which are not converted as receivables by the factor agency are bought back by the client where the credit risk remains with the client instances of non-payment by the debtors i.e. client buys back unpaid bills receivable from the factor.
Explanation of Recourse Factoring
Firstly, we need to understand what factoring is where it means that factoring is a financial form of service where a business will typically sell all its accounts receivables to an external party or a third-party agent at a discounted rate to accumulate funds in one go and rather than waiting for payments from individual debtors. There are generally two types of factoring which are as recourse and non-recourse. Here we are going to talk more about recourse factoring. In recourse factoring whatever bills which are kind of unpaid receivables from the factor are bought back by the client or the business. In this case in case of non-payment by the debtors, the credit risk stays back with the client only. Thus, the risk of bad debt always stays with the business itself.
Recourse factoring is the most common type of invoice factoring. Here the company remains liable for any kind of bad debt which is happening in the course of conducting the business. This can be for any problem faced by the debtor like quality problem, financial problem or intentionally going for default. If an invoice is not getting paid the company either has to provide the factoring company with a new invoice to provide them the scope to debit the reserves or else simply pay them back as required.
Features of Recourse Factoring
The features of recourse factoring are as follows:
- The business is liable for any kind of bad debt which takes place.
- The factor does not take into consideration the risk of bad debt.
- It is one of the most common types of invoice factoring.
- Factors make cash advance to client within twenty-four hours of receiving the documents.
- All transaction which takes place are recorded in computers and stored.
- The collection of payments and follow up procedures are conducted by the factor in its own terms and agreement.
- Recourse factoring helps the client raise funds in one go rather than waiting for each debtor to come up with the payment.
- The factor benefits because the receivables given by the client are given on a discounted basis.
Examples of Recourse Factoring
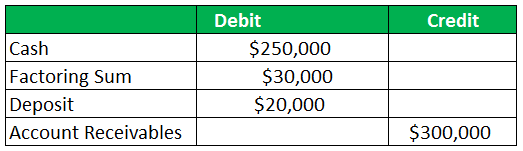
Let us assume a company XYZ Ltd or the client has a total account receivable valuation of $300,000. It enters into a factoring agreement with ABC Ltd with a fee structure of 10%. The factoring company also retained some security for any kind of bad debt which might arise in future. The total amount of cash that is received at one go by the client from the factoring company is $250,000. The excess security amount which is taken by the factor was decided to be returned by the factor at the end of the accounting period.
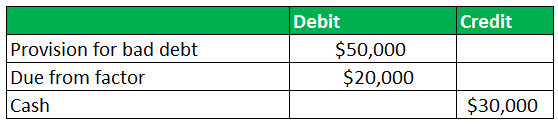
Now when the accounting was done at the end of the accounting period it was seen there was bad debt in excess to the security amount held by the factor. So, typically the factoring charges were $30,000 and security deposit considered was $20,000. The bad debit figure at the year end stood at $50,000 which is $20,000 excess to the security amount considered earlier.
Thus, now to explain recourse factoring lets pass the journal entries to be considered.
At the start of the accounting period:
At the end of the accounting period using recourse factoring:
The excess of this $30,000 bad debt will be borne by the client which is XYZ Ltd and not the factor.
Difference Between Recourse Factoring and Non-Recourse Factoring
In recourse factoring the client or the company is liable to buy back the unpaid bills which are receivables from the factor and the credit risk stays with the client in cases on non-payment by the debtors, whereas, in cases on non-recourse factoring the factor itself will bear the obligation of the unpaid bills which cannot be collected from the debtors and the credit risk stays with them. In non-recourse factoring the client or the business remains unaffected. In recourse factoring there is no need by the factor to get a credit insurance by the seller on the debt but in most cases on non-recourse factoring the factor requires the seller to get a credit insurance on the debt.
Advantages
The advantages of recourse factoring are as follows:
- Recourse factoring is more cost efficient and affordable as compared to non-recourse factoring.
- The approval process involved here is faster and this recourse factoring is more time efficient.
- It offers a greater number of c ash back from invoices.
- Factor here will perform credit check and payment history verification of invoice clients to minimize the risk of default or credit risk.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of recourse factoring are as follows:
- Factor company has the authority to demand payment form the client in case of invoices defaulting.
- The client’s bank account and business income get attached to the factor if the client is not able to pay the factor back in cases of default.
- Less effort is put on credit check of invoice client because the factor knows in case of default the business is going to bear the risk.
- The credit risk of the client or the business is more in case of recourse factoring than non-recourse method of factoring.
Conclusion
As discussed above we see recourse factoring has both its pros and cons which needs to be decided by the client on what basis they want to apply it for. Recourse factoring is a quicker process to collect the accounts receivables due to the business at one go but still, the credit risk of invoice going default still lies with the business.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Recourse Factoring. Here we also discuss the definition and features of recourse factoring along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –