What is Recurring Revenue?
Recurring revenue is when businesses earn steady and consistent income monthly or annually from customers who subscribe to a service and pay on a regular basis.
It gives businesses a sense of financial stability, allowing them to predict and manage their income more effectively. Overall, it is a dependable source of income that keeps the business running smoothly.
Table of Contents
- What is Recurring Revenue?
- Formula
- How to Calculate? Excel Examples
- Types of Models
- Importance
- How to Increase it?
- Recurring Vs. Non-Recurring Revenue
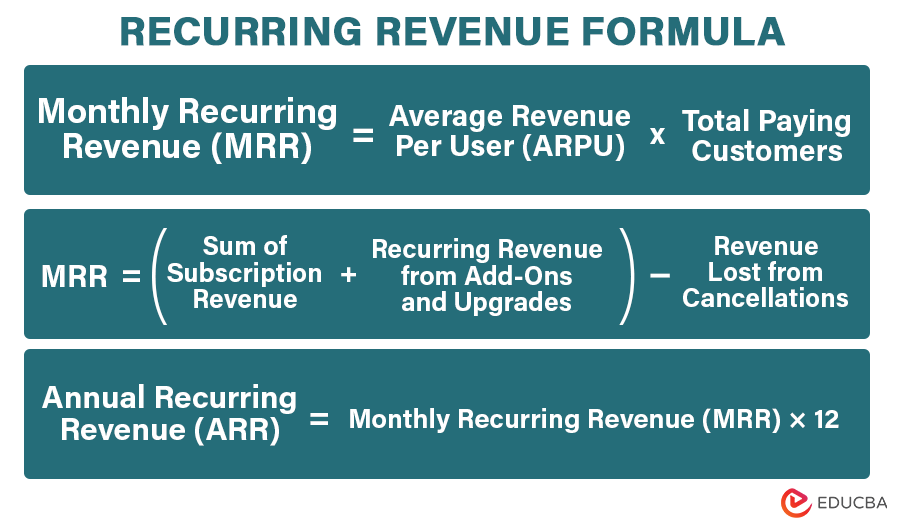
Formula
Two formulas to calculate recurring revenue are monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and annual recurring revenue (ARR).
- Sum of Subscription Revenue: Add up all subscription revenue for the chosen period (month, quarter, or year).
- Recurring Revenue from Add-Ons and Upgrades: Include revenue from additional services or upgrades.
- Subtract Lost Revenue: Deduct revenue lost from cancellations.
- Average Revenue Per User (ARPU): Determine the average income from each customer per month.
- Total Paying Customers: Count the number of customers actively paying during the month.
How to Calculate Recurring Revenue? – Excel Examples
We can easily calculate recurring revenue based on the formulas mentioned above. Following are a few examples to help you understand the calculation.
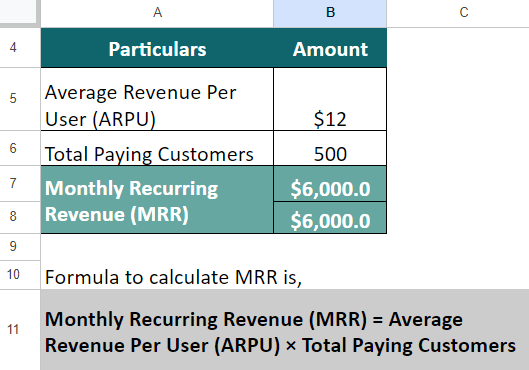
Example #1:
Imagine you are managing a subscription-based service similar to Netflix, and you want to calculate the Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR). You have an Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) of $12 and a current subscriber base of 500. Let us find the MRR and ARR for your subscription-based service.
Solution:
First, let’s calculate MRR,
MRR = ARPU × Total Paying Customers
= $12 x 500 = $6,000
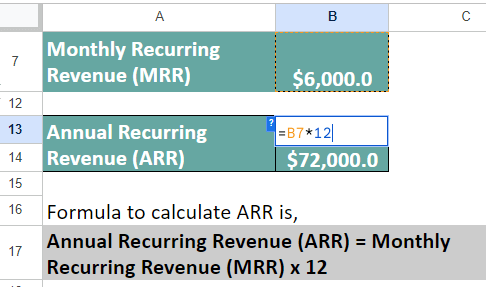
Now, let’s determine ARR,
ARR = MRR × 12
= $3,000 x 12 = $72,000.
Therefore, Your business’s MRR is $6,000, whereas the ARR is $72,000.
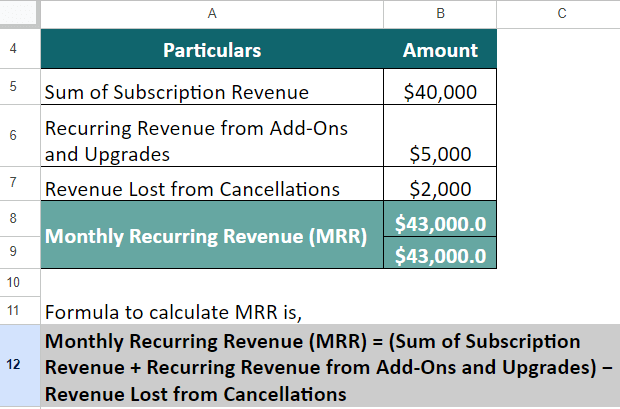
Example #2:
Suppose for your SaaS business,
- The sum of subscription revenue was $40,000,
- Revenue from add-ons and upgrades was $5,000,
- Revenue lost from cancellations was $2,000.
Let us calculate your business’s MRR and ARR.
Solution:
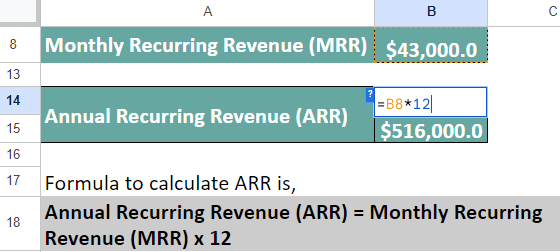
Let us first find your business’s MRR,
MRR = (Sum of Subscription Revenue + Recurring Revenue from Add-Ons and Upgrades) − Revenue Lost from Cancellations
= $40,000 + $5,000 – $2,000 = $43,000
Using calculated MRR, let’s find your service’s ARR,
ARR = MRR × 12
= $43,000 x 12 = $516,000.
Your MRR is $43,000 and your ARR is $516,000.
Types of Recurring Revenue Models
Recurring revenue models come in various shapes to suit different businesses. These models make it easy for businesses to choose a pricing strategy that fits their offerings and customer preferences. Let’s break them down in simple terms:
1. Subscription-Based Model: Customers pay regularly (monthly or yearly) for continuous access to a service.
2. Membership-Based Model: Customers pay to become members and enjoy exclusive benefits.
3. Tiered Billing Model: Customers pay for different tiers (levels) of service at different prices.
4. Usage-Based Model: Customers pay for the quantity of goods or services they actually use.
5. Freemium Model: Customers pay for advanced upgraded goods and services after trying the basic versions for free.
6. License-Based Model: Customers pay for a licensed and legal product or service and receive updates during the subscription.
7. Product as a Service (PaaS): Customers buy a physical product with added services on rent without paying for the product as a whole but as a bundled package.
8. Value-Based Model: Customers pay based on how much the service is worth to them. The more value, the higher the price.
9. Hybrid: Customers pay using a combination of different revenue models.
10. Hard Contracts: Customers pay a predetermined charge for a service over a specific period, securing future revenue.
11. Auto-Renewal: The service provider automatically deducts the charges from the customer’s payment account until the customer decides to cancel their subscription.
12. Sunk Money: Customers initially buy a product and then make recurring purchases for continuous product or service usage.
Importance
Recurring revenue is crucial for several reasons:
1. Predictability: It helps businesses predict how much money they will make regularly, allowing them to plan for the future more accurately. This is why it’s crucial to learn how to recognize revenue, as this Younium guide explains, especially when you’re dealing with custom or mixed pricing plans.
2. Financial Stability: Helps maintain financial stability by reducing the impact of one-time sales fluctuations with a steady income
3. Customer Relationships: Encourages long-term customer relationships, increasing loyalty and reducing customer attraction costs.
4. Business Valuation: Businesses with recurring revenue models often have higher valuations, making them more attractive to investors.
How to Increase Recurring Revenue?
Following are some simple yet impactful strategies to improve your recurring revenue.
- Smart Pricing: Regularly review and adjust your prices to match the value you provide. Small, strategic price increases can make a big difference.
- Offer Variety: Introduce new products or services to your existing offerings. This provides more options for customers, increasing engagement and revenue.
- Flexible Plans: Create different subscription plans with varied features and prices. This gives customers choices and the option to upgrade over time.
- Customer Care: Focus on keeping your existing customers happy. Great service and proactive communication can build long-lasting relationships.
- Upsell and Cross-sell: Encourage customers to upgrade their plans or purchase additional related products. This increases the average amount each customer spends.
- Value Updates: Regularly improve and enhance your products or services to show ongoing value. This keeps customers loyal and justifies their recurring payments.
Recurring Vs. Non-Recurring Revenue
Here are the differences between recurring and non-recurring revenue.
| Aspect | Recurring Revenue | Non-Recurring Revenue |
| Definition | This revenue keeps coming in over time, giving a steady income flow. | It is like a one-shot deal, coming from specific transactions or events. |
| Frequency | Companies regularly and repeatedly generate revenue, like a subscription fee that customers pay every month. | Companies generate revenue when a customer buys a product or from occasional services. |
| Source of Income | It often comes from ongoing customer relationships, creating long-term financial partnerships. | It usually includes specific, one-time activities or transactions like License Fee, Customization Fee, Installation Service, etc. |
| Examples | Netflix earns recurring revenue by offering subscription-based streaming services. Customers pay a monthly fee to access a library of content, ensuring a steady and predictable income for Netflix. | Microsoft receives one-time payments whenever someone purchases their Office suite. This is a non-recurring revenue source because Microsoft doesn’t receive ongoing payments for the same product. |
| Predictability | It is more predictable and stable, making it easier to plan for the future financially. | It is less predictable and can change a lot from one period to another. |
| Business Model | It is common in businesses with subscription models. | It is more common in businesses where sales happen on a per-transaction basis. |
| Financial Planning | It makes it easier to plan financially for the long term. | This requires adjusting financial plans more often due to changing income streams. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are examples of recurring revenue?
Answer: Recurring revenue is prevalent in various industries, providing businesses with consistent and predictable income streams. Here are examples across different sectors:
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): Companies like Adobe offer software subscriptions, and users pay regularly for access.
- Subscription-based Services: Platforms like Netflix charge users every month for streaming movies and shows.
- Membership Programs: Stores like Costco have membership programs where customers pay an annual fee for exclusive discounts.
- Loyalty Programs: Loyalty programs in industries like airlines reward customers with points or discounts for frequent purchases.
- Telecommunications Services: Companies providing internet or mobile services collect monthly fees for ongoing access.
- Insurance Premiums: Insurance companies receive regular premiums for coverage over specific periods.
- Real Estate Rentals: Property owners get monthly rent payments from tenants for residential or commercial spaces.
- Gym Memberships: Gyms earn consistent revenue through membership fees for facility access and services.
- Automated Billings: Essential services like utilities use automated billing, ensuring a steady flow of regular payments.
Q2. What is a good recurring revenue rate?
Answer: A solid recurring revenue rate is typically deemed good when it surpasses 15%. The greater the rate, the more secure a business’s future appears. The specific amount of steady revenue needed for a company to become profitable varies based on factors like overhead costs and customer acquisition expenses. This metric helps companies in tracking their capacity to maintain a steady flow of sales over a long period.
Q3. What are the benefits and challenges of recurring revenue?
Benefits:
- Steady Cash Flow: It ensures businesses have a steady cash flow, making it easier to cover bills.
- Business Scalability: Businesses can plan future expansions because consistent revenue provides a strong foundation, allowing for strategic planning and growth initiatives.
Challenges:
- Market Saturation: In highly competitive markets, attracting and retaining customers for recurring services can be challenging. Businesses need to be unique to attract and keep customers.
- Service Quality: Maintaining the quality of the offered service is critical to preventing customer dissatisfaction and cancellations. Businesses need to provide top-notch service by keeping promises and making sure customers are happy.
- Customer Churn: Sudden customer exit can disturb revenue flow. It means companies need effective retention strategies.
Recommended Articles
If you found this article on Recurring revenue helpful, please check out similar articles recommended below.