Updated July 6, 2023
What is Reflation?
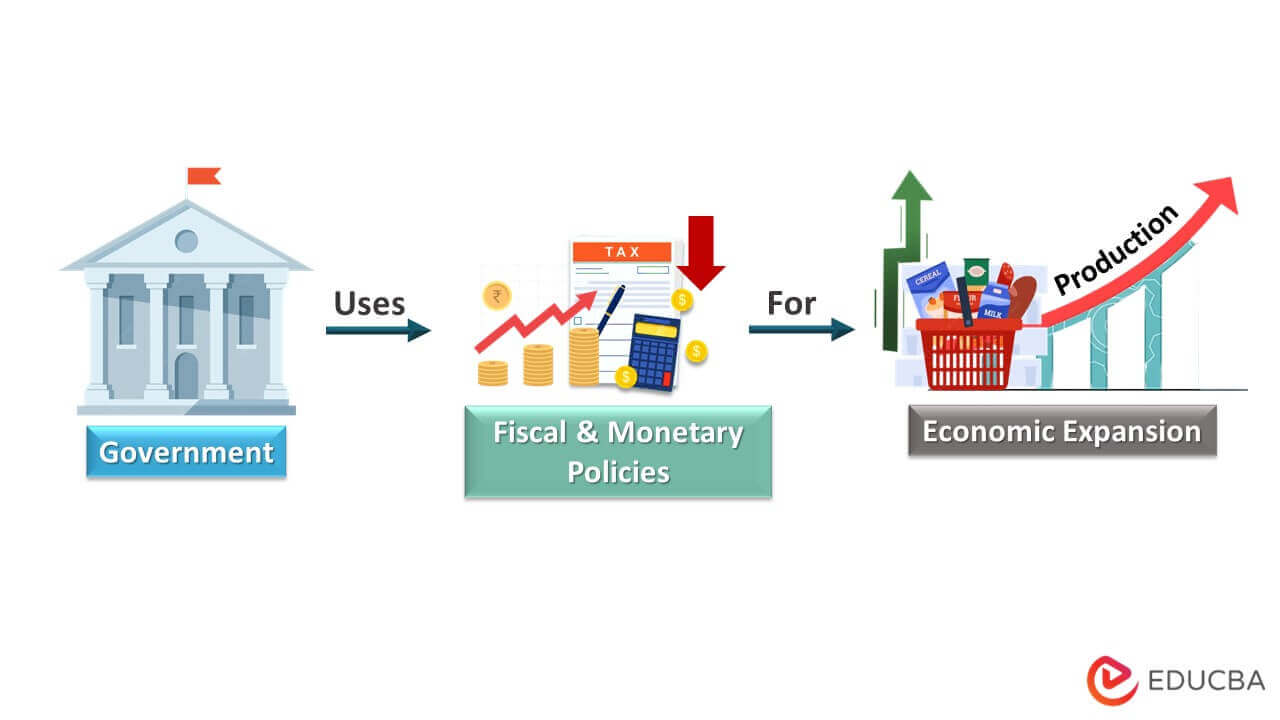
Reflation is a form of economic development where governments aim to increase product prices after a recession by employing fiscal and monetary policies. For example, due to the coronavirus in the USA, almost every business was shut down, and people were forced to be quarantined. It led to no employment and decreased demand for goods/services.
Businesses suffered losses and had to fire employees, skyrocketing unemployment in the country. Thus, to overcome this crisis, the government implemented a monetary and fiscal policy to improve the economy.
The main objective of reflation is to overcome the situation of declined economic growth with the help of factors such as market price, employment, etc. Thus, the economy experiences reflation, and demand increases due to economic stimulus, pushing prices higher.
Key highlights
- Reflation occurs when prices rise, and the economy is not experiencing full employment. On the other hand, inflation happens when prices increase following the economy’s actual work.
- Typical strategies include tax cuts, interest rate decreases, and direct stimulus payments.
- The objective is to boost economic participation and fight recession-related unemployment.
- These reflationary measures usually result in increased economic activity, job growth, positive economic growth, economic boom, and price inflation.
How Does Reflation Work?
Reflation is seen during a recession when governments and central banks offer stimulus to boost economic growth. A central bank like the Federal Reserve can implement monetary stimulus to increase economic activity.
For instance, the Federal Reserve could cut interest rates and buy bonds to increase the money supply. Additionally, it can roll out initiatives like direct lending to small and medium-sized non-financial firms.
As a result of these monetary policy initiatives, the money that banks lend to businesses would rise. The economy would move closer to full employment due to increasing demand and more people being employed. By giving money to small firms or making direct payments to consumers, the government can also use fiscal stimulus to boost economic activity. This will increase the amount of money accessible in the economy.
Examples
Example #1
The American economy remained fragile after the Great Recession. Despite employing several reflationary monetary policy tools, such as lower interest rates and an increase in the money supply, the Federal Reserve (FED) found it difficult to trigger inflation. The passage of the Troubled Asset Recovery Plan (TARP), the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA), and the Trump Tax Cut in 2009 helped to end the Great Recession.
Example #2
To boost the economy and help the financial sector, the federal government purchased bonds from 2020 to 2021. Also, it relaxed bank regulatory standards and directly lent money to state governments and non-financial firms. Additionally, Congress has extended unemployment advantages, directed payments to individuals, and provided loans to local governments. All these actions contributed to reflation while pushing the economy back to full employment.
Reflation vs Inflation
|
Reflation |
Inflation |
|
Meaning |
|
| Reflation is a tactic to boost output and encourage spending. | Inflation is the rise in prices brought on by the economy’s mismatch between supply and demand. |
|
Nature |
|
| It is a controlled procedure. | It is a typical economic process. |
|
Occurrence |
|
| It is usually practiced when the economy is experiencing a recession or depression. | It happens when the economy experiences an increase in demand or a decrease in supply. |
|
Speed |
|
| The process is gradual. | Due to speculation, inflation happens quickly. |
Advantages & Disadvantages
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Lower interest rates are a major effect of inflation, impacting infrastructure and other economic activity. | It can be overdone and could lead to uneven distribution of money in various parts of a country. |
| To match the rising consumer demand and output, inflation causes an increase in the production and manufacturing index. | Budget imbalance results from inflation, forcing the government to borrow money from other nations. |
| It broadens the available quantity of money in the economy and boosts output. Also, more job opportunities are created. | If It is not handled correctly, it can occasionally result in an excessive amount of money in circulation and even hyperinflation. |
| It aids in the stabilization of economies after they have experienced a sharp deflation. | It can make way for Overlanding and heavy debt due to the banks in the economy. This leads to NPA in the banking sector. |
Final Thoughts
Reflation combines fiscal and monetary policy actions to combat decline or lower economic production. The government tries to bring the economy back to normal levels when it is in deflation or degrowth.
Even though almost every government makes an effort to prevent an economy from collapsing after a recent surge, it has yet to be capable of avoiding the business cycle’s contraction phase. Many experts contend that government agitation postpones and worsens the crisis’ impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What does reflation mean in economics?
Answer: Reflation is considered to stimulate the economy by cutting taxes or increasing the money supply rate. The government or federal bank can create a monetary or fiscal policy to restrain deflation’s effect and maintain the output.
Q2. What are the types of reflation?
Answer: Typically, there are four types of reflation policies. This includes increasing the money supply, cutting off the tax rate, a sharp decrease in the interest rates, and making a significant investment in large capital projects.
Q3. What is the difference between inflation and reflation?
Answer: In general, reflation means implementing monetary or fiscal policies to increase an economy’s overall output. In contrast, inflation is considered as the increase in the overall price level following the former one.
Q4. What is the opposite of reflation?
Answer: Disinflation is the opposite of reflation. Disinflation is used to describe situations when the rate of inflation has dropped marginally over a short tenure. However, significant disinflation is important as it prevents the economy’s overheating.
Recommended Articles
This was a complete guide on the topic of reflation. It covers its definition, advantages & disadvantages, examples, and much more. You can learn about similar topics from the following articles.