Updated March 29, 2023
Introduction to Reflection in JAVA
Reflection, as the name suggests, is an API(Application programming interface) functionality in JAVA via which the runtime instance of the class can be fully examined. It is a part of the Java.lang.reflect package. This package has to be imported at the start of the program, and then functions are invoked to understand the functionality of “reflection.” Any class’s behavior can be studied; metadata can be extracted or modified using reflection API in runtime.
Syntax
The syntax of common functions under reflection API to extract the class information is provided below:
- public String getName( parameter ): This function returns the class name.
- public boolean isInterface( parameter ): This function checks if the class is an interface or not and returns a boolean (true or false) value.
- public boolean isArray( parameter ): This function checks if the variable is an array or not and returns a boolean (true or false) value.
- public Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors( parameter ) throws SecurityException: This function checks the constructors in the class and returns the number of constructors used in a particular class. In addition, it has a security exception and catches associated with making the program work break-free.
- public Method[] getDeclaredMethods( parameter ) throws SecurityException: This function checks the methods in the class and returns the number of methods used in a particular class. In addition, it has a security exception and catches associated to make the program work break-free.
- public Class getSuperclass( parameter ): This function returns the superclass of the base class.
- public boolean is primitive( parameter ): This function checks if the given parameter is primitive or not and returns a boolean value.
How does Reflection work in JAVA?
The reflection class uses different methods defined in the Java.lang.reflect package to extract the class information. The information about class can be extracted using getClass() method, Constructors using getConstructors() method and methods using getMethods() method. These methods are defined in reflection API but return the class’s information, including methods, constructors, and more. Reflection API is used in JAVA programs, IDEs (Integrated development environment) like the eclipse, Netbeans. This can be well understood with the help of examples provided in the below section.
Examples of Reflection in JAVA
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
Code:
//package test;
import java.lang.Class;
public class test{
public static void main(String args[]){
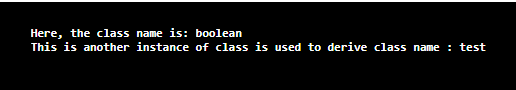
Class<Boolean> c1 = boolean.class;
System.out.println("Here, the class name is: "+c1.getName());
Class<test> c2 = test.class;
System.out.println("This is another instance of class is used to derive class name : "+c2.getName());
}
}Output:
Explanation: Please check the example provided above. This has a package that contains all the classes named “test.” The test package has a class “test declared.” This class also contains the main method from which the execution of the program will start. The class “Class <Boolean> is the identifier reflection class in jAVA. This class is enabled with the help of the library declared above “java.lang.Class”. Boolean itself is a class in JAVA. Boolean is a primitive data type like string, int, or char. This example shows that we can extract the information of primitive data types (which ultimately is the class in JAVA, and that is the reason JAVA is called a pure object-oriented language”. “ getName() “ function is used to get the name of a class which is instantiated here by an object named “C1”.
In the next line, rather than using a primitive data type, a user-defined data type “class” named “test” is taken into consideration to extract the data. “Class<test>” is a reflection class that is instantiated with an object named “C2”. Here the class name is tested, and the object is used to pull out the name of this class using the function “getName().” The final output contains the returned value of these functions and is displayed on the output screen.
Example #2
Code:
//package test;
import java.lang.Class;
class Simple{}
public class test{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
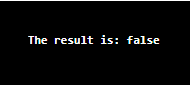
Class<?> c=Class.forName("Simple");
System.out.println("The result is: "+c.isInterface());
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}Output:
Explanation: In the above example, a package is created named” test,” as created in the previous example number 1. This package contains a class name “Simple,” which is not the main class. The main class here is the “test” class which contains the main method from which the execution of the program will start. The “class <?>” is an identifier of reflection class which was instantiated via an object named “c” here. Then this object is used to pull out the decision indicator (True or false) of the function named “isInaterface.” This function pulls in a class as a parameter; in this case, the class which was pulled in as a parameter was the “Simple” class. This class is not an interface, so the “false” is returned as a result in the output screen. To invoke this function, the class object “c” was used.
Advantages
Some of the advantages of using reflection in JAVA are listed below:
- This is one of the best ways to extract information for any class. This information can consist of information from constructors to class and methods.
- One of the biggest advantages of this functionality is that we can also extract information about private methods and classes. So anything, if hidden in the program with bad intention, can be extracted out using this functionality.
- This functionality provides a lot of flexibility to debuggers as they can debug classes easily rather than going to every class separately.
- This also adds as an extensibility feature where one can add external customized classes by using instances.
- This provides a manifestation of the real power of OOP language with the help of instances.
- This is used in the dynamic loading and reloading of classes during a program run.
Conclusion
JAVA reflection makes it possible to introspect the classes, interfaces, methods, and more without knowing the class name at all. This all is done during compile time. This is considered as one of the most powerful properties of JAVA as this can be used to create instances of the class, and private members of the class can be extracted out using this. Developers can use this during runtime and for database-object mapping too.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Reflection in JAVA. Here we discuss How Reflection in JAVA work and Examples along with the codes and outputs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –