Updated July 3, 2023

What are Reserve Requirements?
When people deposit money into a bank, it keeps aside a specific percentage for emergencies, known as the Reserve Requirement. The reserve requirement is also called the cash reserve ratio.
Banks use reserve requirements to prepare for unexpected situations where many people withdraw money from their accounts. The country’s central bank, the Federal Reserve Bank, sets rules for how much money banks have to keep as reserves. Banks can keep their reserved money at their local Central Bank or as physical cash in their vault.
How Does it Work?
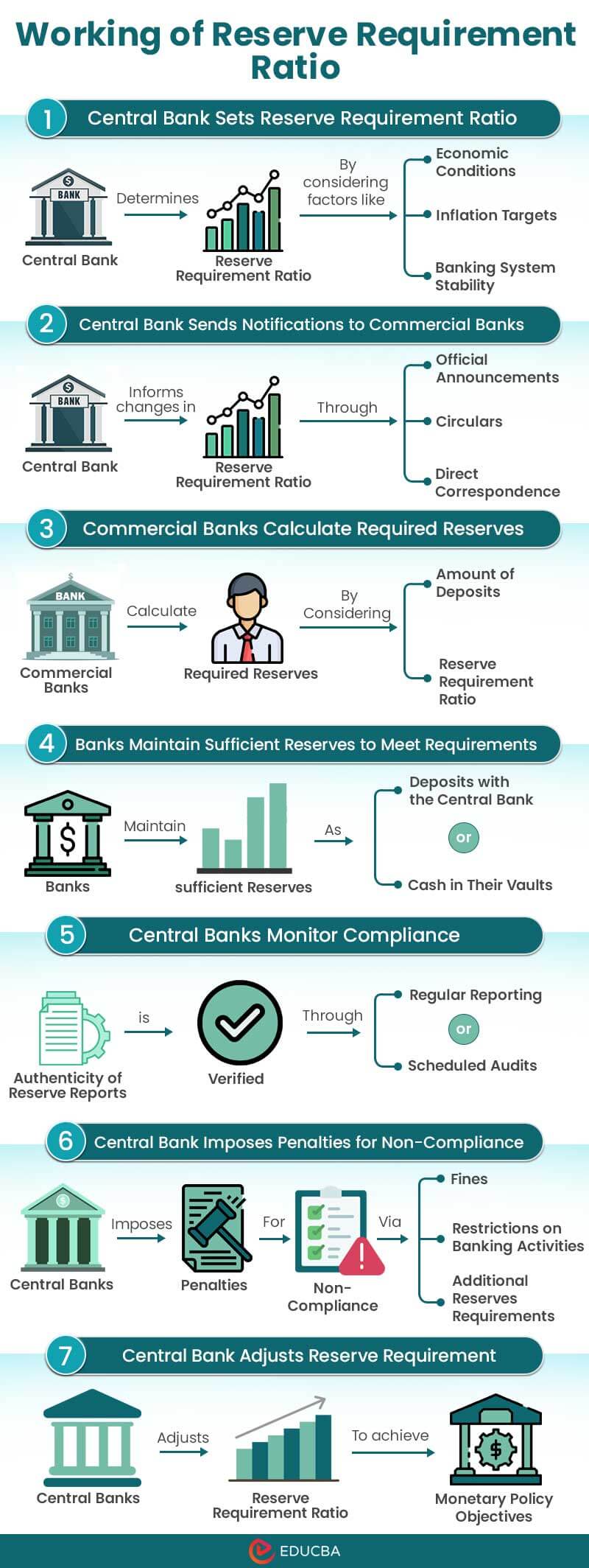
Banks must follow the reserve requirement rules to manage their money well, control how much they can lend, and keep the bank and economy stable. The process is explained in the infographic below along with its explanation:
1. Central Bank Sets Reserve Requirement Ratio
During this process, the central bank determines the reserve requirement ratio by considering factors like economic conditions, inflation targets, and banking system stability.
2. Central Bank Sends Notifications to Commercial Banks
The central bank informs commercial banks about changes in the cash reserve ratio through official announcements, circulars, or direct correspondence.
3. Commercial Banks Calculate Required Reserves
Commercial banks consider the number of deposits (usually demand deposits) and the reserve requirement ratio to calculate the required reserves.
4. Banks Maintain Sufficient Reserves to Meet Requirements
Banks must maintain sufficient reserves as deposits with the central bank or as cash in their vaults to meet the central bank’s requirements.
5. Central Banks Monitor Compliance
Central banks regularly check the reserve reports of commercial banks through reporting and audits to ensure they are accurate and reliable.
6. Central Bank Imposes Penalties for Non-Compliance
Suppose a commercial bank fails to comply with the specified rules. In that case, the central bank can impose penalties like fines and restrictions on banking activities or even require additional reserves in the future.
7. Central Bank Adjusts Reserve Requirement
The central bank regularly adjusts the reserve requirement ratio to achieve monetary policy objectives.
Reserve Requirements Formula
You can use the formula to calculate reserve requirements, which can also be applied to determine parameters such as Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), Bank Rate, Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), Repo, and Reverse Repo Rates.
Examples of Reserve Requirement
Example #1
ABC receives $300 as a demand deposit and $50 as a time deposit, and its reserve requirement ratio is 8%. Compute the total reserve requirements for ABC Bank.
Solution:
To determine the reserve requirements of ABC Bank, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Calculate the required reserves for demand deposits using the formula.
Reserve Requirements = Amount of Demand Deposits * Reserve Requirement Percentage
= $300 * 0.08
= $24
Step 2: Calculate the reserve requirement for time deposits.
Step 3: Calculate the total reserve requirements of ABC Bank
Reserve requirements for demand deposits + Reserve requirements for time deposits
= $24 + $0
= $24
Example #2
A central bank sets a reserve requirement ratio of 4.5% for all depository institutions in the country. If Gringgots Wizarding Bank has $10 million in demand deposits and Bank of Evil has $5 million in demand deposits, calculate the total reserve requirements for both banks.
Solution:
The following table presents calculations and results for both Gringgots Wizarding Bank and Bank of Evil:
| Bank Name | Demand Deposits ($) | Reserve Requirement Ratio | Formula (Amount of Deposits * Reserve Requirement Percentage) |
Total Reserve Requirement ($) |
| Gringgots Wizarding Bank | 10 million | 0.045 (4.5%) | 1,00,00,000 * 0.045 | 15,00,000 |
| Bank of Evil | 5 million | 0.045 (4.5%) | 50,00,000 * 0.045 | 7,50,000 |
Example #3
The Iron Bank of Bravos has $8 million in demand deposits and is required to maintain 10% as reserves. If the bank currently holds $1.2 million in reserves, determine whether the bank is following the rules for reserve requirements.
Solution:
We have the following information:
- Demand Deposits: $8,000,000
- Reserve Requirement Ratio: 10%
- Bank’s Reserves: $1,200,000
To determine whether the bank is compliant with the reserve requirement, follow these calculations:
Step 1: Calculate the Required Reserves
Use the below formula to calculate the required reserves for demand deposits.
Reserve Requirements = Amount of Deposits * Reserve Requirement Percentage
= $8,000,000 * 0.1
= $800,000
Step 2: Compare the Bank’s Reserves with the Required Reserves
The bank’s reserves are $1,200,000.
Since the bank’s reserves ($1,200,000) are greater than the required reserves ($800,000), the bank is compliant with the reserve requirement.
Case Study
Global Financial Crisis (2008)
Background:
Central banks took action to stabilize the financial system during the 2008 financial crisis caused by the collapse of Lehman Brothers. This crisis led to a severe shortage of money and a loss of trust in banks. The U.S. Federal Reserve, along with other central banks globally, implemented measures to address the liquidity and confidence crisis in the banking sector.
Reasons for Banking Sector Collapse:
- There was a scarcity of money available in the banks, causing a shortage of funds.
- The risk of banks failing became higher because they had risky assets.
- Businesses and individuals struggled to get loans and credit because of a shortage of available money.
How did Central Banks Manage this Issue?
| Measures | Description |
| Lowered reserve requirements | Central Banks had to reduce the reserve requirement rate to ensure that banks could increase lending activities. The aim was to support the economy by introducing more currency in the market. |
| Emergency liquidity assistance | Central banks needed to prevent the banking system’s failures and lack of stability. This was possible only through the emergency funds to banks as a last resort. |
| Monetary Stimulus | Central banks increased the cash flow and long-term interest rate system by pushing more money into the financial system. This made the borrowing process easier. |
Purpose of Reserve Requirement
Reserve Requirement affects the financial stability of an economy. Banks need to maintain a certain percentage for reserves as it helps to:
- Deal with upcoming future contingencies
- Meet the reserve responsibilities through cash, deposits with the central bank, and other liquid assets.
- Safeguard banks from unusual disturbances in the market.
- Manage lending levels, deposits, credits, and rates.
- Cancel unexpected liabilities and maintain financial stability.
- Manage the country’s monetary policy and better make decisions about the economy.
- Ensure a stable banking system.
- Control funds held by banks and manage liquidity.
- Control how much money is circulating, influence interest rates, and manage inflation.
- Provide protection during bank runs or withdrawals.
- Maintain regulatory compliance.
- Influence the money supply.
- Regulate inflationary pressures.
- Promote stability and responsible financial practices.
Reserve Requirements vs. Capital Requirements
| Aspects | Reserve Requirements | Capital Requirements |
| Definition | Regulations on maintaining reserve funds to tackle liabilities from sudden withdrawals. | Rules on minimum capital holdings to absorb losses from loans and credit provided. |
| Purpose | Ensure banks have sufficient reserves for market crunch caused by withdrawals. | Ensure banking institutions have sufficient capital to support loans and credit. |
| Influence on Interest Rates | Indirectly affects interest rates. | Indirectly influence interest rates. |
| Options | Reserve deposits or cash in vaults. | Capital in equity or retained earnings. |
| Impact on Money Flow | Indirectly regulates money circulation. | Directly influence money flow and lending. |
| Safeguarding Solvency | Protect against liquidity risk and sudden withdrawals. | Protect depositors and absorb losses. |
| Role in Monetary Policy | Control money supply and manage inflation. | Contribute to monetary policy transmission. |
| Financial Stability | Enhance stability and maintain liquidity. | Enhance stability and mitigate systemic risks. |
Advantages of Reserve Requirements
The advantages are discussed below-
- Equal impact on all banking institutions and a strong effect on the money supply.
- Ensures generous liquidity in the economy.
- Maximizes lending opportunities and generates higher profits for banks.
- Helps banking institutions avoid future contingencies and shortages of funds.
- Increases depositor awareness of the bank’s financial performance and margins.
- Facilitates money circulation and manages overall liquidity.
- Enhances purchasing power by encouraging investment in government securities.
Disadvantages of Reserve Requirements
The disadvantages are as below-
- Slight changes in the cash-reserve ratio lead to major changes in the money supply.
- Liquidity issues for banks with low excess reserves.
- Reserves create limits on other investment or lending opportunities for banks.
- Limits banks’ ability to respond to changing economic conditions.
- Hides credit creation, particularly during economic expansion.
- Impact on profitability, especially for smaller banks.
- Disturbs interbank lending, concentrating reserves in a few large banks.
- Compliance costs and administrative burden for banks.
Conclusion
A reserve requirement is a tool used by most banking institutions for maintaining a percentage of the deposits from depositors as reserves to combat the contingencies ahead in the future due to a sudden rise in withdrawals. It is also known as the cash reserve ratio. Reserve and capital requirements are different from each other. Moreover, the Reserve help in reducing liquidity and slowing economic activity. The higher the reserve requirement level, the lesser the profits earned by banking institutions with their money. The limitations of a reserve no longer make it a substantial aspect of the bank’s regulation.
Reserve Requirement Calculator
Use the following calculator to calculate Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, etc:
| Amount of Deposits | |
| Reserve Requirement Ratio | |
| Total Reserve Requirement = | |
| Total Reserve Requirement = | (Amount of Deposits * Reserve Requirement Ratio) |
| = | (0 * 0 ) = 0 |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the CRR of India in 2023?
Answer: The Reserve Requirement Ratio changes regularly, as the Reserve Bank may think necessary. In India, the CRR has been 4.5% since May 2022. There have been no changes since then.
Q2. What is the journal entry of CRR?
Answer: Here are the journal entries for the cash reserve ratio (CRR):
- When banks are required to maintain the CRR:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
| Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) Liability | X (Amount) | |
| Bank’s Current Account with Central Bank | X (Amount) | |
| Total X | Total X |
- When banks utilize their cash reserves to meet the CRR requirement:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
| Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) Liability | X (Amount) | |
| Cash/Bank Account | X (Amount) | |
| Total X | Total X |
Recommended Articles
This guide overviews Reserve Requirements, including the process, importance, examples, and advantages and disadvantages. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –