Updated July 25, 2023
Definition of Return on Capital Employed
The term “return on capital employed” or ROCE refers to the financial metric that helps in assessing the ability of a company to generate profit by leveraging its capital structure.
In other words, ROCE is the measure of how well and efficiently a company is able to produce dollars in net operating profit by using each dollar of the capital.
Inherently, ROCE is hailed to be one of the better indicators of a company’s return as it compares the profitability relative to both equity and debt. Further, it is used to compare companies of similar scale and operating within the same industry. Also, please note that companies with large cash reserves happen to include that cash as part of the capital employed in the calculation of ROCE, which is not the usual practice.
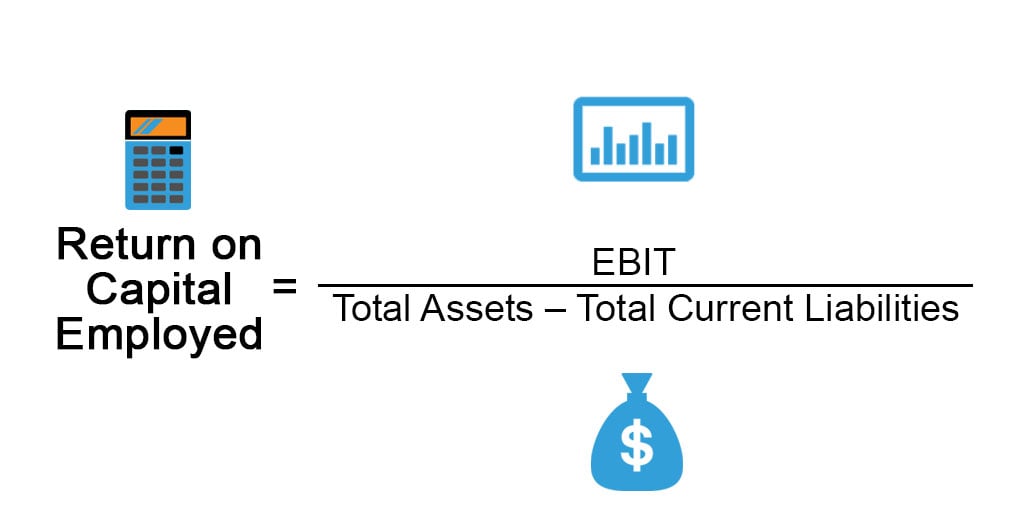
Formula
The formula for ROCE can be derived by diving earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) or net operating profit by the difference between total assets and total current liabilities, and then it is expressed in terms of percentage. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Another formula for ROCE can be derived by dividing net operating profit by aggregate long-term liabilities and shareholder’s equity. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Examples of Return on Capital Employed (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Return on Capital Employed in a better manner.
Example #1
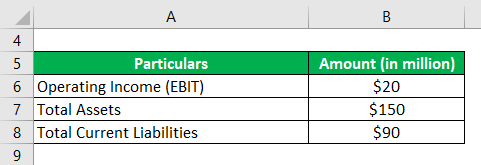
Let us take the example of a company named DFG Inc. to illustrate the computation of ROCE. According to the latest annual report, i.e. for the year 2018, the company made net operating profit is $20 million, while it reported total assets and the total current liabilities of $150 million and $90 million respectively as on balance sheet date. Calculate the ROCE of the company for the year based on the given information.
Solution:
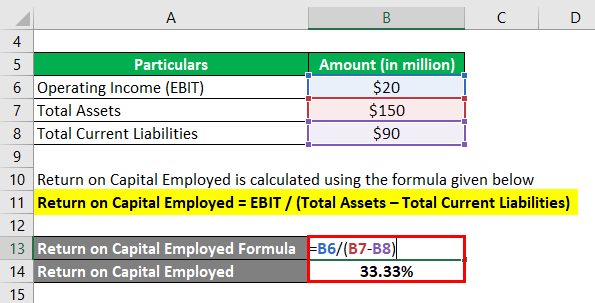
Return on Capital Employed is calculated using the formula given below
Return on Capital Employed = EBIT / (Total Assets – Total Current Liabilities)
- ROCE = $20 million / ($150 million – $90 million)
- ROCE = 33.33%
Therefore, DFG Inc.’s ROCE stood at 33.33% for the year 2018.
Example #2
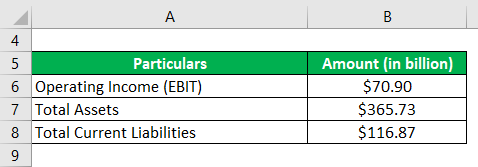
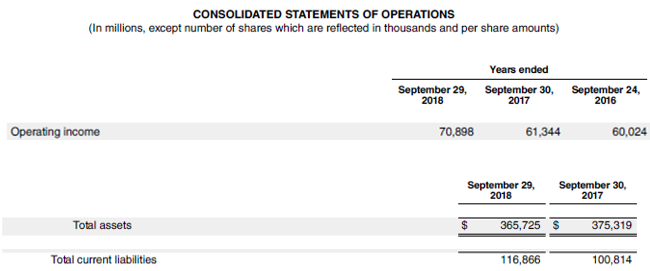
Let us take the example of Apple Inc. to further demonstrate the concept of ROCE in the case of real-life companies. As per the annual report, the company’s operating income stood at $70.90 billion during 2018, while it reported total assets and total current liabilities of $365.73 billion and $116.87 billion, respectively, as of September 29, 2018. Calculate the ROCE of Apple Inc. for the year 2018 based on the given information.
Solution:
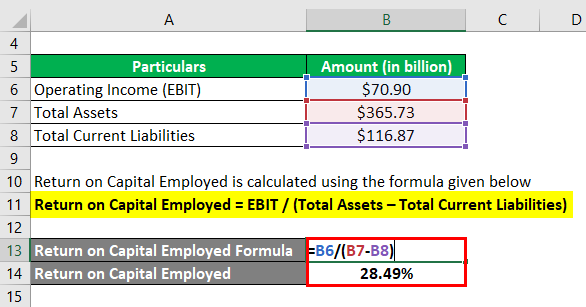
Return on Capital Employed is calculated using the formula given below
Return on Capital Employed = EBIT / (Total Assets – Total Current Liabilities)
- ROCE = $70.90 billion / ($365.73 billion – $116.87 billion)
- ROCE = 28.49%
Therefore, Apple Inc. managed a ROCE of 28.49% during the year 2018.
Source Link: Apple Inc. Balance Sheet
Example #3
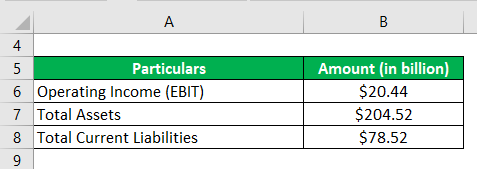
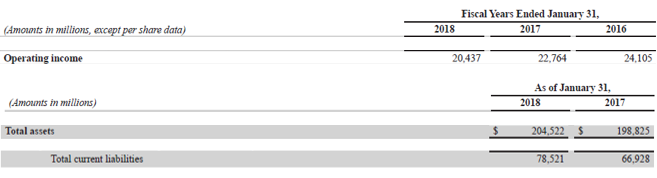
Let us now take the example of Walmart Inc. to illustrate the computation of ROCE. As per the annual report, the company booked operating income of $20.44 billion, while it reported total assets and total current liabilities of $204.52 billion and $78.52 billion, respectively as of January 31, 2018; calculate the ROCE of Walmart Inc. for the year 2018 based on the given information.
Solution:
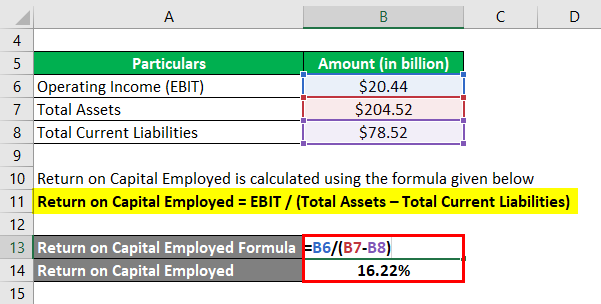
Return on Capital Employed is calculated using the formula given below
Return on Capital Employed = EBIT / (Total Assets – Total Current Liabilities)
- ROCE = $20.44 billion / ($204.52 billion – $78.52 billion)
- ROCE = 16.22%
Therefore, Walmart Inc.’s ROCE for the year 2018 stood at 16.22%.
Source: Walmart Annual Reports (Investor Relations)
Advantages of Return on Capital Employed
Some of the major advantages of ROCE are:
- It is one of the very few financial ratios that capture the monetary return on equity and debt. As such, it is used by most investors as one of the criteria for their investment portfolio and strategy.
- It helps in the comparison of companies with different capital structures, and as such, it is a very good tool for peer comparison.
Limitations of Return on Capital Employed
Some of the major limitations of ROCE are:
- The ROCE is exposed to risk accounting manipulation that can result in elevated returns. Classification of long term liabilities as current liabilities is an example of such accounting manipulation.
- The ratio is calculated based on book value, and so the return is not reflective of the market value.
Conclusion
So, it can be seen that ROCE is one of the financial metrics that investors use to assess the overall investment return of a company that overcomes the shortcomings of varying capital structures. However, this ratio is no exception as it is also vulnerable to accounting misrepresentation, and as such, one needs to be vigilant while analyzing companies on the basis of ROCE.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Return on Capital Employed. Here we discuss how to calculate ROCE along with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –