Updated July 14, 2023
Introduction to Risk Appetite
Risk appetite means the extent or the capacity the level of risk that an entity or trader or business organization, or investor can accept in an asset or security to purchase in the future or any transaction to make in the future and which decides before taking such decision of purchase or transaction.
Explanation
- The dictionary meaning of appetite is the desire to satisfy needs (especially food desire to satisfy the taste). Similarly, in the case of investment, the desire is for satisfactory returns. Risk appetite, therefore, refers to the capacity to bear the risk in case loss occurs.
- This concept widely uses in risk management techniques to provide a bar on the maximum allowable risk for an investor. Risk appetite level famously refers to the tolerance level of risks.
- The level of tolerance may differ from person to person. Tolerance also depends on the nature of the work & the objectives. Where public safety involves, the tolerance level is on the lower side.
- Organizations must decide the risk tolerance or acceptable level of risk before making decisions. Because after the decision is made & action is implemented, there is no backing out. The person exposes to whatever consequences for the said decision.
- The risk appetite statement is innovative nowadays, expressing the acceptable risk for the entire organization. This statement depends on all the concerns of stakeholders & interconnected persons with the entity.
- From an investor’s perspective, risk appetite is the variation he is ready to accept in returns. The variation can be both positive as well as negative.
- A greater risk horizon connects with the equities market, exchange-traded, or equity-based funds. Smaller risk horizons connect with bond markets or bond-based funds. Also, it depends on the investor’s age, net worth, and other demographic factors.
How to Determine Risk Appetite?
- People generally have misconceptions about risk appetite with risk management. Both start at different lines. Risk management is the daily or frequent analysis of the entity’s risks. Based on such analysis, it is that line above which the entity cannot bear the loss in case the risk crystallizes.
- Management of the organization is generally responsible for analyzing the risk situations for the entity. In the case of small organizations, the owner does the job of risk analysis. Departmental heads are given the responsibility for analyzing risk from their perspective. Final conclusions submit to the management for analyzing the risk from the corporate view.
- Determining the risk appetite requires the first determination of the probable risk. Probable risk determines using various techniques such as analyzing the past trend, competitor’s analysis, SWOT of the entity, possible downfall for the entity, change in macro-economic factors for the country & the business, etc.
- Based on such analysis, the management calculated an acceptable figure beyond which the entity would not take a risk. The higher management approves such analysis & then the same implements it throughout the entity.
Types of Risk Appetite
The risk appetite types are nothing but the levels of risk accepting capacity. These levels broadly explain below:
- Aggressive Level: This risk level refers to risk-loving, wherein the entity or the investor wants to take all sorts of logical risks, which would manifold the investment amount. The entity is not concerned with the level of aggressiveness of risk; they just want to grab all available opportunities for gains through a maximum stop-less on the negative returns.
- Moderate Level: This is a mediocre level of risk, where the decision depends on the risk-to-reward ratio. Every risk is positively proportional to rewards. The entity or investor decides the ratio of risk acceptance for a given reward. In the case of moderate levels of risk, the basic objective is increasing the wealth of shareholders.
- Conservative Level: This level also refers to a risk-averse level, wherein the entity or investor does not want to take any risk. It wants to satisfy hunger only through safe positions. As said earlier, risk & return go hand-in-hand. Thus, such a level of risk provides lower returns on capital employed. The basic objective is to safeguard the capital employed & an increase is acceptable only through risk-free investments at a conservative level.
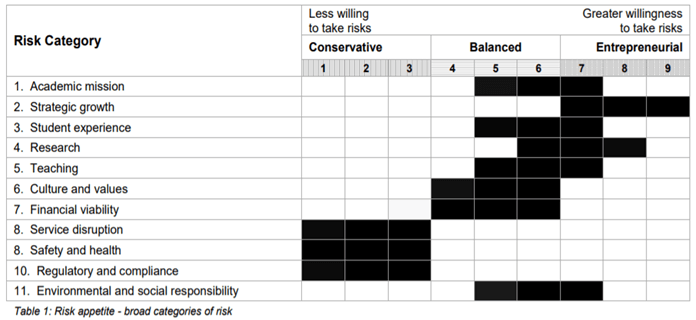
Risk Appetite Table
- The risk appetite table is nothing but the quantum or level of acceptable risk for each risk category.
- The best presentation can depict in the following picture:
Image Source: https://www.adelaide.edu.au/legalandrisk/system/files/media/documents/2020-04/risk-appetite-table.pdf
- In the above table, the categories are various business prospects. The second to fourth column presents the level of willingness to accept risk. Thus, it can be best judged accordingly.
Measurement of Risk Appetite
- It is described through a risk appetite statement since the exact risk calculation is impossible. However, A detailed rationale provides to assess the level of risk.
- The level of risk appetite is different for different types of risk. The entity is risk-averse in case of an increase in raw material prices & thus, enters into possible hedge contracts.
- Risk can measure by computing the maximum financial loss in case the risk crystallizes the maximum amount of delay in constructing a plant.
- Over the period of experience in the relevant field, the managers acquire the possible risks in the business areas. Such as the managers knowing the possible deviation in input prices over the years or possible demand functions for their product.
Benefits of Risk Appetite
- Since the entity knows the level of possible risk, the entity can decide a borderline between the level of innovation and possible precautionary measures.
- It provides a broader picture of the entire business risk.
- If the expected risk is higher than the appetite level, risk management is involved in suggesting risk mitigation measures.
- With a risk appetite level, the company can decide on the growth rates for the entity as a whole. The same goes for an investor; he can decide upon the quantum of return to earn.
- The level of rewards rewards the level of risk appetite. More risk equals more chance of rewards.
- Having the level of risk predefined, the entity can focus on other aspects of business growth without fearing future risk.
Importance of Risk Appetite
- An entity needs to understand where they stand regarding available exposure to risk.
- It supplements the risk analysis of the management.
- As a company or entity has defined the level of risk appetite as applicable to their business, they can focus on further expansion of the business segment & other business policies.
- It helps the entity to evaluate the maximum possible return or ways to curb potential losses. Thus, it amplifies the efficiency of the investor & the entity as a whole.
Conclusion
Risk appetite should not be seen only from the point of the investor. It mainly applies to the business prospects of the entity, whether the business will bear or sustain the possible loss of demand or margins, etc. Risk management deals with counter-measures if risk crosses the risk appetite levels. Thus, risk management & risk appetite are correlated but not the same. The objective of it is to provide clarity over the acceptable level of possible risks to the organization.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Risk Appetite. Here we discuss the introduction and how to determine risk appetite, types, and importance. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –