Updated October 23, 2023

Risk!!!!!!! Whenever we hear this word, we start panicking & thinking about what type of risk it could be, i.e., a physical or financial risk. As per the survey, it’s been found that a person or an individual has always feared losing something of value, which majorly consists of finance. And if we see today, not only individuals but organizations fear losing their money.
As we all know, no one can grow or earn more without taking risks, but the rate of risk and uncertainty has also increased due to modernization, liberalization, and growing competition. This has created trouble for individuals, the banking sector, and financial institutions. Banks have to mitigate or curb these risks to sustain and grow in the market. Thus, the risk management concept has come into the picture, providing guidelines or acting as a roadmap for a banking organization to reduce the risk factor.
The below article will focus on quotients like what risk management is. What risks do banks face, and how do they manage through the risk management process?
What is RISK Management in a Bank?
We all come across the word RISK in our life, but have you ever wondered where this word originates from??? What is the origin of this word??? So, firstly, we will discuss…
What Is Risk?
“Risk” can be a link to the Latin “Rescum,” which means Risk at Sea. Risk can be defined as losing something of value or weighing against the potential to gain something of value. Values can be of any type i.e. health, financial, emotional well-being, etc. Risk can also be an interaction with uncertainty. Risk perception is subjective; people judge the severity of a risk, and it varies from person to person. Every human being carries some risk and defines those risks according to their judgment.
What is Risk Management?
As we all are aware, what is the risk? But how can one tackle risk when they face it?? So, the concept of Risk Management manages the risk or uncertain event. Risk Management refers to the exercise or practice of forecasting the potential risks, thus analyzing and evaluating those risks and taking some corrective measures to reduce or minimize those risks.
Today, many organizations or entities practice risk management to curb the risks they can face in the near future. Whenever an organization makes any investment decision, it tries to determine the number of financial risks attached. Financial risks can be high inflation, recession, volatility in capital markets, bankruptcy, etc. The quantum of such risks depends on the type of financial instruments in which an organization or an individual invests.
So, to reduce or curb such exposure of risks to investments, fund managers and investors practice or exercise risk management. For example, an individual may consider investing in fixed deposits less risky than investing in the share market. As investment in the equity market is riskier than the fixed deposit, through the practice of risk management, equity analysts or investors will diversify their portfolios to minimize the risk.
How Important is Risk Management for Banks?
Until now, we have seen how risk management works and how important it is to curb or reduce risk. As risk is inherent, particularly in financial institutions, banking organizations, and even in general, this article will deal with how Risk Management is important for banking institutions. Banking sectors have been working in a regulated environment and have not been exposed to the risks much. Still, due to the increase of severe competition, banks have been experiencing various types of risks, such as financial and non-financial risks.
The function and process of Risk Management in Banks are complex, so the banks use the simplest and most sophisticated models to analyze and evaluate the risks. Banks should have the expertise and skills to deal with the risks involved in the integration process. To compete effectively, large-scale banking organizations should develop internal risk management models. At a more desired level, Head office staff should be trained in risk modeling and analytic tools to conduct Risk Management in Banks.
Risk Management in the Indian Banking Sector
The practice of Risk Management in Banks is newer in Indian banks. Still, the risk management model has gained importance due to the growing competition, increased volatility, and market fluctuations. The practice of risk management has resulted in increased efficiency in governing Indian banks and has also increased the practice of corporate governance. The essential feature of the risk management model is to minimize or reduce the risks of the products and services that the banks offer; therefore, to mitigate the internal & external risks, there is a need for an efficient risk management framework.
Indian banks must prepare risk management models or frameworks due to the increasing global competition by foreign banks, the introduction of innovative financial products and instruments, and increasing deregulation.
India’s banking sector has made great technological advancements, quality, etc., and has started rapidly diversifying and expanding its horizons. However, the increasing globalization, liberalization, and advancements lead these banks to encounter some risks. Since in banks, risks play a major role in the earnings, therefore higher the risk, the higher the returns. Hence, it is essential to maintain equality between risk and return.
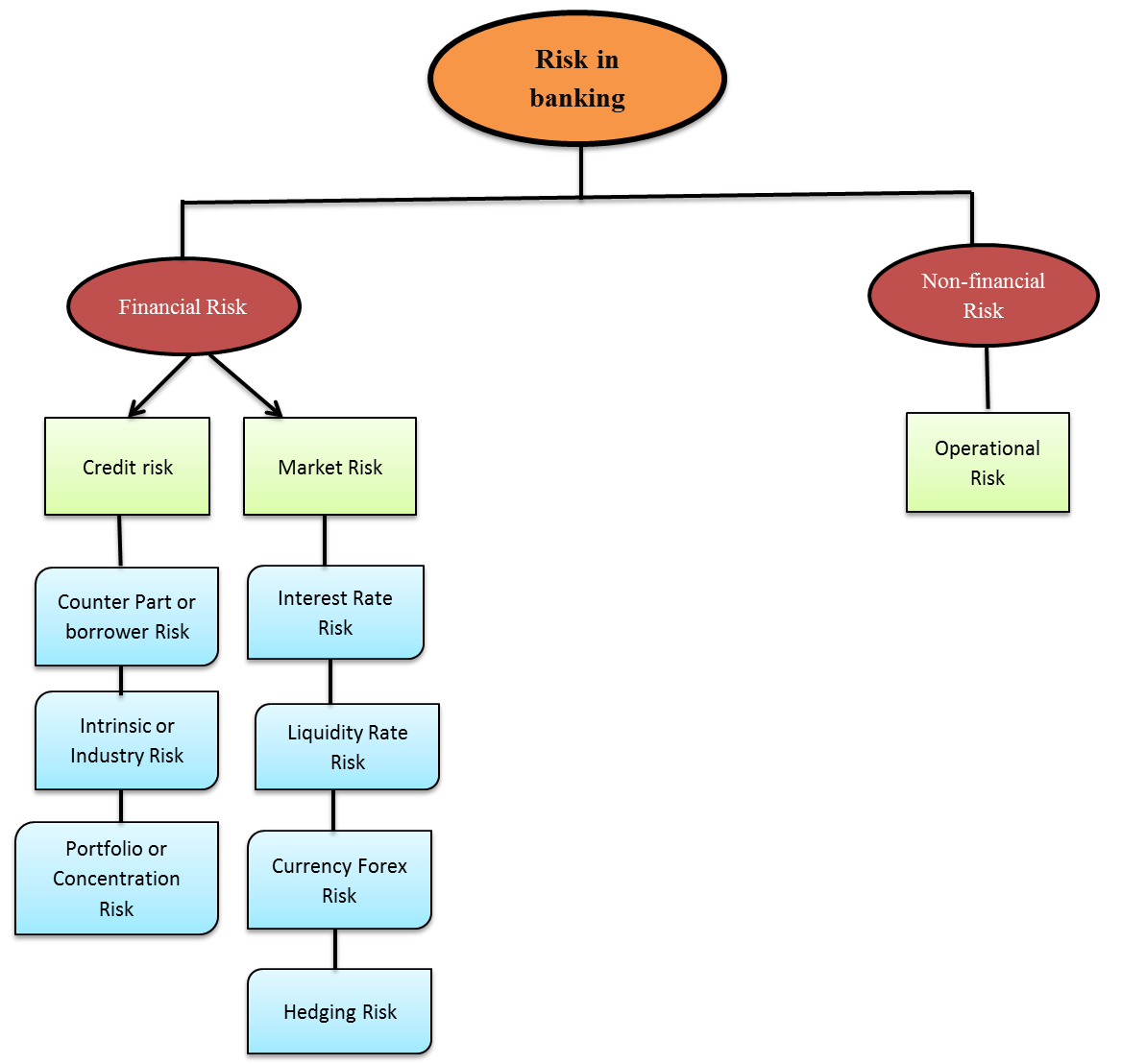
Classification of Risks in the Banking Sector
1. Credit Risk
- Credit risks involve borrower, industry, and portfolio risks as it checks the creditworthiness of the industry, borrower, etc.
- It is also a default risk, which checks the inability of an industry, counterparty, or customer to meet the commitments of making a settlement of financial transactions.
- Internal and external factors both influence the credit risk of a bank portfolio.
- Internal factors consist of a lack of appraisal of the borrower’s financial status, inadequate risk pricing, lending limits are not defined properly, absence of post-sanction surveillance, proper loan agreements or policies are not defined, etc.
- External factors include trade restrictions, fluctuation in exchange and interest rates, fluctuations in commodities or equity prices, tax structure, government policies, political system, etc.
How do Banks Manage this Risk?
- Top management consent or attention is crucial to manage credit risk.
- The Credit Risk Management Process includes the following:
-
- In a loan policy of banks, the risk management process should be articulated.
- Through credit rating or scoring, the degree of risk can be measured.
- It can be quantified by estimating expected and unexpected financial losses and even risk pricing can be made scientifically.
- A Credit Policy Committee should be in each bank to review the credit policies, procedures, and agreements. It thus can analyze, evaluate, and manage a bank’s credit risk widely.
- Credit Risk Management consists of many management techniques that help the bank curb the adverse effects of credit risk. Techniques include credit approving authority, risk rating, prudential limits, loan review mechanism, risk pricing, portfolio management, etc.
2. Market Risk
- Earlier, for all the banks, managing credit risk was the primary task or challenge.
- However, due to the modernization and progress in the banking sector, market risks started arising, such as fluctuations in interest rates, changes in market variables, fluctuations in commodity prices or equity prices, and even fluctuations in foreign exchange rates.
- So, it became essential to manage the market risk, too. Even a minute change in market variables results in a substantial change in the economic value of banks.
- Market risk comprises liquidity risk, interest rate risk, foreign exchange rate risk, and hedging risk.
How do Banks Manage this Risk?
- The top management of banks’ major concern is managing the market risk.
- Top management of banks should clearly articulate the market risk policies, agreements, review mechanisms, auditing & reporting systems, etc. These policies should clearly mention the risk measurement systems that capture the sources of materials from banks and thus have an effect on banks.
- Banks should form an Asset-Liability Management Committee, whose main task is to maintain & manage the balance sheet within the risk or performance parameters.
- Banks should set up an independent middle office to track the market risk on a real-time basis.
- The middle office should consist of members who are market experts in analyzing the market risk. The experts can be economists, statisticians, and general bankers.
- The members of the middle office should be separate from treasury departments or in the daily activities of the treasury department.
3. Operational Risk
- Managing operational risk has become essential for better risk management practice.
- Operational risk arose due to the banking sector’s and financial markets’ modernization. It gave rise to structural changes, an increase in the volume of transactions, and complex support systems.
- Operational risk cannot be categorized as market risk or credit risk. This risk can be related to the settlement of payments, interruption in business activities, and legal and administrative risk.
- As operational risk involves risk related to business interruption or problem, this could trigger market or credit risks. Therefore, operational risk has some sort of linkage with credit or market risks.
How do Banks Manage this Risk?
- There is no uniform approach to measuring the operational risk of banks. To date, simple and experimental methods are useful, but foreign banks have introduced advanced techniques to manage operational risk.
- Measuring operational risk requires an estimation of the probability of operational loss and the potential size of the loss.
- Banks can use analytical and judgmental techniques to measure operational risk levels.
- Risk of operations can be audit ratings, data on quality, historical loss experience, data on turnover or volume, etc. Some international banks have developed rating matrices similar to bond credit ratings.
- Operational risk should be assessed & reviewed at regular intervals.
- For quantifying operational risk, Indian banks have not evolved any scientific methods and are using a simple benchmark system that measures business activity.
Recommended Articles
Here are some articles that will help you to get more details about Risk Management in Banks. So, just go through the link.
- Why should I go for PRM (Professional Risk Manager)?
- 10 Top Most Important Marketing Management Functions
Risk Management in Banks Infographic
Learn the juice of this article in just a single minute, Infographic of Risk Management in Banks