Updated March 13, 2023
Definition of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
Robots operated by artificial intelligence are known as artificially intelligent robots. AI is the intellect, and robotics is the body when used together. Artificially intelligent robots are a relatively new technology. Efforts are underway using sensing materials and machine-learning algorithms. Randomly positioned sensors can detect touch and pressure and provide data to a machine-learning system, which analyses the signals in one scenario.
Introduction robotics and artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming more popular in robotic solutions, bringing flexibility and learning capabilities to formerly rigid applications. Artificial intelligence has made modern robotics conceivable. As a result of AI, processes become significantly more versatile and adaptable. Artificial intelligence-enabled robots act as a link between robotics and artificial intelligence. These are artificial intelligence-controlled robots (AI).AI algorithms are designed whenever we want the robot to perform increasingly complex tasks. A warehousing robot might employ a path-finding method to explore the warehouse. Artificial Intelligence raises problems about the information required for different types of thinking. Robotics, on the other hand, introduces artificial intelligence into the actual world and allows it to interact with materials in real-time.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) aid robots in seeing, walking, speaking, smelling and moving in progressively human-like manners. Artificial intelligence and robotics are two distinct branches of engineering with little overlap. While designing, creating, and controlling robots is part of robotics, AI is not limited to physical robots. Robotics and the two main types of artificial intelligence are compatible. The first is software intelligence (supplied by microprocessors and microcontrollers), which directs the hardware to perform specific actions and make judgments. With practice, the programme learns and adjusts even more. The second type is hardware intelligence, in which the robot is permitted to use learning circuits to mimic how people process information.
Artificial intelligence can be used in a variety of ways.
1. In robotic assembly applications, assembly AI is a very useful tool. When AI is used in conjunction with advanced vision systems, it can aid in real-time course correction, which is very valuable in complicated manufacturing areas like aerospace.
2. Packing: For faster, lower-cost, and more precise packaging, robotic packaging frequently employs AI.
3. Customer service: The majority of these robots use AI natural language processing to communicate with clients more humanly.
Note: The use of artificial intelligence in robotics is based on the fact that computers can only solve issues with a specific input. So, the researcher provides the robots a training data set and a variety of inputs, and their Artificial Intelligence is left to evaluate the provided input to the training sample and decide which path to take. This allows computers to make their own choices. The Alpha Go is a great example.
Head to Head Comparison Between Robotics and Artificial Intelligence (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between Robotics and Artificial Intelligence:
Key Differences Between Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence and robotics are two distinct fields. Only a few commonalities exist, but the contrasts are numerous. Without a question, both sectors are on the rise in recent years and will continue to dominate the technology industry for many years to come. Let’s see the differences here:
1. Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the intelligence demonstrated by machines or robots (such as problem-solving and learning) through the use of methods or algorithms such as search, logic, if-then rules, decision trees, and deep learning. In a nutshell, AI can help with learning, problem-solving, language translation, and logical reasoning.
2. AI can be found in phones, laptops, and even robots, and it performs activities that are most often related to systems, algorithms, and data – analysing and computing a specific result. There is one form of robot that is immobile and without a body, such as the popular chatbots that operate within programmes.
3. Though AI algorithms are used to drive robots, they are only one component of a larger robotic system that also includes sensors, actuators, and non-AI programming. Robots simply control and process the information via computer systems, simulating human activities without the need for human involvement.
4. Robotics are machines that can act without the need for external commands. Artificial intelligence refers to the software which studies and advances on its own.
5. Social care is one of the most significant advantages of artificially intelligent robots. They can assist people, particularly the elderly, using robot social skills and powerful processing. Only by comparing inputs from the outside environment to stored instructions could robots make a decision. Artificial intelligence should be used to make a robot understand, and that’s where artificial intelligence and robotics collide, resulting in artificially machine intelligence.
6. Robots employ artificial intelligence to learn and improve their independent functions. As they are bound to a set of instructions, repetitive actions are not artificial intelligence. For robots to do complex jobs, AI algorithms are required.
7. It’s all about reproducing known results over and over again in robotics (apart from AI). When the external situation and eventualities change dramatically, robots will malfunction, especially if they are not prepared to adapt appropriately.
Comparison robotics and artificial intelligence
While robotics and artificial intelligence may coexist, scientists are focusing attention on integrating the two due to the inherent potential that such a combination offers. Let’s see a few comparisons between them.
| Robotics | Artificial Intelligence | |
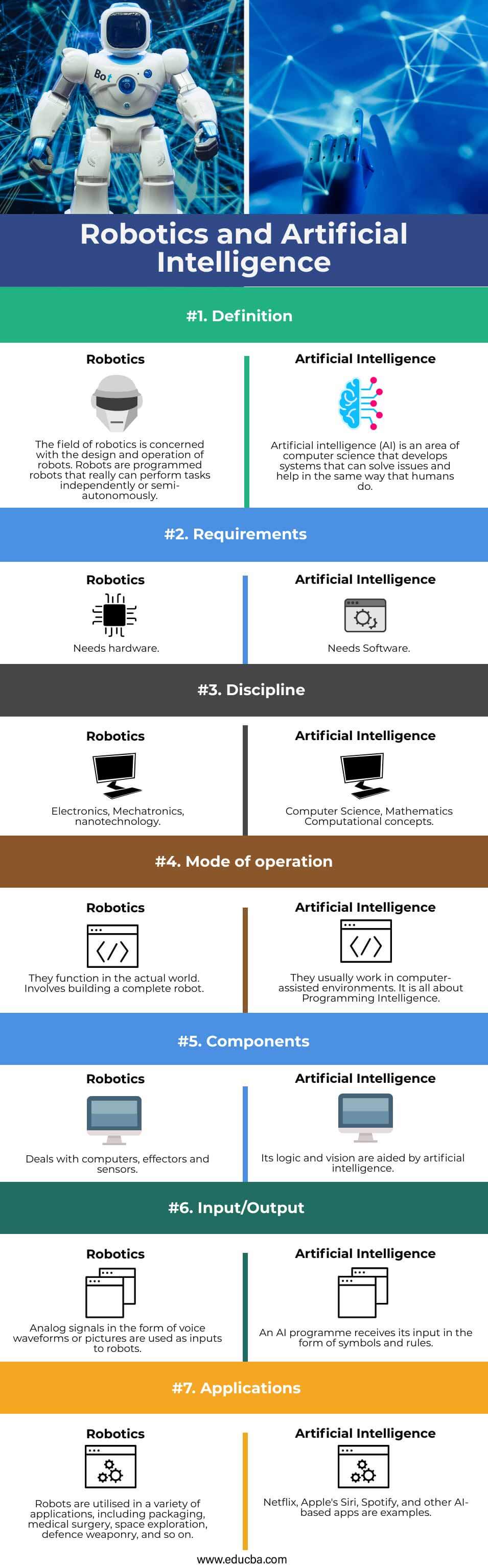
| Definition | The field of robotics is concerned with the design and operation of robots. Robots are programmed robots that really can perform tasks independently or semi-autonomously. | Artificial intelligence (AI) is an area of computer science that develops systems that can solve issues and help in the same way that humans do. |
| Requirements | Needs hardware | Needs Software. |
| Discipline | Electronics, Mechatronics, nanotechnology | Computer Science, Mathematics Computational concepts. |
| Mode of operation | They function in the actual world. Involves building a complete robot. | They usually work in computer-assisted environments. It is all about Programming Intelligence. |
| Components | Deals with computers, effectors and sensors | Its logic and vision are aided by artificial intelligence. |
| Input/Output | Analog signals in the form of voice waveforms or pictures are used as inputs to robots. | An AI programme receives its input in the form of symbols and rules. |
| Applications | Robots are utilised in a variety of applications, including packaging, medical surgery, space exploration, defence weaponry, and so on. | Netflix, Apple’s Siri, Spotify, and other AI-based apps are examples. |
Conclusion
Even though the phrases “robots” and “artificial intelligence” are sometimes used interchangeably, they perform fundamentally different functions. To make meaningful progress in the consumer arena, AI has taken a tremendous risk.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Robotics and Artificial Intelligence. Here we discuss key differences with infographics and comparison table, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –