Updated March 13, 2023
Difference Between Robotics and Automation
“Robotic” refers to the software that we can create to complete tasks and use robotics machines. Automation makes the work occur on its own and is used in a variety of industries and businesses. Advanced AI skills such as machine learning models, natural language processing (NLP), character and image recognition, and more may now be incorporated into RPA robots.
Introduction Robotics and Automation
Robotics is a branch of engineering concerned with the design and perpetration of robots and the use of computers to manipulate and reuse them. In manufacturing assiduity, robots are utilized to speed up the process.RPA is a fantastic fit for large firms with huge human resources, IT, and finance departments since it automates labor-intensive workflow, infrastructure, and back-office procedures. Robotics is a sub-category of industrial automation because a robot is nothing more than a set of sensors and processors with which it can accomplish an industrial task, much like a PLC. Software robots, also known as workstation automation or robotic process automation, are computer programs that automate virtual operations instead of physical ones.
Software automation and industrial automation are the two most common types of automation. The areas of application and technologies used to implement various forms of automation differ. Software automation is a program programmed to perform repeated chores using the same logic humans use when using computer applications. Let’s imagine we need to speed up our production operations and need to assemble a product faster. A robot might be able to help. Software-driven process automation would be more suited if we wanted to make repetitious administrative activities more efficient. Controlling and maintaining physical processes is at the heart of industrial automation. Amazon’s fully automated manufacturing is a case in point:
Amazon’s warehouse has robots: That may explain why FBA shipping times are so short. There are various different sorts of machines in industrial automation. In the industrial sector, CNC machines, for example, are commonly employed. A robot is the only type of machine.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Robotics and Automation (Infographics)
Below are the top 9 differences between Robotics and Automation:
Key Differences Between Robotics and Automation
Although the phrases ‘robotics’ and ‘automation are sometimes used interchangeably, there are several key distinctions between the two terms and what they signify.
1. Robotics is better defined as a sub-category of automation, including software agents that do not require hardware.
2. It is controlled by a set of programming and mechatronics, allowing it to perform a variety of sophisticated series of movements. Automation varies by the component used.
3. Manufacturers, on the other hand, deal with robotics and automation daily since they create electrical products that make our lives easier.
4. When it comes to automating a system or machine to complete a task quickly, and with the maximum amount of precision, robotics, and automation go hand in hand. Both of them are industrial machines that work mechanically.
5. Robots aren’t used in all sorts of automation, and not all robots are built for process automation. However, most robots are used for that precise purpose – particularly in industrial settings. A toy line-following robot, for instance, can follow a line painted on the floor independently. It isn’t automation, though, because it isn’t carrying out a defined duty. Instead of moving drugs throughout a hospital, the line-following robot would be considered automation.
6. Automation and robotics aim not to eliminate all human workers from the workplace. They’re just employed to speed up manufacturing and reduce the number of errors that might otherwise occur. There are many different sorts of automation, ranging from completely mechanical to completely virtual. They also range in difficulty from simple to mind-boggling. A collaborative robot dispensing system is an excellent example of combining the two.
7. Many automation will not include a robot as a component. Robots are simply one piece of industrial equipment that can be combined to form a semi-automated or fully automated system.
8. The primary goal of RPA is to reduce staff, whereas the other automation techniques aim to reduce processing time. Non-technical people can use the RPA technique to boost productivity by allowing them to focus on more vital duties that cannot be automated. In contrast, traditional automation is solely available to technical users.
Comparison of Robotics and Automation
|
Points |
Robotics | Automation |
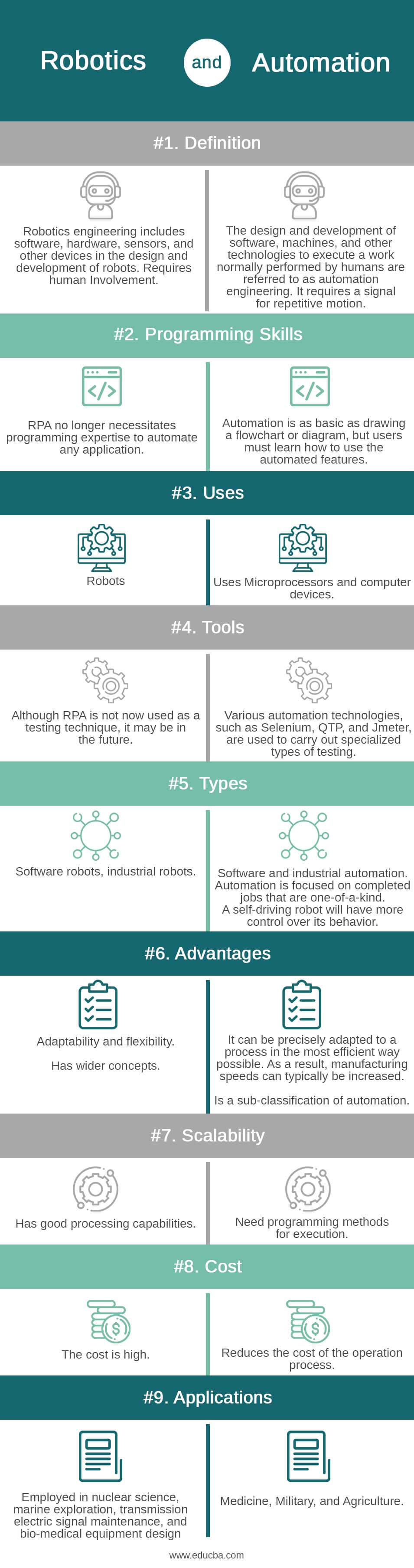
| Definition | Robotics engineering includes software, hardware, sensors, and other devices in the design and development of robots. Requires human Involvement | The design and development of software, machines, and other technologies to execute a work normally performed by humans are referred to as automation engineering. It requires a signal for repetitive motion. |
| Programming skills | RPA no longer necessitates programming expertise to automate any application.
|
Automation is as basic as drawing a flowchart or diagram, but users must learn how to use the automated features. |
| Uses | Robots | Uses Microprocessors and computer devices. |
| Tools | Although RPA is not now used as a testing technique, it may be in the future. | Various automation technologies, such as Selenium, QTP, and Jmeter, are used to carry out specialized types of testing. |
| Types | Software robots, industrial robots | Software and industrial automation. Automation is focused on completed jobs that are one-of-a-kind. A self-driving robot will have more control over its behavior. |
| Advantages
|
Adaptability and flexibility.
Has wider concepts. |
It can be precisely adapted to a process in the most efficient way possible. As a result, manufacturing speeds can typically be increased.
Is a sub-classification of automation. |
| Scalability | Has good processing capabilities. | Need programming methods for execution. |
| Cost | The cost is high. | Reduces the cost of the operation process. |
| Applications | employed in nuclear science, marine exploration, transmission electric signal maintenance, and bio-medical equipment design | Medicine, Military, and Agriculture. |
Conclusion
We have seen the distinctions and explored some of how collaborative robots have revolutionized the worlds of conventional robotics and production as we reached the end of this article. We can only conclude that the gadgets and instruments utilized to automate a machine or unit varied in both technologies. When compared to automation, robotics is a much more advanced form of technology.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Robotics and Automation. Here we discuss key differences with infographics and comparison tables, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –