What is Sales Tax?
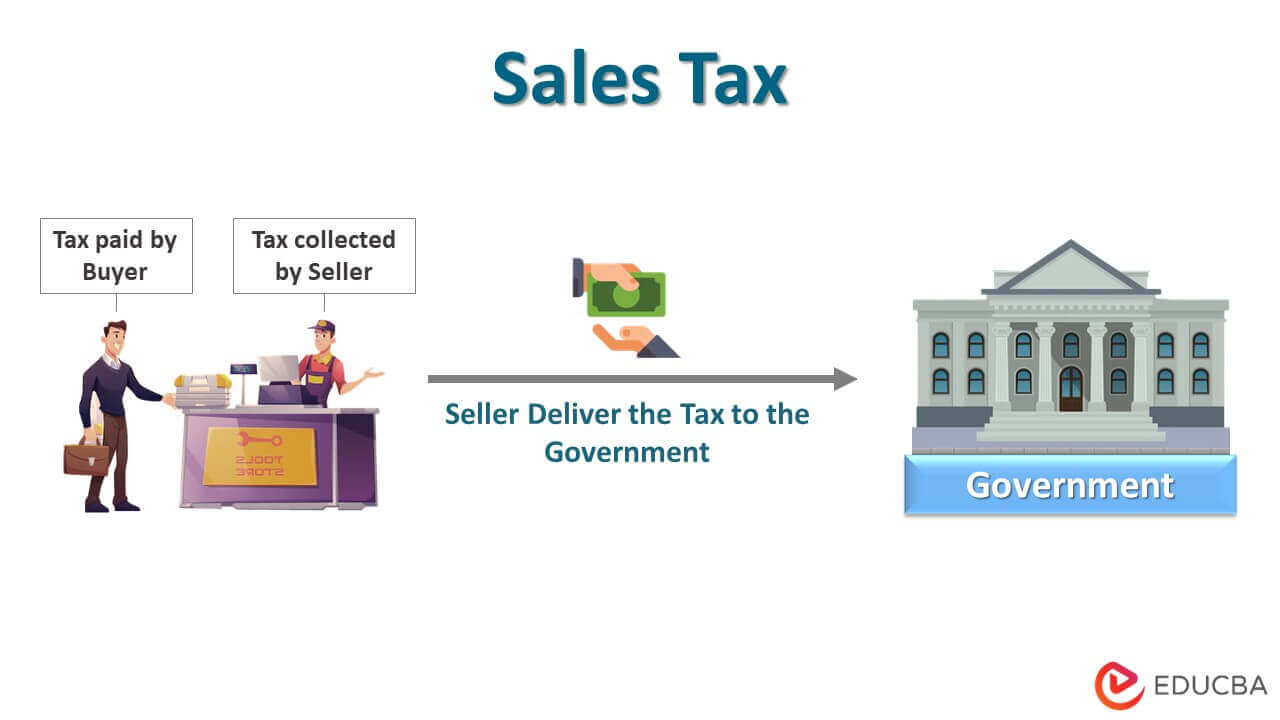
The term “sales tax” refers to the tax that the government levies based on the value of goods sold or services offered. Typically, it is charged at the time of the transaction or point of sale, paid by the buyer, collected by the seller, and then delivered to the government.
Please note that it is not revenue for the seller, but the seller is a mere intermediary that collects the tax on behalf of the government authority of the city or state.
Explanation
When a customer purchases an item at any retail shop, he or she pays the final price relatively higher than the price of the product bought. This occurs because it is added to the product’s price to arrive at the final price. It is the additional money charged as a percentage of the selling price of goods and services.
Objectives
Some of the objectives are mentioned below:
- To build the basis for ascertaining the sale of goods or services during intrastate trade, interstate trade, import, and export.
- To frame strict guidelines for levying taxes, exemptions, penalties, etc.
- To lay down the rules and regulations under state laws for imposing taxes on the sale of goods of particular importance.
Examples of Sales Tax
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
Let us take the example of ASD Inc., which operates in Colorado, US. This state charges a total tax of 7.2% (state tax of 2.9% + local tax of 4.3%) on the sale of goods or services. Calculate the sales tax that must be collected if a product’s price before tax is $550.
- Given, Price before tax = $550
- Sales tax rate = 7.2%
Now, the sales tax to be collected by ASD Inc. can be calculated as,
Sales Tax = Price Before Tax * Sales Tax Rate
- Sales Tax = $550 * 7.2%
- Sales Tax = $39.60
Therefore, ASD Inc. has to collect a sales tax of $39.60 for sale.
Example #2
Let us take the example of QRT Inc., operating in the state of Alabama, US. This state’s total tax on goods or services is 9.2% (state tax of 4.0% + local tax of 5.2%). Determine the price of goods before tax if the final price collected by QRT Inc. is $736.
- Given, Final Price = $736
- Sales Tax Rate = 9.2%
Now, the price before tax of the product can be calculated as,
Price Before Tax = Finale Price / (1 + Sales Tax Rate)
- Price Before Tax = $750 / (1 + 9.2%)
- Price Before Tax = $674
Therefore, the product’s price before the tax levy is $674.
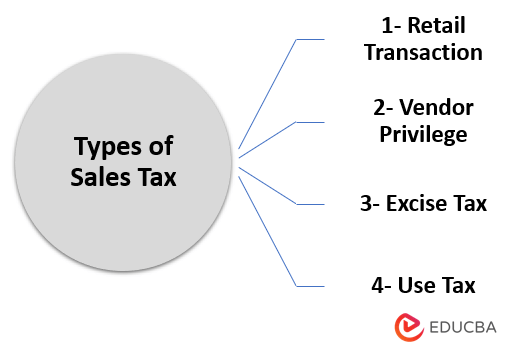
Types of Sales Tax
It can be broadly categorized into four major types:
- Retail Transaction: It is one of the most common types of tax that state and local governments use to generate revenue. Its value lies in a few percentages to more than 10% of the selling price. The customers are more or less familiar with this type of tax as they often pay it during shopping.
- Vendor Privilege: This tax is levied on vendors as a permit for business in the region. It is slightly different from the retail transaction sales tax as it is paid by the sellers, not the customers or buyers. However, sometimes, businesses can pass these taxes on customers through higher prices.
- Excise Tax: This tax is often levied on items not considered essential for survival. For instance, alcohol and cigarettes are subject to excise tax. The producers or wholesalers usually bear this type of tax. Nevertheless, these taxes also result in increased prices.
- Use Tax: This tax is charged to customers instead of retail transaction sales tax. For instance, if a consumer purchases something online where it didn’t pay the retail tax but was supposed to pay, he or she must declare and pay the use tax for the same in their home state.
Effects
Some of the significant effects are mentioned below:
- Immediate increase in the selling price of goods and services.
- Consumers are left with lesser money to spend on additional goods, which can adversely impact the overall demand scenario.
- Businesses may find it difficult to earn sufficient profits due to shifts in consumer behavior.
Who Pays Sales Tax?
In those states where the seller has a legal presence, it is the seller’s responsibility to collect the sales tax and pay it to the tax authorities. However, if the seller is not legally present in the buyer’s state, then the buyer is primarily responsible for declaring and paying the sales tax, as seen in the case of use tax.
Advantages
Some of the significant advantages are as follows:
- It is one of the essential sources of revenue for any government.
- It helps foster equality and welfare of the society as the government can use the taxes earned from the rich to support the financially weak people.
Disadvantages
Some of the major disadvantages are as follows:
- Its structure can be complex and complicated as different states and countries follow different taxation norms.
- Sometimes such a tax structure can result in double taxation for the consumers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Sales Tax. Here we also discuss the introduction and types along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –