Introduction to SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud
Choosing the right cloud infrastructure is crucial as businesses worldwide pursue digital transformation. SAP S/4HANA is a leading ERP system that offers real-time insights and streamlined processes, making it a strong choice. However, deciding whether to deploy SAP S/4HANA on a Public or Private Cloud is important. Each option has its benefits and is suited to different business needs. This guide will explore SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud, covering their features, advantages, and ideal use cases. This will help you make an informed choice that fits your organization’s goals.
SAP S/4HANA Overview
SAP S/4HANA is a progressive ERP suite developed by SAP that utilizes the in-memory computing database SAP HANA to provide real-time data processing and support various business functions like finance, supply chain management, and customer relationship management. Accely’s SAP S/4 HANA builds on this foundation by offering a customized version of the ERP suite, leveraging SAP S/4HANA’s capabilities while enhancing it with additional features and industry-specific expertise to better address the unique needs of different organizations.
SAP S/4HANA is known for its capability to:
- Streamline business processes through automation and integration.
- Provide real-time analytics and insights to enhance decision-making.
- Support digital transformation initiatives across various industries.
What is SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud?
SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud is a multi-tenant environment, meaning multiple organizations share the same cloud infrastructure. SAP manages this shared infrastructure, maintenance, updates, and tenant security. The Public Cloud model offers a standardized set of features that businesses can configure to meet their needs, though it does not allow for the deep customization found in other models.
Key Features of SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud:
- Cost Efficiency: One of the most compelling aspects of the Public Cloud is its cost structure. Organizations benefit from lower upfront costs and predictable, subscription-based pricing by sharing resources. This model is especially attractive for small—to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or large organizations looking to manage IT costs effectively.
- Rapid Deployment: You can quickly implement the Public Cloud. With standardized processes and configurations, businesses can go live faster than complex deployment models. This speed to market allows organizations to take advantage of SAP S/4HANA’s capabilities rapidly.
- Automatic Updates: SAP handles all software updates and upgrades in the Public Cloud, so businesses always use the latest version. This automatic update process eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming upgrade projects, allowing organizations to focus on their core activities.
- Scalability: The Public Cloud allows businesses to easily increase or decrease resources as needed. This flexibility is especially useful for companies experiencing fast growth or seasonal changes in their operations.
- Standardization: While the Public Cloud offers some configuration, it is best suited for organizations that can operate within standardized processes. Industries with less complex regulatory requirements or businesses that do not require extensive customization will find the Public Cloud an attractive option.
What is SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud?
In contrast, SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud offers a single-tenant environment where one organization exclusively uses the cloud infrastructure. This deployment model offers greater environmental control, allowing for more customization, enhanced security, and tailored solutions.
Key Features of SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud:
- Customization: The Private Cloud offers a high degree of flexibility, allowing businesses to tailor the solution to their needs. Whether customizing workflows, integrating with existing systems, or adapting to unique industry requirements, the Private Cloud provides the environment needed for these enhancements.
- Enhanced Security: Businesses have greater control over security measures and compliance protocols in a Private Cloud environment. This control is crucial for healthcare, finance, or government industries, where data protection and regulatory compliance are paramount.
- Flexibility in Updates: Unlike the Public Cloud, where SAP automatically manages and installs updates, the Private Cloud lets organizations control when and how they apply updates. This flexibility helps prevent disruptions to critical business operations and allows updates to fit internal schedules.
- Dedicated Resources: With the Private Cloud, the infrastructure is not shared with other organizations, resulting in exclusive access to computing resources. This exclusivity can enhance performance, reliability, and reduce latency, especially for resource-heavy applications.
- Data Sovereignty: For organizations operating in regions with strict data sovereignty laws, the Private Cloud offers the ability to choose data centers that comply with local regulations. This control over data location is often a deciding factor for businesses in regulated industries.
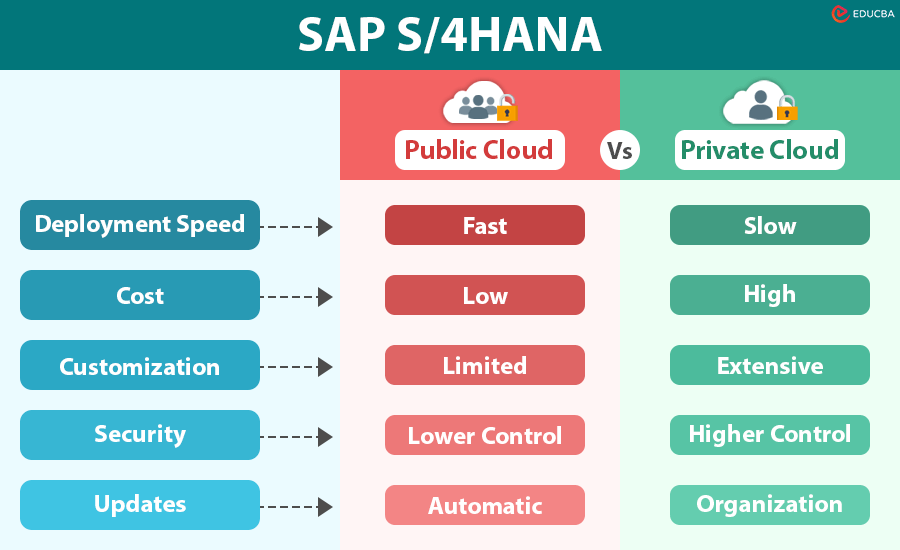
Comparison Table – SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud
To better understand the differences between these two deployment models, let’s compare them across several key criteria:
| Criteria | SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud | SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud |
| Deployment Speed | Fast (with pre-configured setups) | Slower (due to customization needs) |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs (subscription-based) | Higher initial costs but potential savings over time |
| Customization | Limited (standardized processes) | Extensive (tailored to business needs) |
| Security | Managed by SAP (lower control) | Higher control (customizable security) |
| Updates | Automatic (managed by SAP) | Controlled by the organization |
| Scalability | Easily scalable within shared resources | Scalable with dedicated resources |
| Performance | Shared resources may impact performance | Better performance with dedicated resources |
| Data Sovereignty | Limited control over data location | Full control over data location |
Use Cases for SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud
The SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud is an excellent choice for organizations that:
- Prioritize Cost-Efficiency: Businesses looking for a low-cost entry point into SAP S/4HANA will find the Public Cloud’s subscription-based pricing model appealing. The reduced need for in-house IT infrastructure and maintenance further enhances its cost-effectiveness.
- Need Rapid Deployment: Startups, SMEs, or large enterprises with urgent needs to deploy a robust ERP system can benefit from the public cloud’s rapid deployment capabilities. This model allows businesses to start leveraging SAP S/4HANA’s benefits quickly without the delays associated with custom implementations.
- Operate with Standardized Processes: Industries with relatively standardized business processes, such as retail, wholesale, or professional services, can effectively use the Public Cloud. These organizations may not require the deep customization that other industries demand.
- Prefer Automatic Updates: The Public Cloud’s automatic update feature is a major benefit for businesses looking to reduce the hassle of managing software updates and stay up-to-date with the latest technology.
Use Cases for SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud
The SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud is better suited for organizations that:
- Require Extensive Customization: Large enterprises or businesses with complex operational needs, such as manufacturing, aerospace, or pharmaceuticals, often require a tailored solution that the Private Cloud can provide. The ability to customize workflows, integrate with specialized systems, and adapt to unique industry requirements makes the Private Cloud the ideal choice.
- Operate in Regulated Industries: Organizations in highly regulated sectors such as healthcare, finance, or government must ensure that their ERP systems comply with strict security and compliance regulations. The Private Cloud’s enhanced security features and control over data location make it the preferred option for these industries.
- Demand High Performance: Businesses running resource-intensive applications or those that cannot afford downtime may benefit from the Private Cloud’s dedicated resources. The exclusive use of infrastructure often results in better performance and reliability.
- Control Over Updates: For organizations that need to manage when and how software updates are applied, the Private Cloud offers the flexibility to schedule updates to minimize disruption to critical business operations.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud is crucial and depends on your organization’s size, industry, budget, and specific needs. The Public Cloud offers cost-efficiency, quick deployment, and automatic updates, while the Private Cloud provides more customization, better security, and control over infrastructure.
Understanding the unique benefits of each option is important to align with your digital transformation goals. You can carefully evaluate your organization’s needs and goals and make a smart choice that maximizes the benefits of SAP S/4HANA.
Recommended Articles
We hope this comparison of SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud helps you make an informed decision. Check out these additional resources for more insights into ERP systems and cloud solutions.
