Difference between SAS vs SSD
SAS is a serial drive interface based on Serial-Attached SCSI. SAS supports both SCSI and ATI. SAS is a performance over traditional SCSI. They are designed for high-performance enterprise purposes. It enables multiple devices of different sizes to connect with longer cables. Those cables can be hot-plugged. It is a point-to-point protocol moves data to and from computer storage devices. SSD is a drive technology like cd, DVD, and a Solid-state drive (also known as flash drives). SSD data are stored on flash memory chips, so the data can be retained without power. Basically, the same type of memory used in SD cards or non-volatile memory in mobile devices.
What is SAS?
SAS devices have two ports; each resides in a different domain. IN the case of failover, if one path fails, it takes another independent path for communication. SAS ports fall in Transport and physical layer. SAS has a well-defined address/ID unique to each of its drive.
In layman terms, it is a connector that connects the server motherboard with hard drives. They replace traditional SCSI drives. The key attribute is serial interconnect.
What is SSD?
THE first SSD is launched in the year of 1970 for INM supercomputers. SSD refers to a type of internal technology. They are built from silicon memory chip with no moving parts and rotational delay, which reduces response time. They deliver end-to-end data integrity and include a function like error correction to improve reliability.
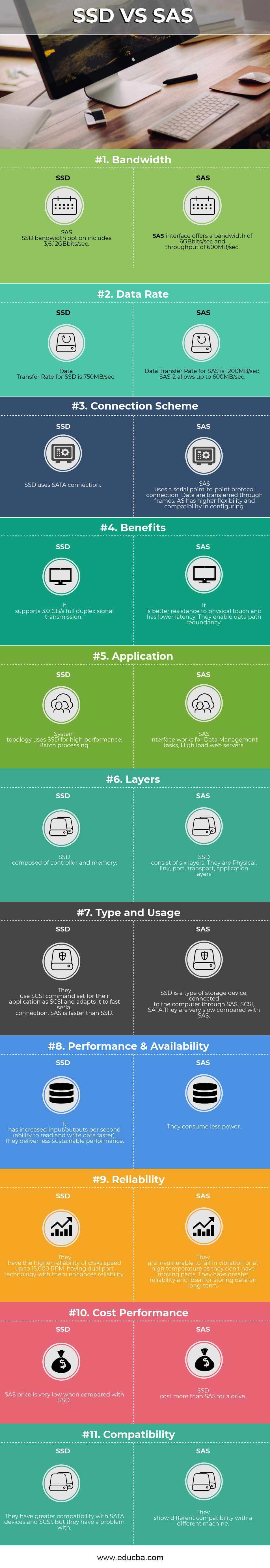
Head to Head Comparison Between SAS and SSD (Infographics)
Below is the top 11 difference between SAS and SSD:
Key Differences Between SAS and SSD
Let us discuss some of the major Difference Between SAS and SSD:
- SSD can be valuable to applications that need high performance from a limited capacity. They make no noise as they are non-mechanical.
- The special feature of SSD is data retention capability; for example, if SSD is removed from the server, a piece of information stored will be available for years. Since SSD has no movable parts, it is likely to keep our data safe.
- It consumes less power and Immune to data Fragmentation that’s the main advantage.
- SSD uses an SSD cache mechanism to store a temporary copy of active data.
- SSD has zero latency and a much higher random IOPS rate.
- SSD has disadvantages: they consume more battery power; they are not very fast at sequential workloads but fast at random workloads. They have a limited
- SAS drives fit into multiple- port storage arrays so that business enterprise use to store the data. SAS disks can deliver sequential data rates.
- SAS reduces storage system failure rates by reducing the no of physical connectors.
- SAS drive has a greater Mean time between failures (MTBF). They have advanced error correction for data integrity.
- SAS allows each device to utilize the complete bandwidth for multiple devices. The SAS interface supports SATA (serial ATA )devices at 150MBps.
- For non-critical servers, SAS is a good SAS protocol is a stable and faster protocol and ensures high user data and have high reliability.
- SAS had a disadvantage: The storage capacity is less in SAS, and the cost is higher.
SAS and SSD Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between SAS and SSD.
| Basis of Comparison Between SAS vs SSD | SAS | SSD |
| Type and Usage | They use the SCSI command set for their application as SCSI and adapts it to a fast serial connection. SAS is faster than SSD. | SSD is a type of storage device connected to the computer through SAS, SCSI, SATA. They are very slow compared with SAS. |
| Performance & Availability | It has increased Input/outputs per second (ability to read and write data faster). They deliver less sustainable performance. | They consume less power. |
| Reliability | They have higher reliability of disks speed up to 15,000 RPM. Having dual-port technology with them enhances reliability. | They are invulnerable to fail in vibration or at high temperature as they don’t have moving parts. They have greater reliability and ideal for storing data in the long-term. |
| Cost Performance | SAS price is very low when compared with SSD. | SSD costs more than SAS for a drive. |
| Compatibility | They have greater compatibility with SATA devices and SCSI. But they have a problem with | They show different compatibility with a different machine. |
| Bandwidth | SAS interface offers a bandwidth of 6GBbits/sec and a throughput of 600MB/sec. | SAS SSD bandwidth option includes 3,6,12GBbits/sec. |
| Data Rate | Data Transfer Rate for SAS is 1200MB/sec. SAS-2 allows up to 600MB/sec. | Data Transfer Rate for SSD is 750MB/sec. |
| Connection Scheme | SAS uses a serial point-to-point protocol connection. Data are transferred through frames AS has higher flexibility and compatibility in configuring. | SSD uses a SATA connection. |
| Benefits | It is better resistance to physical touch and has lower latency. They enable data path redundancy. | It supports a 3.0 GB/s full-duplex signal transmission. |
| Application | SAS interface works for Data Management tasks, High load web servers | System topology uses SSD for high performance, Batch processing. |
| Layers | SSD consist of six layers. They are Physical, link, port, transport, application layers. | SSD composed of controller and memory |
Conclusion
Customers should consider both SSD vs SAS performance and cost ratios when deciding with SSD vs SAS. SAS is suitable for enterprise server storage. SCSI is required to manage multiple SAS at the servers. Using SAS Storage will reduce the risk or loss of data and overall reduces hosting- induced headache. SAS drives are used for Banking transactions and commerce (high reliability).
SSD has become significant in achieving high storage I/O performance. It meets the demands of today challenging environment. SSD is hard to erase and recover. SSD equipped PC will boot in a few secs and transfers a file faster. They are becoming more widespread in high-end laptops like MAC.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between SAS vs SSD. We also discuss the SAS vs SSD head to head comparison, key differences, and infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.