Satellite Weather Data: Overview
Extreme events like hurricanes, heat waves, tornadoes, and floods are happening more often and becoming stronger because of climate change. Accurate forecasting of these weather events is therefore very critical in reducing the impact on life, infrastructure, and economies. One of the most useful tools for meteorologists is satellite weather data. It provides comprehensive, timely information, the key requirement for predicting extreme weather events.Evolution of Satellite Weather Data
The first weather satellite was launched in 1960; it was the Television Infrared Observation Satellite, TIROS-1. Since then, satellite technology has advanced even further, offering increasingly sophisticated data that has greatly improved our knowledge of the Earth’s atmosphere. Satellites like those in the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite series provide detailed images and data about the atmosphere, including cloud cover, sea surface temperatures, and more, with much higher resolution than ever.
How does Satellite Weather Data Work?
Satellites collect data by using instruments like radiometers, spectrometers, and radar systems. These instruments are designed to measure various features in the Earth’s atmosphere, temperature, humidity, and cloud formation. Here is the detailed information:
- Radiometers: Radiometers measure the intensity of the radiation emitted or reflected by the Earth; temperature and moisture are inferred from this radiation.
- Spectrometers: These examine the light spectrum to identify the chemical makeup of the atmosphere and surface conditions.
- Radar Systems: These provide information on precipitation, wind speed, and storm structure by reflecting radio waves from objects in the atmosphere.
The data collected is transmitted to ground stations, where it is processed and analyzed to generate weather models and forecasts.
Role of Satellite Data in the Prediction of Extreme Weather Events
Satellite weather data is invaluable in predicting a wide range of extreme weather events. Here is how it contributes to forecasting specific types of extreme weather-
#1. Hurricanes and Typhoons
Satellites are instrumental in monitoring the formation and developing stages of tropical cyclones. They provide information on sea surface temperatures, one of the most important variables in cyclone formation.
For instance, the GOES-16 satellite carries the ABI sensor, which can detect rapid hurricane intensification by observing changes in sea surface temperature and atmospheric moisture.
Satellites such as the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) provide consistent coverage, which allows meteorologists to see the movement and strength of the storms in real time. This data was used to forecast the trajectories of hurricanes in the past, including Hurricane Ida in 2021, which enabled the administration to issue early warnings and evacuate people, thereby saving their lives.
#2. Floods
Satellite data is key in predicting and monitoring floods, above all, in remote areas where ground-based observation is limited. A satellite designated as the Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM supplies near-real-time rainfall data that assist in predicting when and where flooding is most likely to take place. This data integrates with ground-based observations and hydrological models in forecasting flood risks.
For instance, satellite data from the GPM during the 2020 flooding in Southeast Asia gave forecasters an advance warning of the intensity of the flood. This enabled them to carry out disaster responses on time.
#3. Tornadoes
Since tornadoes are very hard to forecast, especially because they emerge suddenly, satellite data improve the forecast models that outline the atmospheric conditions that allow for the development of tornadoes. Satellites are designed in a way they can detect temperature and moisture changes that can potentially indicate severe thunderstorm outbreaks, which may spawn tornadoes.
In 2011, the ravaging outbreak of tornadoes in the United States was predicted well in advance thanks to satellite data, thus enabling early warnings that saved many lives.
#4. Heat Waves
Satellites monitor land surface temperatures, providing critical data for predicting heat waves. For example, ESA’s Sentinel-3 satellite measures land and sea surface temperatures, which helps to identify areas especially susceptible to extreme heat.During the heatwave in the Pacific Northwest in 2021, satellite data played a key role in predicting the severity of the event, helping to issue public health warnings and heat safety measures.
Advantages of Satellite Weather Data
Satellite weather information has many advantages over traditional observation techniques based on ground stations. These are discussed below.
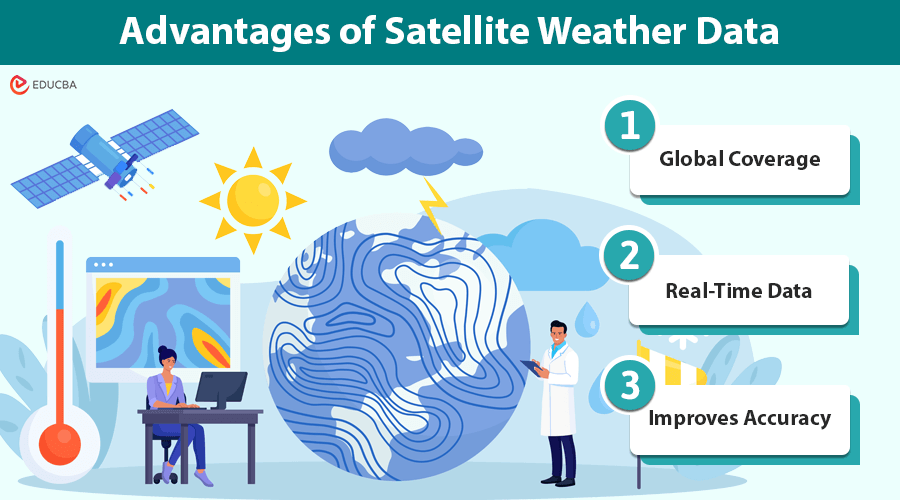
1. Global Coverage
Satellites have full coverage over massive areas of the Earth’s surface, encompassing remote areas and oceans where ground observations are scarce or nil. Their global perspective is essential to describing large-scale weather features and predicting extreme activities.
2. Real-Time Data
Because satellites are located in a position to observe the Earth’s atmosphere continually, data comes in real-time. In fact, real-time data is fundamental in enabling forecasters to predict and take action on fast-developing weather events, like hurricanes or tornadoes, that offer almost no warning.
3. Improves Accuracy
Satellite data refines the accuracy of any weather model through high-resolution data on atmospheric conditions. This results in more accurate forecasts, helping us prepare better and respond to severe weather events.
Challenges and Future Developments
Although satellite weather data has dramatically improved weather predictions, some issues must be addressed. For instance, the amount of data gathered from these satellites is massive; therefore, equally complex methods are needed to analyze it. Furthermore, satellite sensors can sometimes be obscured by cloud cover, which distorts their readings and provides inconsistent data.With all said and done, advancements in satellite technology and data processing are continually improving the accuracy and reliability of satellite weather data despite risks such as the 5G network interfering with weather forecasting frequencies. Newly launched satellites, such as GOES-T, continue enhancing the predictability of extreme weather events.
Final Thoughts
Satellite weather data is very important in predicting extreme weather conditions, as it offers real-time and high-resolution information necessary for monitoring these events accurately. In this regard, as satellite technology advances, the ability to forecast and prevent or minimize the effects of such weather conditions on human lives and property is also bound to advance.
