Definition of Scope Management Plan
A scope management plan is the blueprint or draft or layout drafted by the project manager which defines the scope of the project including the work breakdown structure of the project. The scope management plan describes how the project will be developed, monitored, and verified under the supervision of the project manager.
Drafting the scope management plan effectively helps to execute the project efficiently and properly in a synchronized manner. Many factors and parameters are taken into consideration while designing the scope management plan. A good scope management plan must include the following points into consideration:
- Requirements of the project
- The owners or the stakeholders
- Scope statement
- Scope planning
- Scope execution
- Work Breakdown Structure of the project
- Roles and responsibilities
- Deliverables
- Scope control
The scope management plan is basically an integral part of the project management plan and once the project planning is executed it becomes easy for the project manager to define the scope of the project and to control the project scope. Thus a project manager is expected to have a clear understanding of the scope management plan as the scope management plan is also essential for identifying and working on other aspects of the project.
Salient Features of Scope Management Plan
There are certain key elements of the scope management plan which are taken into consideration:
1. Requirements of the Project
Identifying the requirements of the project is the most essential step as it helps to identify and estimate the budget of the project. Complete requirement identification helps to present the project requirement report to the stakeholder and to prioritize the requirements among the myriads of requirements, some of which are being raised from the stakeholder’s end. Nowadays, we have various tools that help to track the requirement one of them being the Requirement Traceability matrix which helps to trace the requirements from the stakeholders at different stages during the project management cycle.
2. Owner/ Stakeholder of the Project
A good scope management plan must comprise of details regarding the stakeholder as the owner or the stakeholder is the once who gives the vision of the project and the project is planned and executed to give the output as desired by the stakeholder. The stakeholder is the ultimate decision-maker for the project and so needs to be aware of the progress and advancement of the project at every stage.
3. Scope Statement
The scope statement is very crucial for the scope management plan as it defines the whole project. The scope statement is in a written format comprising of the deliverables and the constraints of the project. It consists of each and every kind of assumptions made for the successful completion of the project as directed under the guidance of the project manager.
let us move to the next scope management plan example.
4. Scope Planning and Execution
Scope planning basically starts with the scope management plan and scope baseline. It defines how the product or the deliverables will be obtained within the stipulated time. Also, quality management and process improvement are two important aspects of this scope planning. The advantage of scope planning and controlled execution is that it defines the complete layout of the project management avoiding any discrepancy and dilemma regarding the roles and responsibilities. Scope planning is considered as a valuable input to the project management process.
5. Work Breakdown Structure
Work breakdown structure is basically breaking the entire project plan into tasks or activities to be executed. Each task or activity is then separately analyzed for scheduling and budget analysis which helps to analyze the overall budget of the project. The work breakdown structure can be graphical or in a flow chart form describing the various phases of the project.
6. Roles and Responsibilities
Scope management plan defines the roles and responsibilities of each member of the team. There is a supervisor or lead for monitoring that all roles and responsibilities are carried out in the defined manner and the productivity is not hampered.
7. Deliverables / Desired Outcome of the Project
Deliverables are nothing but the desired outcome or the vision of the stakeholder which represents the objects that the project has been designed and developed to produce. These deliverables or outcomes are considered as a definite part of the project management plan.
8. Scope Control
Scope control is necessary to avoid any unnecessary delays and waste in project planning. It is necessary to examine and control the tasks and procedures of the project at regular time intervals to set the benchmarks and to deliver the project on time. Scope control is also important for maintaining effective communication among the project team members and to run the process smoothly.
How to Create an Effective and Efficient Scope Management Plan?
The project manager is expected to have deep knowledge and experience about the scope management plan. Below mentioned are some of the key steps while developing a successful scope management plan:
- Gathering the requirement details of the project is the most important step in any scope management plan. Defining the requirements is the basic steps without which the project cannot be started.
- The objectives and demands of the project and the stakeholder must be clearly defined. Defining the objectives and demands ensures that the deliverables are attainable or not. Workforce management is also crucial as it is very important to know the workforce with the help of which the project is going to be accomplished.
- Draft the scoping plan of the project with all the details and essential components listed at one point. This step also includes the detailed discussions, presentations, discussing roles and responsibilities, budget and costing of the project, workforce management, and scheduling and prioritizing of the phases and sub-phases of the project.
- All the aspects of the project scope must be clarified in advance during the scope management plan in order to make it easier to identify the project requirements and deliverables.
- A guide or a supervisor is important to control the entire scope execution process and who can be used as a reference at any step during the project execution. One should be well aware of the tools and strategies being used in the process and execution of the scope management plan.
Example
Examples of the Scope Management Plan are as follows:
The scope management plan is the blueprint or draft or layout drafted by the project manager which defines the scope of the project including the work breakdown structure of the project. The scope management plan describes how the project will be developed, monitored and verified under the supervision of the project manager.
Developing / Creating a Scope Management Plan:
- Gathering Requirements
- Scope definition and statement
- Work Breakdown structure
- Scope Validation
- Scope Control/Scope Supervision
The scope management plan starts with the scope baseline which comprises the scope statement and work breakdown structure dictionary.
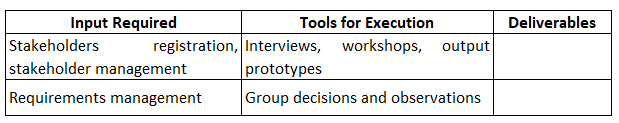
1. Gathering Requirement
Identifying the requirements of the project is the most essential step as it helps to identify and estimate the budget of the project. Complete requirement identification helps to present the project requirement report to the stakeholder and to prioritize the requirements among the myriads of requirements, some of which being raised from the stakeholder’s end. Nowadays, we have various tools that help to track the requirement one of them being the Requirement Traceability matrix which helps to trace the requirements from the stakeholders at different stages during the project management cycle.
2. Scope Definition and Statement
The scope statement is very crucial for the scope management plan as it defines the whole project. The scope statement is in a written format comprising of the deliverables and the constraints of the project. It consists of each and every kind of assumptions made for the successful completion of the project as directed under the guidance of the project manager.
3. Work Breakdown Structure
Work breakdown structure is basically breaking the entire project plan into the tasks or activities to be executed. Each task or activity is then separately analyzed for scheduling and budget analysis which helps to analyze the overall budget of the project. The work breakdown structure can be graphical or in a flow chart form describing the various phases of the project.
4. Scope Validation
Scope Validation is a method of project management used to officially recognize the finished results of the project. Its primary benefit is that by validating the deliverables, it gives the acceptance process objectivity and enhances the completed item, service, or outcome.
5. Scope Control/Scope Supervision
Scope control is necessary to avoid any unnecessary delays and waste in project planning. It is necessary to examine and control the tasks and procedures of the project at regular time intervals to set the benchmarks and to deliver the project on time. The scope control is also important for maintaining effective communication among the project team members and to run the process smoothly.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Scope Management Plan Example. Here we discuss the Features and How to Create an Effective and Efficient Scope Management Plan examples. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more