Updated May 22, 2023
Overview of Scrum Method
Scrum is a methodology in the agile framework which works on transparency, keen observation of processes, and adaptability. This method is used in product development. The co-founders of Scrum are Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland in the early 1990s. The name ‘scrum’ originated from the game Rugby. In this topic, we are going to learn about Scrum Method.
Creating a scrum aims to provide high performance within a small team, with everyone having an objective task to work on and to provide effective results. Hence keeping this concept, the project methodology has been broken down into sprints. Sprints can go from a week to months, depending on the complexity. Sprint logs consist of Forecast, To-Do, In-Progress, and Done.
Roles of the Scrum Method
Scrum suggests three roles in project development the team, Scrum Master, and product owner.
1. Team
This is the self-development team that collaborates and functions in an organized structure. It’s the core, base, and entire team which works in an organized way, also providing effective work in developing a product.
2. Scrum Master
The scrum master is a team facilitator, an expert in agile methodologies, and works according to the principles. The scrum master manages the information collaboration within the different departments in a project team. The scrum master will quickly bring in any changes in the project stage. The scrum master will provide high yield and ensure everything falls in the right place using the scrum values and principles.
3. Product Owner
The scrum product owner is the point of vision for the scrum team of the agile development projects. He will make sure to elevate the team’s goal and make it possible for them to work as per sprints. He is also the motivator of the team toward a clear goal. His vision will be to convey to the team the best they can do successfully. The product owner can be from any vertical, including marketing or product management having an understanding of markets and project trends. He should be business savvy and with good communication skills to work cross-functionally in the organization.
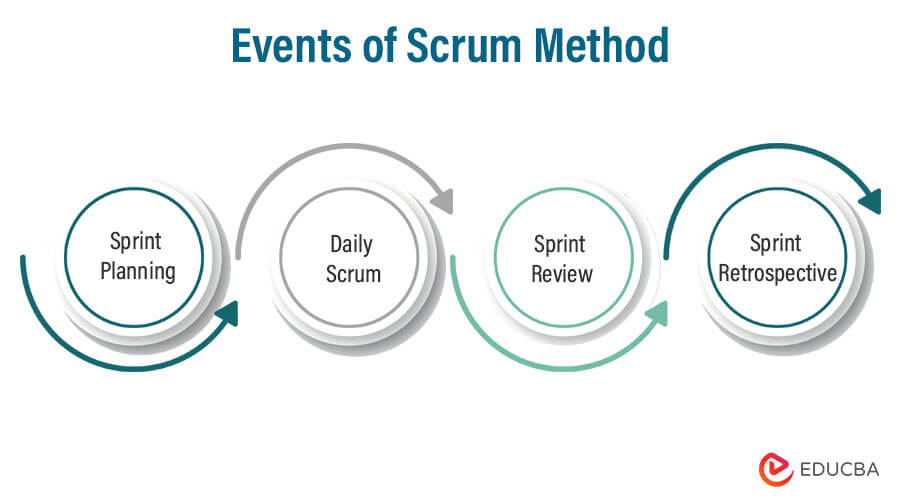
Events of Scrum Method
Four events occur during each Sprint:
1. Sprint Planning
It’s the first event in the Sprint. The team is involved in the backlog work they should do during sprints. The team decides what to work on for the current period. The team comprises a Scrum Master, the developer’s team, and the product owner. This planning stage takes place on the first day of the Sprint. The next Sprint only occurs after completing the previous sprint review and retrospective. Based on the previous sprint discussion, newsprint planning is considered. The team decides the goals using the questionnaire to determine the scope and plan the delivery accordingly.
2. Daily Scrum
The scrum team meets for 15 minutes daily during the Sprint to inspect progress and decide what to work on for the next 24 hours. The daily scrum is held every day in sprints. The intention here is to create a planned work for an adequate understanding of what is going on right now and how and when we can reach our goal. This also helps in effective communication between the teams.
3. Sprint Review
This is the stage where the development team presents to the product owner. The team collaborates about what was done and adapts the Backlog as needed. They present the work which is “done.” This is the end of the Sprint. The sprint review meeting can last one hour per week at an ideal stage.
4. Sprint Retrospective
The scrum master leads the sprint retrospective stage of the meeting, which takes place after the sprint review. The team discusses what went right, what went wrong, and how to improve in the next Sprint. This means it looks back on past events and ways to improve. It allows the team to give the management feedback on the project’s progress. This creates a plan for improvement in the next Sprint.
Artifacts in Scrum Method
There are three artifacts in the scrum method: product increment, product backlog, and sprint backlog.
1. Product Backlog
The product backlog is the detailed document of the scrum team. It’s the final document that is referred to for any details regarding the product. The PO owns this, and he uses this to explain the top requirements for any sprint to be carried out.
For ease, the product backlog should contain a few rules:
- The product backlog should contain priorities. This helps in delivering as per priority.
- The product backlog should not contain any detailed statement; it’s a top requirements document.
- Product backlog must be dynamic; it should change when the requirement gets into detailed work. The document changes and a new requirements area is added to accommodate the changes per requirement.
2. Sprint Backlog
There are two major points to remember in the sprint backlog.
- Making decisions in a group: The whole team should group every state.
- Organize task: The Scrum team should not need the assigned task from the Scrum master. They are self-organized to pick and work on tasks.
3. Product Increments
The sum of all product backlog items committed during the Sprint constitutes the Product Increments. This is generally a piece of software collaborating across the organization, creating transparency. This can also be in the type of task boards or charts.
Conclusion
This article tells us about sprints in the scrum, the scrum cycle, their artifacts, four events that occur in the scrum, the logs, and various roles in scrum methodology. The article also informs us about the product members involved and their key roles in a scrum cycle.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Scrum Method. Here we discuss the scrum method’s roles, events, and artifacts for better understanding. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –