Updated July 15, 2023
Difference Between Secured Loan vs Unsecured Loan
The following article provides an outline for a Secured Loan vs Unsecured Loan. A secured loan refers to the borrower’s borrowing from the lender, which is secured by a mortgage, pledge, hypothecation, or lien mark of certain collateral assets, which can take different forms in terms of being tangible or intangible. Such collateral assets can be liquid collateral such as Marketable Securities or fixed Assets such as Buildings, Factories, etc., which are not that liquid. In short, lending secured by eligible collateral is called a Secured loan. Common examples of Secured loans include Home loans, Vehicle Loans, etc.
An unsecured Loan refers to the borrower’s borrowing from the lender without any collateral underlying such loan. Due to the higher risk involved in the borrower’s case of default, such loans carry a higher rate of interest than Secured Loans to compensate the lender for the additional risk undertaken. One of the most common types of Unsecured Loan is a Personal Loan offered by almost all types of Financial Institutions and new-age Fintech companies to meet the varied needs of borrowers.
What is a Secured Loan?
The name Secured Loan itself defines the characteristics of such a loan. The lender secures a loan by accepting underlying collateral, which can be offered as a prime asset or as collateral against the borrowed amount. Also secured loan provides a cushion to the lender as they can fall upon such collateral in the event of any default to reduce their overall risk exposure and risky proposition.
Typically big-ticket loans require collaterals in the form of eligible security and, as such, are more secure. An important thing to remember is that just because any underlying collateral secures a loan doesn’t make it risk-free and financial institutions have to set aside a portion of their capital for such assets denoted in terms of a risk-weighted concept Assets, which signifies the risk of such secured assets.
What is an Unsecured Loan?
Unsecured Loans lack underlying security and typically involve small ticket sizes, reaching as high as a few million Indian currencies. Lenders typically grant these loans for various purposes, but they primarily target retail borrowers with a credible credit history and high credit scores, demonstrating their repayment capacity.
Credit Cards and Personal Loans are some of the popular types of Unsecured Loans, and these carry high-interest income for financial institutions due to the high rates charged on such loans. These loans also have high capital for the financial institution to set aside, denoted in terms of Risk-Weighted Assets.
Head to Head Comparison between Secured Loan vs Unsecured Loan (Infographics)
Key Differences Between Secured Loan vs Unsecured Loan
Despite the inherent differences as enumerated above in the Secured Loan and Unsecured Loan, the similarities lie in the following areas:
- Both require a high level of credit underwriting with a focus on the repayment capacity of counterparty borrowers.
- Both require a high credit score of the borrower to be eligible for availing such a loan (although the eligibility criteria vary within different Financial Institutions)
Secured Loan vs Unsecured Loan Comparison Table
Below are the key differences between the two types as enumerated below:
|
Basis |
Secured Loan |
Unsecured Loan |
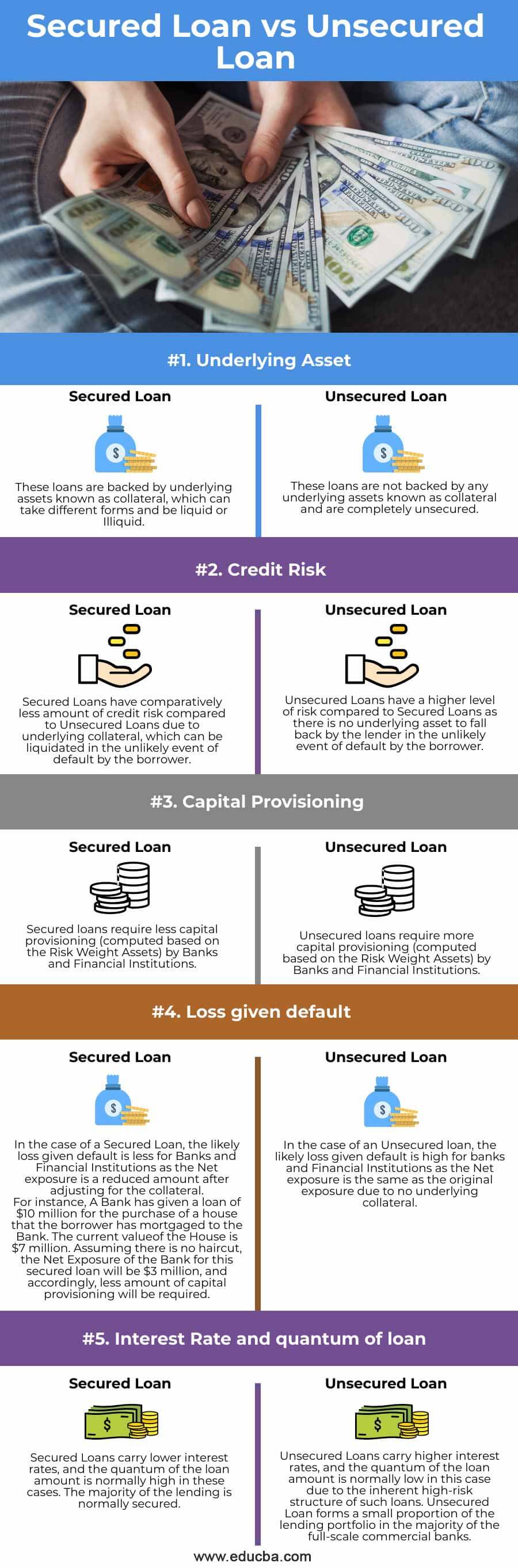
| Underlying Asset | These loans are backed by underlying assets known as collateral, which can take different forms and be liquid or Illiquid. | These loans are not backed by any underlying assets known as collateral and are entirely unsecured. |
| Credit Risk | Secured Loans have comparatively less credit risk than Unsecured Loans due to the underlying collateral, which can be liquidated in the unlikely event of default by the borrower. | Lenders face a higher risk level with Unsecured Loans compared to Secured Loans due to the absence of an underlying asset to rely on in the unlikely event of borrower default. |
| Capital Provisioning | Secured loans require less capital provisioning (computed based on the Risk Weight Assets) by Banks and Financial Institutions. | Unsecured loans require more capital provisioning (computed based on the Risk Weight Assets) by Banks and Financial Institutions. |
| Loss Given Default | In the case of a Secured Loan, the likely loss given default is less for Banks and Financial Institutions as the Net exposure is a reduced amount after adjusting for the collateral.
For instance, A Bank has given a loan of $10 million to purchase a house that the borrower has mortgaged to the Bank. The current value of the House is $7 million. Assuming there is no haircut, the Net Exposure of the Bank for this secured loan will be $3 million, and accordingly, less capital provisioning will be required. |
In the case of an Unsecured loan, the likely loss given default is high for banks and Financial Institutions as the Net exposure is the same as the original exposure due to no underlying collateral. |
| Interest Rate and Quantum of Loan | Secured Loans carry lower interest rates, and the quantum of the loan amount is ordinarily high in these cases. The majority of the lending is usually secured. | Unsecured Loans carry higher interest rates, and the quantum of the loan amount usually is low in this case due to the inherent high-risk structure of such loans. Unsecured loans form a small proportion of the lending portfolio in most full-scale commercial banks. |
Conclusion
Secured Loans and Unsecured Loans are a part of any Bank or financial institution’s lending portfolio and complement each other. Unsecured Loans act as a building block in creating a good credit history for the borrower and for the lender to assess and cultivate credit discipline in the borrower, enabling lending institutions to fund Secured Loans later. However, this chronology doesn’t happen in all cases; it helps Lending Institutions and acts as one factor in underwriting decisions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Secured Loans vs Unsecured Loan. Here we also discuss the secured loan vs unsecured loan key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –